Can Googzilla Read a Manifesto and Exhibit Fear?
February 7, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Let’s think about scale. A start up wants to make a dent in Google’s search traffic. The start up has 2,000 words to blast away at the Google business model. Looking at the 2,000 words from a search tower buttressed by Google’s fourth quarter 2023 revenues of $86.31 billion (up 13% year over the same period in 2022). Does this look like a mismatch? I think it is more of a would-be competitor’s philosophical view of what should be versus what could be. Microsoft Bing is getting a clue as well.
Viewed from the perspective of a student of Spanish literature, the search start up may be today’s version of Don Quixote. The somewhat addled Alonso Quijano pronounced himself a caballero andante or what fans of chivalry in the US of A call a knight errant. What’s errant? In the 16th century, “errant” was self appointed, a bit like a journalism super star who road to fame on the outputs of the unfettered Twitter service and morphs into a pundit, a wizard, a seer.
A modern-day Don Quixote finds himself in an interesting spot. The fire-breathing dragon is cooking its lunch. The bold knight explains that the big beastie is toast. Yeah. Thanks, MSFT Copilot Bing thing. Actually good enough today. Wow.
With a new handle, Don Quixote leaves the persona of Sr. Quijano behind and goes off the make Spain into a better place. The cause of Spanish angst is the windmill. The good Don tries to kill the windmills. But the windmills just keep on grinding grain. The good Don fails. He dies. Ouch!
I thought about the novel when I read “The Age of PageRank is Over [Manifesto].” The author champions a Web search start up called Kagi. The business model of Kagi is to get people to pay to gain access to the Kagi search system. The logic of the subscription model is that X number of people use online search. If our system can get a tiny percentage of those people to pay, we will be able to grow, expand, and deliver good search. The idea is that what Google delivers is crappy, distorted by advertisers who cough up big bucks, and designed to convert more and more online users to the One True Source of Information.
The “manifesto” says:
The websites driven by this business model became advertising and tracking-infested giants that will do whatever it takes to “engage” and monetize unsuspecting visitors. This includes algorithmic feeds, low-quality clickbait articles (which also contributed to the deterioration of journalism globally), stuffing the pages with as many ads and affiliate links as possible (to the detriment of the user experience and their own credibility), playing ads in videos every 45 seconds (to the detriment of generations of kids growing up watching these) and mining as much user data as possible.
These indeed are the attributes of Google and similar advertising-supported services. However, these attributes are what make stakeholders happy. These business model components are exactly what many other companies labor to implement and extend. Even law enforcement likes Google. At one conference I learned that 92 percent of cyber investigators rely on Google for information. If basic Google sucks, just use Google dorks or supplementary services captured in OSINT tools, browser add ins, and nifty search widgets.
Furthermore, switching from one search engine is not a matter of a single click. The no-Google approach requires the user pick a path through a knowledge mine field; for example:
- The user must know what he or she does invokes Google. Most users have no clue where Google fits in one’s online life. When told, those users do not understand.
- The user must identify or learn about one or more services that are NOT Google related.
- The user must figure out what makes one “search” service better than another, not an easy task even for alleged search experts
- The user must make a conscious choice to spit out cash
- The user must then learn how to get a “new” search system to deliver the results the user (trained and nudged by Google for 90 percent of online users in the US and Western Europe)
- The user must change his or her Google habit.
Now those six steps may not seem much of a problem to a person with the neurological wiring of Alonso Quijano or Don Quixote in more popular parlance. But from my experience in online and assorted tasks, these are tricky obstacles to scale.
Back to the Manifesto. I quote:
Nowadays when a user uses an ad-supported search engine, they are bound to encounter noise, wrong and misleading websites in the search results, inevitably insulting their intelligence and wasting their brain cycles. The algorithms themselves are constantly leading an internal battle between optimizing for ad revenue and optimizing for what the user wants.
My take on this passage is that users are supposed to know when they “encounter noise, wrong and misleading websites in the search results.” Okay, good luck with that. Convenience, the familiar, and easy everything raises electrified fences. Users just do what they have learned to do; they believe what they believe; and they accept what others are doing. Google has been working for more than two decades to develop what some call a monopoly. I think there are other words which are more representative of what Google has constructed. That’s why I don’t put on my armor, get a horse, and charge at windmills.
The Manifesto points to a new future for search; to wit:
In the future, instead of everyone sharing the same search engine, you’ll have your completely individual, personalized Mike or Julia or Jarvis – the AI. Instead of being scared to share information with it, you will volunteer your data, knowing its incentives align with yours. The more you tell your assistant, the better it can help you, so when you ask it to recommend a good restaurant nearby, it’ll provide options based on what you like to eat and how far you want to drive. Ask it for a good coffee maker, and it’ll recommend choices within your budget from your favorite brands with only your best interests in mind. The search will be personal and contextual and excitingly so!
Right.
However, here’s the reality of doing something new in search. An outfit like Google shows up. The slick representatives offer big piles of money. The start up sells out. What happens? Where’s Dodgeball now? Transformics? Oingo? The Google-type outfits buy threats or “innovators”. Google then uses what it requires. The result?
Google-type companies evolve and remain Googley. Search was a tough market before Google. My team built technology acquired by Lycos. We were fortunate. Would my team do Web search today? Nope. We are working on a different innovative system.
The impact of generative information retrieval applications is difficult to predict. New categories of software are already emerging; for example, the Arc AI search browser innovation. The software is novel, but I have not installed it. The idea is that it is smart and will unleash a finding agent. Maybe this will be a winner? Maybe.
The challenge is that Google and its “finding” functions are woven into many applications that don’t look like search. Examples range from finding an email to the new and allegedly helpful AI additions to Google Maps. If someone can zap Googzilla, my thought is that it will be like the extinction event that took care of its ancestors. One day, nice weather. The next day, snow. Is a traditional search engine enhanced with AI available as a subscription the killer asteroid? One of the techno feudalists will probably have the technology to deflect or vaporize the intruder. One cannot allow Googzilla to go hungry, can one?
Manifestos are good. The authors let off steam. Unfortunately getting sustainable revenues in a world of techno feudalists is, in my opinion, as difficult as killing a windmill. Someone will collect all the search manifestos and publish a book called “The End of Googzilla.” Yep, someday, just not at this time.
PS. There are angles to consider, just not the somewhat tired magazine subscription tactic. Does anyone care? Nah.
Stephen E Arnold, February 7, 2024
Discovering and Sharing Good Websites: No Social Media Required
February 6, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
The Web has evolved over the last decade or two, and largely not in a good way. Blogger Jason Velazquez ponders, “Where Have All the Websites Gone?” Much of it, sadly, is the influence of SEO and Google—every year it gets harder to see the websites for the ads. But Velazquez points to another trend: the way we access web content has changed. Instead of curating it for ourselves and each other, we let social-media algorithms do the job. He points out:
“Somewhere between the late 2000’s aggregator sites and the contemporary For You Page, we lost our ability to curate the web. Worse still, we’ve outsourced our discovery to corporate algorithms. Most of us did it in exchange for an endless content feed. By most, I mean upwards of 90% who don’t make content on a platform as understood by the 90/9/1 rule. And that’s okay! Or, at least, it makes total sense to me. Who wouldn’t want a steady stream of dopamine shots? The rest of us, posters, amplifiers, and aggregators, traded our discovery autonomy for a chance at fame and fortune. Not all, but enough to change the social web landscape. But that gold at the end of the rainbow isn’t for us. ‘Creator funds’ pull from a fixed pot. It’s a line item in a budget that doesn’t change, whether one hundred or one million hands dip inside it. Executives in polished cement floor offices, who you’ll never meet, choose their winners and losers. And I’m guessing it’s not a meritocracy-based system. They pick their tokens, round up their shills, and stuff Apple Watch ads between them.”
But all is not lost. Interesting websites are still out there. Those of us who miss discovering and sharing them can start doing so again. To start, Velazquez offers a list of 13 of his favorites, so see the post for those. He also swapped out the Instagram link in his LinkedIn bio for links to several indie blogging platforms. He suggests readers can do something similar to share their favorite autonomous websites: artists, bloggers, aggregator sites run by humans (hi there!). Any “digital green spaces” will do. The websites have not gone anywhere. We just have to help each other find them.
Cynthia Murrell, February 6, 2024
Answering a Question Posed in an Essay about Search
February 1, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
One of my research team asked me to take a look at an essay located at TomCritchlow.com. “Notes on Search and AI: More Questions Than Answers” reflects the angst generated by generative artificial intelligence. The burr under the saddle of many online users is festering. The plumbing of search is leaking and many of the thumb-typing generation are getting their Airbirds soaked. The discomfort is palpable. One of the people with whom I chat mentioned that some smart software outfits did not return the financial results the MBA whiz kid analysts expected. (Hello, Microsoft?)
The cited essay ends with a question:
Beep boop. What are you thinking about?
Since the author asked, I will answer the question to the best of my ability.
Traditional research skills are irrelevant. Hit the mobile and query, “Pizza near me.” Yep, that works, just not for the small restaurant or “fact”. Thanks, MSFT Copilot Bing thing. How is your email security today? Good enough I bet.
First, most of those who consider themselves good or great online searchers, the emergence of “smart” software makes it easy to find information. The problem is that for good or great online searchers, their ability to locate, verify, analyze, and distill “information” lags behind their own perception of their expertise. In general, the younger online searching expert, the less capable some are. I am basing this on the people with whom I speak in my online and in-person lectures. I am thinking that as these younger people grow older, the old-fashioned research skills will be either unknown, unfamiliar, or impossible. Information cannot be verified nor identified as authoritative. I am thinking that the decisions made based on actionable information is going to accelerate doors popping off aircraft, screwed up hospital patient information systems, and the melancholy of a young cashier when asked to make change by a customer who uses fungible money. Yes, $0.83 from $1.00 is $0.17. Honest.
Second, the jargon in the write up is fascinating. I like words similar to “precision,” “recall,” and “relevance,” among others. The essay explains the future of search with words like these:
Experiences, AI-generated and indexable
Interfaces, adaptive and just-in-time
LLM-powered alerts
Persistence
Predictability
Search quality
Signs
Slime helper
I am thinking that I cannot relate my concept of search and retrieval to the new world the write up references. I want to enter a query into a data base. For that database, I want to know what is in it, when it was updated, and why the editorial policies are for validity, timeliness, coverage, and other dinobaby concepts. In short, I want to do the research work using online when necessary. Other methods are usually required. These include talking to people, reading books, and using a range of reference tools at that endangered institution, the library.
Third, I am thinking that the equipment required for analytic thinking, informed analysis, and judicious decision making is either discarded or consigned to the junk heap.
In short, I am worried because I don’t want indexable experiences, black-box intermediaries, and predictability. I want to gather information and formulate my views based on content I can cite. That’s the answer, and it is not one the author of the essay is seeking. Too bad. Yikes, slime helper.
Stephen E Arnold, February 1, 2024
Why Stuff Does Not Work: Airplane Doors, Health Care Services, and Cyber Security Systems, Among Others
January 26, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
“The Downward Spiral of Technology” stuck a chord with me. Think about building monuments in the reign of Cleopatra. The workers can check out the sphinx and giant stone blocks in the pyramids and ask, “What happened to the technology? We are banging with bronze and crappy metal compounds and those ancient dudes were zipping along with snappier tech.? That conversation is imaginary, of course.
The author of “The Downward Spiral” is focusing on less dusty technology, the theme might resonate with my made up stone workers. Modern technology lacks some of the zing of the older methods. The essay by Thomas Klaffke hit on some themes my team has shared whilst stuffing Five Guys’s burgers in their shark-like mouths.
Here are several points I want to highlight. In closing, I will offer some of my team’s observations on the outcome of the Icarus emulators.
First, let’s think about search. One cannot do anything unless one can find electronic content. (Lawyers, please, don’t tell me you have associates work through the mostly-for-show books in your offices. You use online services. Your opponents in court print stuff out to make life miserable. But electronic content is the cat’s pajamas in my opinion.)
Here’s a table from the Mr. Klaffke essay:
Two things are important in this comparison of the “old” tech and the “new” tech deployed by the estimable Google outfit. Number one: Search in Google’s early days made an attempt to provide content relevant to the query. The system was reasonably good, but it was not perfect. Messrs. Brin and Page fancy danced around issues like disambiguation, date and time data, date and time of crawl, and forward and rearward truncation. Flash forward to the present day, the massive contributions of Prabhakar Raghavan and other “in charge of search” deliver irrelevant information. To find useful material, navigate to a Google Dorks service and use those tips and tricks. Otherwise, forget it and give Swisscows.com, StartPage.com, or Yandex.com a whirl. You are correct. I don’t use the smart Web search engines. I am a dinobaby, and I don’t want thresholds set by a 20 year old filtering information for me. Thanks but no thanks.
The second point is that search today is a monopoly. It takes specialized expertise to find useful, actionable, and accurate information. Most people — even those with law degrees, MBAs, and the ability to copy and paste code — cannot cope with provenance, verification, validation, and informed filtering performed by a subject matter expert. Baloney does not work in my corner of the world. Baloney is not a favorite food group for me or those who are on my team. Kudos to Mr. Klaffke to make this point. Let’s hope someone listens. I have given up trying to communicate the intellectual issues lousy search and retrieval creates. Good enough. Nope.
Yep, some of today’s tools are less effective than modern gizmos. Hey, how about those new mobile phones? Thanks, MSFT Copilot Bing thing. Good enough. How’s the MSFT email security today? Oh, I asked that already.
Second, Mr Klaffke gently reminds his reader that most people do not know snow cones from Shinola when it comes to information. Most people assume that a computer output is correct. This is just plain stupid. He provides some useful examples of problems with hardware and user behavior. Are his examples ones that will change behaviors. Nope. It is, in my opinion, too late. Information is an undifferentiated haze of words, phrases, ideas, facts, and opinions. Living in a haze and letting signals from online emitters guide one is a good way to run a tiny boat into a big reef. Enjoy the swim.
Third, Mr. Klaffke introduces the plumbing of the good-enough mentality. He is accurate. Some major social functions are broken. At lunch today, I mentioned the writings about ethics by Thomas Dewey and William James. My point was that these fellows wrote about behavior associated with a world long gone. It would be trendy to wear a top hat and ride in a horse drawn carriage. It would not be trendy to expect that a person would work and do his or her best to do a good job for the agreed-upon wage. Today I watched a worker who played with his mobile phone instead of stocking the shelves in the local grocery store. That’s the norm. Good enough is plenty good. Why work? Just pay me, and I will check out Instagram.
I do not agree with Mr. Klaffke’s closing statement; to wit:
The problem is not that the “machine” of humanity, of earth is broken and therefore needs an upgrade. The problem is that we think of it as a “machine”.
The problem is that worldwide shared values and cultural norms are eroding. Once the glue gives way, we are in deep doo doo.
Here are my observations:
- No entity, including governments, can do anything to reverse thousands of years of cultural accretion of norms, standards, and shared beliefs.
- The vast majority of people alive today are reverting back to some fascinating behaviors. “Fascinating” is not a positive in the sense in which I am using the word.
- Online has accelerated the stress on social glue; smart software is the turbocharger of abrupt, hard-to-understand change.
Net net: Please, read Mr. Klaffke’s essay. You may have an idea for remediating one or more of today’s challenges.
Stephen E Arnold, January 25, 2024
Search Market Data: One Click to Oblivion Is Baloney, Mr. Google
January 24, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Do you remember the “one click away” phrase. The idea was and probably still is in the minds of some experts that any user can change search engines with a click. (Eric Schmidt, the adult once in charge of the Google) also suggested that he is kept awake at night worrying about Qwant. I know? Qwant what?
 “I have all the marbles,” says the much loved child. Thanks, MSFT second string Copilot Bing thing. Good enough.
“I have all the marbles,” says the much loved child. Thanks, MSFT second string Copilot Bing thing. Good enough.
I read an interesting factoid. I don’t know if the numbers are spot on, but the general impression of the information lines up with what my team and I have noted for decades. The relevance champions at Search Engine Roundtable published “Report: Bing Gained Less Than 1% Market Share Since Adding Bing Chat.”
Here’s a passage I found interesting:
Bloomberg reported on the StatCounter data, saying, “But Microsoft’s search engine ended 2023 with just 3.4% of the global search market, according to data analytics firm StatCounter, up less than 1 percentage point since the ChatGPT announcement.”
There’s a chart which shows Google’s alleged 91.6 percent Web search market share. I love the precision of a point six, don’t you? The write up includes a survey result suggesting that Bing would gain more market share.
Yeah, one click away. Oh, Qwant.com is still on line at https://www.qwant.com/. Rest easy, Google.
Stephen E Arnold, January 24, 2024
How Do You Foster Echo Bias, Not Fake, But Real?
January 24, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Research is supposed to lead to the truth. It used to when research was limited and controlled by publishers, news bureaus, and other venues. The Internet liberated information access but it also unleashed a torrid of lies. When these lies are stacked and manipulated by algorithms, they become powerful and near factual. Nieman Labs relates how a new study shows the power of confirmation in, “Asking People ‘To Do The Research’ On Fake News Stories Makes Them Seem More Believable, Not Less.”
Nature reported on a paper by Kevin Aslett, Zeve Sanderson, William Godel, Nathaniel Persily, Jonathan Nagler, and Joshua A. Tucker. The paper abstract includes the following:
Here, across five experiments, we present consistent evidence that online search to evaluate the truthfulness of false news articles actually increases the probability of believing them. To shed light on this relationship, we combine survey data with digital trace data collected using a custom browser extension. We find that the search effect is concentrated among individuals for whom search engines return lower-quality information. Our results indicate that those who search online to evaluate misinformation risk falling into data voids, or informational spaces in which there is corroborating evidence from low-quality sources. We also find consistent evidence that searching online to evaluate news increases belief in true news from low-quality sources, but inconsistent evidence that it increases belief in true news from mainstream sources. Our findings highlight the need for media literacy programs to ground their recommendations in empirically tested strategies and for search engines to invest in solutions to the challenges identified here.”
All of the tests were similar in that they asked participants to evaluate news articles that had been rated “false or misleading” by professional fact checkers. They were asked to read the articles, research and evaluate the stories online, and decide if the fact checkers were correct. Controls were participants who were asked not to research stories.
The tests revealed that searching online increase misinformation belief. The fifth test in the study explained that exposure to lower-quality information in search results increased the probability of believing in false news.
The culprit for bad search engine results is data voids akin to rabbit holes of misinformation paired with SEO techniques to manipulate people. People with higher media literacy skills know how to better use search engines like Google to evaluate news. Poor media literacy people don’t know how to alter their search queries. Usually they type in a headline and their results are filled with junk.
What do we do? We need to revamp media literacy, force search engines to limit number of paid links at the top of results, and stop chasing sensationalism.
Whitney Grace, January 24, 2024
Kagi For-Fee Search: Comments from a Thread about Search
January 2, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Comparisons of search engine performance are quite difficult to design, run, and analyze. In the good old days when commercial databases reigned supreme, special librarians could select queries, refine them, and then run those queries via Dialog, LexisNexis, DataStar, or another commercial search engine. Examination of the results were tabulated and hard copy print outs on thermal paper were examined. The process required knowledge of the search syntax, expertise in query shaping, and the knowledge in the minds of the special librarians performing the analysis. Others were involved, but the work focused on determining overlap among databases, analysis of relevance (human and mathematical), and expertise gained from work in the commercial database sector, academic training, and work in a special library.
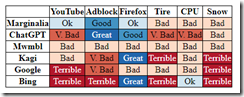
Who does that now? Answer: No one. With this prefatory statement, let’s turn our attention to “How Bad Are Search Results? Let’s Compare Google, Bing, Marginalia, Kagi, Mwmbl, and ChatGPT.” Please, read the write up. The guts of the analysis, in my opinion, appear in this table:
The point is that search sucks. Let’s move on. The most interesting outcome from this write up from my vantage point is the comments in the Hacker News post. What I want to do is highlight observations about Kagi.com, a pay-to-use Web search service. The items I have selected make clear why starting and building sustainable revenue from Web search is difficult. Furthermore, the comments I have selected make clear that without an editorial policy, specific information about the corpus, its updating, and content acquisition method — evaluation is difficult.
Long gone are the days of precision and recall, and I am not sure most of today’s users know or care. I still do, but I am a dinobaby and one of those people who created an early search-related service called The Point (Top 5% of the Internet), the Auto Channel, and a number of other long-forgotten Web sites that delivered some type of findability. Why am I roadkill on the information highway? No one knows or cares about the complexity of finding information in print or online. Sure, some graduate students do, but are you aware that the modern academic just makes up or steals other information; for instance, the former president of Stanford University.l
Okay, here are some comments about Kagi.com from Hacker News. (Please, don’t write me and complain that I am unfair. I am just doing what dinobabies with graduate degrees do — Provide footnotes)
hannasanario: I’m not able to reproduce the author’s bad results in Kagi, at all. What I’m seeing when searching the same terms is fantastic in comparison. I don’t know what went wrong there. Dinobaby comment: Search results, in the absence of editorial policies and other basic information about valid syntax means subjectivity is the guiding light. Remember that soap operas were once sponsored influencer content.
Semaphor: This whole thread made me finally create a file for documenting bad searches on Kagi. The issue for me is usually that they drop very important search terms from the query and give me unrelated results. Dinobaby comment: Yep, editorial functions in results, and these are often surprises. But when people know zero about a topic, who cares? Not most users.
Szundi: Kagi is awesome for me too. I just realize using Google somewhere else because of the sh&t results. Dinobaby comment: Ah, the Google good enough approach is evident in this comment. But it is subjective, merely an opinion. Just ask a stockholder. Google delivers, kiddo.
Mrweasel: Currently Kagi is just as dependent on Google as DuckDuckGo is on Bing. Dinobaby comment: Perhaps Kagi is not communicating where content originates, how results are generated, and why information strikes Mrweasel as “dependent on Google. Neeva was an outfit that wanted to go beyond Google and ended up, after marketing hoo hah selling itself to some entity.
Fenaro: Kagi should hire the Marginalia author. Dinobaby comment: Staffing suggestions are interesting but disconnected from reality in my opinion.
ed109685: Kagi works because there is no incentive for SEO manipulators to target it since their market share is so small. Dinobaby comment: Ouch, small.
shado: I became a huge fan of Kagi after seeing it on hacker news too. It’s amazing how good a search engine can be when it’s not full of ads. Dinobaby comment: A happy customer but no hard data or examples. Subjectivity in full blossom.
yashasolutions: Kagi is great… So I switch recently to Kagi, and so far it’s been smooth sailing and a real time saver. Dinobaby comment: Score another happy, paying customer for Kagi.
innocentoldguy: I like Kagi and rarely use anything else. Kagi’s results are decent and I can blacklist sites like Amazon.com so they never show up in my search results. Dionobaby comment: Another dinobaby who is an expert about search.
What does this selection of Kagi-related comments reveal about Web search? Here’s snapshot of my notes:
- Kagi is not marketing its features and benefits particularly well, but what search engine is? With Google sucking in more than 90 percent of the query action, big bucks are required to get the message out. This means that subscriptions may be tough to sell because marketing is expensive and people sign up, then cancel.
- There is quite a bit of misunderstanding among “expert” searchers like the denizens of Hacker News. The nuances of a Web search, money supported content, metasearch, result matching, etc. make search a great big cloud of unknowing for most users.
- The absence of reproducible results illustrates what happens when consumerization of search and retrieval becomes the benchmark. The pursuit of good enough results in loss of finding functionality and expertise.
Net net: Search sucks. Oh, wait, I used that phrase in an article for Barbara Quint 35 years ago.
PS. Mwmbl is at https://mwmbl.or in case you are not familiar with the open source, non profit search engine. You have to register, well, because…
Stephen E Arnold, January 2, 2024
A Dinobaby Misses Out on the Hot Searches of 2023
December 28, 2023
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
I looked at “Year in Search 2023.” I was surprised at how out of the flow of consumer information I was. “Out of the flow” does not not capture my reaction to the lists of the news topics, dead people, and songs I was. Do you know much about Bizarrap? I don’t. More to the point, I have never heard of the obviously world-class musician.
Several observations:
First, when people tell me that Google search is great, I have to recalibrate my internal yardsticks to embrace queries for entities unrelated to my microcosm of information. When I assert that Google search sucks, I am looking for information absolutely positively irrelevant to those seeking insight into most of the Google top of the search charts. No wonder Google sucks for me. Google is keeping pace with maps of sports stadia.
Second, as I reviewed these top searches, I asked myself, “What’s the correlation between advertisers’ spend and the results on these lists? My idea is that a weird quantum linkage exists in a world inhabited by incentivized programmers, advertisers, and the individuals who want information about shirts. Its the game rigged? My hunch is, “Yep.” Spooky action at a distance I suppose.
Third, from the lists substantive topics are rare birds. Who is looking for information about artificial intelligence, precision and recall in search, or new approaches to solving matrix math problems? The answer, if the Google data are accurate and not a come on to advertisers, is almost no one.
As a dinobaby, I am going to feel more comfortable in my isolated chamber in a cave of what I find interesting. For 2024, I have steeled myself to exist without any interest in Ginny & Georgia, FIFTY FIFTY, or papeda.
I like being a dinobaby. I really do.
Stephen E Arnold, December 28, 2023
Why Google Dorks Exist and Why Most Users Do Not Know Why They Are Needed
December 4, 2023
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Many people in my lectures are not familiar with the concept of “dorks”. No, not the human variety. I am referencing the concept of a “Google dork.” If you do a quick search using Yandex.com, you will get pointers to different “Google dorks.” Click on one of the links and you will find information you can use to retrieve more precise and relevant information from the Google ad-supported Web search system.
Here’s what QDORKS.com looks like:
The idea is that one plugs in search terms and uses the pull down boxes to enter specific commands to point the ad-centric system at something more closely resembling a relevant result. Other interfaces are available; for example, the “1000 Best Google Dorks List." You get a laundry list of tips,commands, and ideas for wrestling Googzilla to the ground, twisting its tail, and (hopefully) yield relevant information. Hopefully. Good work.
Most people are lousy at pinning the tail on the relevance donkey. Therefore, let someone who knows define relevance for the happy people. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Nice animal with map pins.
Why are Google Dorks or similar guides to Google search necessary? Here are three reasons:
- Precision reduces the opportunities for displaying allegedly relevant advertising. Semantic relaxation allows the Google to suggest that it is using Oingo type methods to find mathematically determined relationships. The idea is that razzle dazzle makes ad blasting something like an ugly baby wrapped in translucent fabric on a foggy day look really great.
- When Larry Page argued with me at a search engine meeting about truncation, he displayed a preconceived notion about how search should work for those not at Google or attending a specialist conference about search. Rational? To him, yep. Logical? To his framing of the search problem, the stance makes perfect sense if one discards the notion of tense, plurals, inflections, and stupid markers like “im” as in “impractical” and “non” as in “nonsense.” Hey, Larry had the answer. Live with it.
- The goal at the Google is to make search as intellectually easy for the “user” as possible. The idea was to suggest what the user intended. Also, Google had the old idea that a person’s past behavior can predict that person’s behavior now. Well, predict in the sense that “good enough” will do the job for vast majority of search-blind users who look for the short cut or the most convenient way to get information.
Why? Control, being clever, and then selling the dream of clicks for advertisers. Over the years, Google leveraged its information framing power to a position of control. I want to point out that most people, including many Googlers, cannot perceive. When pointed out, those individuals refuse to believe that Google does [a] NOT index the full universe of digital data, [b] NOT want to fool around with users who prefer Boolean algebra, content curation to identify the best or most useful content, and [c] fiddle around with training people to become effective searchers of online information. Obfuscation, verbal legerdemain, and the “do no evil” craziness make the railroad run the way Cornelius Vanderbilt-types implemented.
I read this morning (December 4, 2023) the Google blog post called “New Ways to Find Just What You Need on Search.” The main point of the write up in my opinion is:
Search will never be a solved problem; it continues to evolve and improve alongside our world and the web.
I agree, but it would be great if the known search and retrieval functions were available to users. Instead, we have a weird Google Mom approach. From the write up:
To help you more easily keep up with searches or topics you come back to a lot, or want to learn more about, we’re introducing the ability to follow exactly what you’re interested in.
Okay, user tracking, stored queries, and alerts. How does the Google know what you want? The answer is that users log in, use Google services, and enter queries which are automatically converted to search. You will have answers to questions you really care about.
There are other search functions available in the most recent version of Google’s attempts to deal with an unsolved problem:
As with all information on Search, our systems will look to show the most helpful, relevant and reliable information possible when you follow a topic.
Yep, Google is a helicopter parent. Mom will know what’s best, select it, and present it. Don’t like it? Mom will be recalcitrant, like shaping search results to meet what the probabilistic system says, “Take your medicine, you brat.” Who said, “Mother Google is a nice mom”? Definitely not me.
And Google will make search more social. Shades of Dr. Alon Halevy and the heirs of Orkut. The Google wants to bring people together. Social signals make sense to Google. Yep, content without Google ads must be conquered. Let’s hope the Google incentive plans encourage the behavior, or those valiant programmers will be bystanders to other Googlers’ promotions and accompanying money deliveries.
Net net: Finding relevant, on point, accurate information is more difficult today than at any other point in the 50+ year work career. How does the cloud of unknowing dissipate? I have no idea. I think it has moved in on tiny Googzilla feet and sits looking over the harbor, ready to pounce on any creature that challenges the status quo.
PS. Corny Vanderbilt was an amateur compared to the Google. He did trains; Google does information.
Stephen E Arnold, December 4, 2023
Using Smart Software to Make Google Search Less Awful
November 16, 2023
 This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
Here’s a quick tip: to get useful results from Google Search, use a competitor’s software. Digital Digging blogger Henk van Ess describes “How to Teach ChatGPT to Come Up with Google Formulas.” Specifically, Ess needed to include foreign-language results in his queries while narrowing results to certain time frames. These are not parameters Google handles well on its own. It was Chat GPT to the rescue—after some tinkering, anyway. He describes an example search goal:
“Find any official document about carbon dioxide reduction from Greek companies, anything from March 24, 2020 to December 21, 2020 will do. Hey, can you search that in Greek, please? Tough question right? Time to fire up Bing or ChatGPT. Round 1 in #chatgpt has a terrible outcome.”
But of course, Hess did not stop there. For the technical details on the resulting “ball of yarn,” how Hess resolved it, and how it can be extrapolated to other use cases, navigate to the write-up. One must bother to learn how to write effective prompts to get these results, but Hess insists it is worth the effort. The post observes:
“The good news is: you only have to do it once for each of your favorite queries. Set and forget, as you just saw I used the same formulae for Greek CO2 and Japanese EV’s. The advantage of natural language processing tools like ChatGPT is that they can help you generate more accurate and relevant search queries in a faster and more efficient way than manually typing in long and complex queries into search engines like Google. By using natural language processing tools to refine and optimize your search queries, you can avoid falling into ‘rabbit holes’ of irrelevant or inaccurate results and get the information you need more quickly and easily.”
Google is currently rolling out its own AI search “experience” in phases around the world. Will it improve results, or will one still be better off employing third-party hacks?
Cynthia Murrell, November 16, 2023