Google AI: Invention Is the PR Game
April 17, 2025
Google was so excited to tout its AI’s great achievement: In under 48 hours, It solved a medical problem that vexed human researchers for a decade. Great! Just one hitch. As Pivot to AI tells us, "Google Co-Scientist AI Cracks Superbug Problem in Two Days!—Because It Had Been Fed the Team’s Previous Paper with the Answer In It." With that detail, the feat seems much less impressive. In fact, two days seems downright sluggish. Writer David Gerard reports:
"The hype cycle for Google’s fabulous new AI Co-Scientist tool, based on the Gemini LLM, includes a BBC headline about how José Penadés’ team at Imperial College asked the tool about a problem he’d been working on for years — and it solved it in less than 48 hours! [BBC; Google] Penadés works on the evolution of drug-resistant bacteria. Co-Scientist suggested the bacteria might be hijacking fragments of DNA from bacteriophages. The team said that if they’d had this hypothesis at the start, it would have saved years of work. Sounds almost too good to be true! Because it is. It turns out Co-Scientist had been fed a 2023 paper by Penadés’ team that included a version of the hypothesis. The BBC coverage failed to mention this bit. [New Scientist, archive]"
It seems this type of Googley AI over-brag is a pattern. Gerard notes the company claims Co-Scientist identified new drugs for liver fibrosis, but those drugs had already been studied for this use. By humans. He also reminds us of this bit of truth-stretching from 2023:
"Google loudly publicized how DeepMind had synthesized 43 ‘new materials’ — but studies in 2024 showed that none of the materials was actually new, and that only 3 of 58 syntheses were even successful. [APS; ChemrXiv]"
So the next time Google crows about an AI achievement, we have to keep in mind that AI often is a synonym for PR.
Cynthia Murrell, April 17, 2026
Google Wears a Necklace and Sneakers with Flashing Blue LEDs. Snazzy.
April 15, 2025
 No AI. Just an old dinobaby pointing out some exciting developments in the world “beyond search.”
No AI. Just an old dinobaby pointing out some exciting developments in the world “beyond search.”
I can still see the flashing blue light in Aisle 7. Yes, there goes the siren. K-Mart in Central Illinois was running a big sale on underwear. My mother loved those “blue light specials.” She would tell me as I covered my eyes and ears, “I don’t want to miss out.” Into the scrum she would go, emerging with two packages of purple boxer shorts for my father. He sat in the car while my mother shopped. I accompanied her because that’s what sons in Central Illinois do. I wonder if procurement officials are familiar with blue light specials. The sirens in DC wail 24×7.
Thanks, OpenAI. You produced a good enough illustration. A first!
I thought about K-Mart when I read “Google Slashes Business Software Prices for US Federal Agencies.” I see that flickering blue light as I type this short blog post. The trusted “real” news source reports:
Google will offer steep discounts to U.S. federal agencies for its business apps package as the company looks to capitalize on the Trump administration’s cost-cutting push and chip away at Microsoft’s longstanding grip on the government software market.
Yep, discounts. Now Microsoft has some traction in the US government. I cannot imagine what life would be like for aides to a senior Pentagon if he did not have nifty PowerPoint presentations. Perhaps offering a deal will get some Microsoft afficionados to learn to live without Excel and Word? I don’t know, but Google is giving the “discount” method a whirl.
What’s up with Google? I think someone told me that Gemini 2.5 was free. Now a discount on GSA listed services which could amount to $2 billion in savings … if — yes, that magic word — if the US government dumps the Softies’ outstanding products for the cloudy goodness of the Google’s way. Yep, “if.”
I have a cute anecdote about Google and the US government from the year 2000, but, alas, I cannot share it. Trust me. It is a knee slapper. And, no, it is not about Sergey wearing silver sparkle sneakers to meetings with US elected officials. Those were indeed eye catchers among shoes with toes that looked like potatoes.
Several observations:
- Google, like Amazon, is trying to obtain US government business. I think the flashing blue lights, if I were still working in the hallowed halls, would impair my vision. Price cutting seems to be the one true way right now.
- Will lower prices have an impact on US government procurement? I am not sure. The procurement process chugs along every day and in quite predictable ways. How long does it take to turn a battleship, assuming the captain can pull off the maneuver without striking a small fishing boat, of course.
- Google seems to think that slashing prices for its “products” will boost sales. My understanding of Google is that its sale to government agencies pivots on several characteristics; for example, [a] listening and understanding what government professionals say, [b] providing a modicum of customer support or at the very least answering a phone call from a government professional, and [c] delivering products that the aides, assistants, and contractors understand and can use to crank out documents with numbered lines, dense charts, and bullet points that mostly stay in place after a graphic is inserted.
To sum up, I find the idea of price cuts interesting. My initial reaction is that price cuts and procurement are not necessarily lined up procedurally. But I am a dinobaby. But after 50 years of “government” work I have a keen desire to see if the Google can shine enough blue lights to bedazzle people involved in purchasing software to keep the admirals happy. (I speak from a little experience working with the late Admiral Craig Hosmer, R-Calif. whom I thank for his service.)
Stephen E Arnold, April 15, 2025
Extra Effort Required to Find Some Google Information
April 10, 2025
 Dinobaby says, “No smart software involved. That’s for “real” journalists and pundits.
Dinobaby says, “No smart software involved. That’s for “real” journalists and pundits.
We are plugging along on a little project. As part of our checking assorted publicly accessible sources for being publicly accessible, we were delighted to verify that Exploit Database is alive and kicking. Plus, it appears to be current as of August 2024.
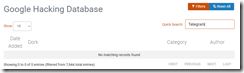
Since we are doing some poking around for information related to the newly-almost-free Pavel Durov, we were interested in the Google Hacking Database. You can locate that list of “Google dorks” at this link. The most recent additions or dorks provide some information about finding files containing passwords.
Here’s the little discovery. None of the almost 8,000 dorks are Telegram specific. However, many of the methods can be applied to Pavel Durov’s interesting outfit. We tried a handful and learned that Google’s index either is filtering Telegram-related content or simply does not make much of an effort to provide pointers to certain types of public Telegram information.
How does an analyst or researcher locate current, comprehensive information about bots, Groups, Channels, and third-party specialized services for that platform? That is an excellent question which leads to some Russian resources which are often presented in Russian, semi low profile outfits like Forbidden Stories.
Net net: OSINT professionals depend on Google. However, certain large services engaged in a wide range of activities require pushing beyond the Google and its ever-helpful smart software.
Stephen E Arnold, April 10, 2025
Click Counting: It Is 1992 All Over Again
March 31, 2025
 Dinobaby says, “No smart software involved. That’s for “real” journalists and pundits.
Dinobaby says, “No smart software involved. That’s for “real” journalists and pundits.
I love it when search engine optimization experts, online marketing executives, and drum beaters for online advertising talk about clicks, clickstreams, and click metrics. Ho ho ho.
I think I was involved in creating a Web site called Point (The Top 5% of the Internet). The idea was simple: Curate and present a directory of the most popular sites on the Internet. It was a long shot because the team did not want to do drugs, sex, and a number of other illegal Web site profiles for the directory. The idea was that in 1992 or so, no one had a Good Housekeeping Seal of Approval-type of directory. There was Yahoo, but if one poked around, some interesting Web sites would display in their low resolution, terrible bandwidth glory.
To my surprise, the idea worked and the team wisely exited the business when someone a lot smarter than the team showed up with a check. I remember fielding questions about “traffic”. There was the traffic we used to figure out what sites were popular. Then there was traffic we counted when visitors to Point hit the home page and read profiles of sites with our Good Housekeeping-type of seal.
I want to share that from those early days of the Internet the counting of clicks was pretty sketchy. Scripts could rack up clicks in a slow heartbeat. Site operators just lied or cooked up reports that served up a reality in terms of tasty little clicks.
Why are clicks bogus? I am not prepared to explain the dark arts of traffic boosting which today is greatly aided by scripts instantly generated by smart software. Instead I want to highlight this story in TechCrunch: “YouTube Is Changing How YouTube Shorts Views Are Counted.” The article does a good job of explaining how one monopoly is responding to its soaring costs and the slow and steady erosion of its search Nile River of money.
The write up says:
YouTube is changing how it counts views on YouTube Shorts to give creators a deeper understanding of how their short-form content is performing
I don’t know much about YouTube. But I recall watching little YouTubettes which bear a remarkable resemblance to TikTok weaponized data bursts just start playing. Baffled, I would watch a couple of seconds, check that my “autoplay” was set to off, and then kill the browser page. YouTubettes are not for me.
Most reasonable people would want to know several things about their or any YouTubette; for example:
- How many times did a YouTubette begin to play and then was terminated in less that five seconds
- How many times a YouTubette was viewed from start to bitter end
- How many times a YouTubette was replayed in its entirety by a single user
- What device was used
- How many YouTubettes were “shared”
- The percentage of these data points compared against the total clicks of a short nature or the full view?
You get the idea. Google has these data, and the wonderfully wise but stressed firm is now counting “short views” as what I describe as the reality: Knowing exactly how many times a YouTubette was played start to finish.
According to the write up:
With this update, YouTube Shorts will now align its metrics with those of TikTok and Instagram Reels, both of which track the number of times your video starts or replays. YouTube notes that creators will now be able to better understand how their short-form videos are performing across multiple platforms. Creators who are still interested in the original Shorts metric can view it by navigating to “Advanced Mode” within YouTube Analytics. The metric, now called “engaged views,” will continue to allow creators to see how many viewers choose to continue watching their Shorts. YouTube notes that the change won’t impact creators’ earnings or how they become eligible for the YouTube Partner Program, as both of these factors will continue to be based on engaged views rather than the updated metric.
Okay, responding to the competition from one other monopolistic enterprise. I get it. Okay, Google will allegedly provided something for a creator of a YouTubette to view for insight. And the change won’t impact what Googzilla pays a creator. Do creators really know how Google calculates payments? Google knows. With the majority of the billions of YouTube videos (short and long) getting a couple of clicks, the “popularity” scheme boils down to what we did in 1992. We used whatever data was available, did a few push ups, and pumped out a report.
Could Google follow the same road map? Of course not. In 1992, we had no idea what we were doing. But this is 2025 and Google knows exactly what it is doing.
Advertisers will see click data that do not reflect what creators want to see and what viewers of YouTubettes and probably other YouTube content really want to know: How many people watched the video from start to finish?
Google wants to sell ads at perhaps the most difficult point in its 20 year plus history. That autoplay inflates clicks. “Hey, the video played. We count it,” can you conceptualize the statement? I can.
Let’s not call this new method “weaponization.” That’s too strong. Let’s describe this as “shaping” or “inflating” clicks.
Remember. I am a dinobaby and usually wrong. No high technology company would disadvantage a creator or an advertiser. Therefore, this change is no big deal. Will it help Google deal with its current challenges? You can now ask Google AI questions answered by its most sophisticated smart software for free.
Is that an indication that something is not good enough to cause people to pay money? Of course not. Google says “engaged views” are still important. Absolutely. Google is just being helpful.
Stephen E Arnold, March 31, 2025
Google: Android and the Walled Garden
March 31, 2025
 Dinobaby says, “No smart software involved. That’s for “real” journalists and pundits.
Dinobaby says, “No smart software involved. That’s for “real” journalists and pundits.
In my little corner of the world, I do not see Google as “open.” One can toss around the idea 24×7, and I won’t change my mind. Despite its unusual approach to management, the company has managed to contain the damage from Xooglers’ yip yapping about the company. Xoogler.co is focused on helping people. I suppose there are versions of Sarah Wynn-Williams “Careless People” floating around. Few talk much about THE Timnit Gebru “parrot” paper. Google is, it seems, just not the buzz generator it was in 2006, the year the decline began to accelerate in my opinion.
We have another example of “circling the wagons” strategy. It is a doozy.
“Google Moves All Android Development Behind Closed Doors” reports with some “real” writing and recycling of Google generated slick talk an interesting shift in the world of the little green man icon:
Google had to merge the two branches, which lead to problems and issues, so Google decided it’s now moving all development of Android behind closed doors
How many versions of messaging apps did Google have before it decided that “let many flowers bloom” was not in line with the sleek profile the ageing Google want to flaunt on Wall Street?
The article asks a good question:
…if development happens entirely behind closed doors, with only the occasional code drop, is the software in question really open source? Technically, the answer is obviously ‘yes’ – there’s no requirement that development take place in public. However, I’m fairly sure that when most people think of open source, they think not only of occasionally throwing chunks of code over the proverbial corporate walls, but also of open development, where everybody is free to contribute, pipe in, and follow along.
News flash from the dinobaby: Open source software, when bandied about by folks who don’t worry too much about their mom missing a Social Security check means:
- We don’t want to chase and fix bugs. Make it open source and let the community do it for free.
- We probably have coded up something that violates laws. By making it open source, we are really benefiting those other developers and creating opportunities for innovation.
- We can use the buzzword “open source” and jazz the VCs with a term that is ripe with promise for untold riches
- A student thinks: I can make my project into open source and maybe it will help me get a job.
- A hacker thinks: I can get “cred” by taking my exploit and coding a version that penetration testers will find helpful and possibly not discover the backdoor.
I have not exhausted the kumbaya about open source.
It is clear that Google is moving in several directions, a luxury only Googzillas have:
First, Google says, “We will really, really, cross my fingers and hope to die, share code … just like always.
Second, Google can add one more oxen drawn wagon to its defensive circle. The company will need it when the licensing terms for Android include some very special provisions. Of course, Google may be charitable and not add additional fees to its mobile OS.
Third, it can wave the “we good managers” flag.
Fourth, as the write up correctly notes:
…Darwin, the open source base underneath macOS and iOS, is technically open source, but nobody cares because Apple made it pretty much worthless in and of itself. Anything of value is stripped out and not only developed behind closed doors, but also not released as open source, ensuring Darwin is nothing but a curiosity we sometimes remember exists. Android could be heading in the same direction.
I think the “could” is a hedge. I penciled in “will.” But I am a dinobaby. What do I know?
Stephen E Arnold, March 31, 2025
Google Experiment: News? Nobody Cares So Ad Impact Is Zero, Baby, Zero
March 24, 2025
 Dinobaby, here. No smart software involved unlike some outfits.
Dinobaby, here. No smart software involved unlike some outfits.
I enjoy reading statistically valid wizard studies from monopolistic outfits. “Our Experiment on the Value of European News Content” reports a wonderful result: Nobody cares if Googzilla does not index “real” news. That’s it. The online ad outfit conclusively proves that “real” news is irrelevant.
The write up explains:
The results have now come in: European news content in Search has no measurable impact on ad revenue for Google. The study showed that when we removed this content, there was no change to Search ad revenue and a <1% (0.8%) drop in usage, which indicates that any lost usage was from queries that generated minimal or no revenue. Beyond this, the study found that combined ad revenue across Google properties, including our ad network, also remained flat.
What should those with a stake in real news conclude? From my point of view, Google is making crystal clear that publishers need to shut up or else. What’s the “else”? Google stops indexing “real” news sites. Where will those “real” news sites get traffic. Bear Blog, a link from YCombinator Hacker News, a Telegram Group, Twitter, or TikTok?
Sure, absolutely.
Several observations:
- Fool around with a monopoly in the good old days, and some people would not have a train stop at their town in Iowa or the local gas stations cannot get fuel. Now it is search traffic. Put that in your hybrid.
- Google sucks down data. Those who make data available to the Google are not likely to be invited to the next Sundar & Prabhakar Comedy Show.
- Google will continue to flip the digital bird at the EU, stopping when the lawsuits go away and publishers take their medicine and keep quiet. The crying and whining is annoying.
One has to look forward to Google’s next research study, doesn’t one?
Stephen E Arnold, March 24, 2025
A NewPlay for Google and Huawei: A Give and Go?
March 14, 2025
Time for Google to get smarmy in court. We learn from TorrentFreak, "Google Must Testify as LaLiga Demands Criminal Liability for ‘Piracy Profits’." Writer Andy Maxwell summarizes:
"A court in Murcia, Spain, has ordered Google to testify in a criminal case concerning IPTV app, NewPlay. Football league LaLiga, whose matches were allegedly offered illegally through the app, previously called for the directors of Google, Apple, and Huawei to face criminal charges. LaLiga criticized the companies for failing to disable copies of NewPlay already installed on users’ devices. Google and Huawei must now testify as ‘profit-making participants’ in an alleged piracy scheme."
See the write-up for the twists and turns of the case thus far. The key point: Removing NewPlay from app stores was not enough for LaLiga. The league demands they reach in and remove the player from devices it already inhabits. The court agrees. We learn:
"The court order required Google, Apple, and Huawei to disable or delete NewPlay to prevent future use on users’ mobile devices. That apparently didn’t happen. Unhappy with the lack of compliance, in 2024 LaLiga called on the investigating judge to punish the tech companies’ directors. LaLiga says that the installed NewPlay apps still haven’t been remotely disabled but given the precedent that may set, LaLiga seems unlikely to let the matter go without a fight. With support from Telefónica, Mediapro and rights group EGEDA, LaLiga wants to hold Google and Huawei responsible for pirated content reportedly made available via the NewPlay app."
So now the court is requiring reps from Google and Huawei to appear and address this partial compliance. Why not Apple, too? That is a mystery, reports Maxwell. He also wonders about the bigger picture. The Newplay website is still up, he notes, though both its internal and external links are currently disabled. Besides, at least one other app exists that appears to do the same thing. Will the court become embroiled in a long-term game of IPTV whack-a-mole? Google is a magnet for the courts it seems.
Cynthia Murrell, March 14, 2025
Sergey Says: Work Like It Was 1975 at McKinsey or Booz, Allen
March 6, 2025
 Yep, another dinobaby original.
Yep, another dinobaby original.
Sergey Brin, invigorated with his work at the Google on smart software, has provided some management and work life tips to today’s job hunters and aspiring Alphabet employees. “In Leaked Memo to Google’s AI Workers, Sergey Brin Says 60 hours a Week Is the Sweet Spot and Doing the Bare Minimum Can Demoralize Peers”, Mr. Brin offers his view of sage management and career advice. (I do want to point out that the write up does not reference the work ethic and other related interactions of the Google Glass marketing team. My view of this facet of Mr. Brin’s contributions suggest that it is tough to put in 60 hours a week while an employee is ensconced in the Stanford Medical psychiatric ward. But that’s water under the bridge, so let’s move on to the current wisdom.)
The write up reports:
Sergey Brin believes Google can win the race to artificial general intelligence and outlined his ideas for how to do that—including a workweek that’s 50% longer than the standard 40 hours.
Presumably working harder will allow Google to avoid cheese mishaps related to pizza and Super Bowl advertising. Harder working Googlers will allow the company to avoid the missteps which have allowed unenlightened regulators in the European Union and the US to find the company exercising behavior which is not in the best interest of the service’s “users.”
The write up says:
“A number of folks work less than 60 hours and a small number put in the bare minimum to get by,” Brin wrote on Wednesday. “This last group is not only unproductive but also can be highly demoralizing to everyone else.”
I wonder if a consistent, document method for reviewing the work of employees would allow management to offer training, counseling, or incentives to get the mavericks back in the herd.
The protests, the allegations of erratic punitive actions like firing people who use words like “stochastic”, and the fact that the 60-hour information comes from a leaked memo — each of these incidents suggests that the management of the Google may have some work to do. You know, that old nosce teipsum stuff.
The Fortune write up winds down with this statement:
Last year, he acknowledged that he “kind of came out of retirement just because the trajectory of AI is so exciting.” That also coincided with some high-profile gaffes in Gemini’s AI, including an image generator that produced racially diverse Na#is. [Editor note: Member of a German affiliation group in the 1930s and 1940s. I have to avoid the Google stop words list.]
And the cheese, the Google Glass marketing tours, and so much more.
Stephen E Arnold, March 6, 2025
We Have to Spread More Google Cheese
March 4, 2025
A Super Bowl ad is a big deal for companies that shell out for those pricy spots. So it is a big embarrassment when one goes awry. The BBC reports, “Google Remakes Super Bowl Ad After AI Cheese Gaffe.” Google was trying to how smart Gemini is. Instead, the ad went out with a stupid mistake. Writers Graham Fraser and Tom Singleton tell us:
“The commercial – which was supposed to showcase Gemini’s abilities – was created to be broadcast during the Super Bowl. It showed the tool helping a cheesemonger in Wisconsin write a product description by informing him Gouda accounts for ’50 to 60 percent of global cheese consumption.’ However, a blogger pointed out on X that the stat was ‘unequivocally false’ as the Dutch cheese was nowhere near that popular.”
In fact, cheddar and mozzarella vie for the world’s favorite cheese. Gouda is not even a contender. Though the company did remake the ad, one top Googler at first defended Gemini with some dubious logic. We learn:
“Replying to him, Google executive Jerry Dischler insisted this was not a ‘hallucination’ – where AI systems invent untrue information – blaming the websites Gemini had scraped the information from instead. ‘Gemini is grounded in the Web – and users can always check the results and references,’ he wrote. ‘In this case, multiple sites across the web include the 50-60% stat.'”
Sure, users can double check an AI’s work. But apparently not even Google itself can be bothered. Was the company so overconfident it did not use a human copyeditor? Or do those not exist anymore? Wrong information is wrong information, whether technically a hallucination or not. Spitting out data from unreliable sources is just as bad as making stuff up. Google still has not perfected the wildly imperfect Gemini, it seems.
Cynthia Murrell, February 28, 2025
Google and Personnel Vetting: Careless?
February 20, 2025
 No smart software required. This dinobaby works the old fashioned way.
No smart software required. This dinobaby works the old fashioned way.
The Sundar & Prabhakar Comedy Show pulled another gag. This one did not delight audiences the way Prabhakar’s AI presentation did, nor does it outdo Google’s recent smart software gaffe. It is, however, a bit of a hoot for an outfit with money, smart people, and smart software.
I read the decidedly non-humorous news release from the Department of Justice titled “Superseding Indictment Charges Chinese National in Relation to Alleged Plan to Steal Proprietary AI Technology.” The write up states on February 4, 2025:
A federal grand jury returned a superseding indictment today charging Linwei Ding, also known as Leon Ding, 38, with seven counts of economic espionage and seven counts of theft of trade secrets in connection with an alleged plan to steal from Google LLC (Google) proprietary information related to AI technology. Ding was initially indicted in March 2024 on four counts of theft of trade secrets. The superseding indictment returned today describes seven categories of trade secrets stolen by Ding and charges Ding with seven counts of economic espionage and seven counts of theft of trade secrets.
Thanks, OpenAI, good enough.
Mr. Ding, obviously a Type A worker, appears to have quite industrious at the Google. He was not working for the online advertising giant; he was working for another entity. The DoJ news release describes his set up this way:
While Ding was employed by Google, he secretly affiliated himself with two People’s Republic of China (PRC)-based technology companies. Around June 2022, Ding was in discussions to be the Chief Technology Officer for an early-stage technology company based in the PRC. By May 2023, Ding had founded his own technology company focused on AI and machine learning in the PRC and was acting as the company’s CEO.
What technology caught Mr. Ding’s eye? The write up reports:
Ding intended to benefit the PRC government by stealing trade secrets from Google. Ding allegedly stole technology relating to the hardware infrastructure and software platform that allows Google’s supercomputing data center to train and serve large AI models. The trade secrets contain detailed information about the architecture and functionality of Google’s Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) chips and systems and Google’s Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) systems, the software that allows the chips to communicate and execute tasks, and the software that orchestrates thousands of chips into a supercomputer capable of training and executing cutting-edge AI workloads. The trade secrets also pertain to Google’s custom-designed SmartNIC, a type of network interface card used to enhance Google’s GPU, high performance, and cloud networking products.
At least, Mr. Ding validated the importance of some of Google’s sprawling technical insights. That’s a plus I assume.
One of the more colorful items in the DoJ news release concerned “evidence.” The DoJ says:
As alleged, Ding circulated a PowerPoint presentation to employees of his technology company citing PRC national policies encouraging the development of the domestic AI industry. He also created a PowerPoint presentation containing an application to a PRC talent program based in Shanghai. The superseding indictment describes how PRC-sponsored talent programs incentivize individuals engaged in research and development outside the PRC to transmit that knowledge and research to the PRC in exchange for salaries, research funds, lab space, or other incentives. Ding’s application for the talent program stated that his company’s product “will help China to have computing power infrastructure capabilities that are on par with the international level.”
Mr. Ding did not use Google’s cloud-based presentation program. I found the explicit desire to “help China” interesting. One wonders how Google’s Googley interview process run by Googley people failed to notice any indicators of Mr. Ding’s loyalties? Googlers are very confident of their Googliness, which obviously tolerates an insider threat who conveys data to a nation state known to be adversarial in its view of the United States.
I am a dinobaby, and I find this type of employee insider threat at Google. Google bought Mandiant. Google has internal security tools. Google has a very proactive stance about its security capabilities. However, in this case, I wonder if a Googler ever noticed that Mr. Ding used PowerPoint, not the Google-approved presentation program. No true Googler would use PowerPoint, an archaic, third party program Microsoft bought eons ago and has managed to pump full of steroids for decades.
Yep, the tell — Googlers who use Microsoft products. Sundar & Prabhakar will probably integrate a short bit into their act in the near future.
Stephen E Arnold, February 20, 2025