Another Baby Step Toward the Metaverse
June 17, 2022
Not one to be outdone by rivals like Meta and Snap, VentureBeat reports, “TikTok Launches Avatars for Creative Expression.” We wonder what what’s Mr. Zuckerberg’s avatar looks like. Citing the company’s blog post, writer Dean Takahashi reports:
“Available globally, TikTok Avatars is a new way for people to express themselves and create content on TikTok, opening doors to new and dynamic content. It feels like a step toward multiplayer gaming, where avatars are very popular, as well as the metaverse. Users will be able to select from a variety of preferences within the app, from hairstyles to accessories, to create an avatar that reflects a unique look and personality. Once customized, users can record videos as their avatars. TikTok said it created TikTok Avatars for everybody and worked to make sure the experience is as inclusive as possible. It will continue to improve and innovate to make sure the experience is representative of everyone on TikTok and will continue to listen to the community for feedback at every step of the development.”
Yes, they must be very careful not to run afoul of the inclusion police. The brief write-up continues:
“The company said it is building spaces across TikTok for virtual self expression and exploring ways people can connect and create across our global community.”
Might those spaces be metaverse-adjacent, perhaps? It seems TikTok is joining Meta and others on the cliff’s edge, getting ready to make the virtual-reality leap.
Cynthia Murrell, June 17, 2022
Disadvantaged Groups and Simple Explanations
June 16, 2022
Bias in machine learning algorithms is a known problem. Decision makers, like admissions officers for example, sometimes turn to explanation models in an effort to avoid this issue. These tools construct simplified approximations of larger models’ predictions that are easier to understand. But wait, one may ask, aren’t these explanations also generated by machine learning AI? Indeed they are. MIT News examines this sticky wicket in its piece, “In Bias We Trust?” A team of MIT researchers checked for bias in some widely used explanation models and, low and behold, they found it. Writer Adam Zewe tells us:
“They found that the approximation quality of these explanations can vary dramatically between subgroups and that the quality is often significantly lower for minoritized subgroups. In practice, this means that if the approximation quality is lower for female applicants, there is a mismatch between the explanations and the model’s predictions that could lead the admissions officer to wrongly reject more women than men. Once the MIT researchers saw how pervasive these fairness gaps are, they tried several techniques to level the playing field. They were able to shrink some gaps, but couldn’t eradicate them. ‘What this means in the real-world is that people might incorrectly trust predictions more for some subgroups than for others. So, improving explanation models is important, but communicating the details of these models to end users is equally important. These gaps exist, so users may want to adjust their expectations as to what they are getting when they use these explanations,’ says lead author Aparna Balagopalan, a graduate student in the Healthy ML group of the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL).”
Or we could maybe go back to using human judgment for decisions that affect the lives of others? Nah. See the article for details of how the researchers evaluated explanation models’ fidelity and their work to narrow (but not eliminate) the gaps. Zewe reports the team plans to extend its research to ways fidelity gaps affect decisions in the real world. We look forward to learning what they find, though we suspect we will not be surprised by the results.
Cynthia Murrell, June 16, 2022
Zuckbook and Addiction: Let the Legal Eagles Loose
June 10, 2022
I find the addiction to an online service or to a fungible device difficult to understand. The one year I taught in a high school, I did encounter students on drugs. For the most part, these individuals dozed, mumbled, and seemed pretty happy. The principal (remember, the principal is your pal) did not care as long as there was no trouble which would attract the local Live at Five TV crew.
I did not understand the need, desire, hunger, or whatever for controlled substances. I still don’t. Now I cannot fathom an addiction to online content or a computing device. Obviously I am not a good person to consult about getting hooked on anything other than “work” like writing blog posts and working on my new monograph for law enforcement and intelligence professionals. (A US government entity gets a preview in July! You don’t. Grab your mobile phone and zone out, okay?)
“Meta Was Sued for Its Algorithm. Section 230 Might Not Be a Shield” makes it clear that I have zero comprehension of this chain of activity:
Mobile phone –> Service providers –> Online content –> Algorithms = Digital heroin.
The write up tries to get through to my brain infused with a 500 ML Pellegrino and a granola bar:
Meta was slapped with eight different complaints, filed in as many states, alleging that its algorithms have contributed to mental health issues such as eating disorders, sleeplessness and suicidal thoughts or tendencies in younger users. The complaints allege that excessive time on Instagram and Facebook pose serious risks to mental health, with one plaintiff claiming that Meta “misrepresented the safety, utility, and non-addictive properties” of its platforms.
And the fix from my point of view? How about these tips? For parents, take the phone away. For 20 somethings, get a van and go off grid. For those older, grow up. But I am in the minority because this ecosystem of online is chugging along like an aggressive cancer in one’s pancreas. I learned:
Rather than going after the content itself, these complaints target the algorithm that serves it to users…
Okay, that will be fun to figure out and then explain to other lawyers, a judge, and maybe a jury. Most algorithms are combinations of mathematical procedures taught in every college and university math class in the world. Assembling them is a bit like building a model airplane. The cuteness is in the threshold settings, the desired feedback inputs, and that old razzle dazzle of looking at user behavior. Bingo. Math works like heroin.
The write up makes this point:
“Basically, it’s [winning one of the suits against the Zuckbook] like a lottery,” said Goldman. [big wheel legal eagle] “You only really need to win one in order to open up a very, very big door for future litigation.”
Since the 1970s, online has been a thing. Now it is society wide and suddenly we are setting up the largest flight of legal eagles in recorded history. “Big door”? Probably like the door for the old moon rockets.
Will the Zuckbook take the fall? Will parents take away mobile phones and limit Chromebook time? Will adults of different ages go back to typing stuff on a typewriter as one European intelligence entity has?
Probably not. Therefore, legal eagles aloft. Everyone benefits from the actions of legal eagles just not as much as the legal eagles. Will there be substantive change? Ho ho ho.
Stephen E Arnold, June 10, 2022
TikTok: Can One Monetize Human Smuggling?
June 6, 2022
Selling or renting people for illegal purposes remains an area of interest to government officials. Disruptions like Russia’s special action in Ukraine have contributed to the flow of product. I read “Inside the Risky World of Migrant TikTok” and learned:
migrant TikTok[is] an ecosystem of content by and for migrants often repurposed to advertise and promote perilous, sometimes deadly journeys across closed European borders.
The write up added:
experts pointed to migrant TikTok as a new entry point for young people into the world of irregular migration. The absence of reliable information means that social media has long played a role in helping people share advice, with Facebook groups and other private channels acting as informal hubs for knowledge: how to travel, whom to contact. But with the rise of apps like TikTok where posts are public, compounded by recommender algorithms that repeatedly suggest similar content, virality [sic] has given this information greater reach among people who aren’t actively searching for it.
The article includes an interesting observation about the smart software in use at Zuckbook and TikTok; to wit:
Social media companies like TikTok and Meta increasingly employ AI systems to moderate content at scale. But since these AI systems are context-blind, digital rights activists say they can end up missing, for example, a key word in dialect. That keyword may continue to feed similar content onto a user’s timeline.
The European Union is poking into this subject and regulations may emerge:
New EU legislation attempts to mandate the monitoring of online smuggling networks and even algorithm transparency, while agencies like Frontex and Europol have tried to use data scraping to inform predictive analysis models for what routes illegal migrants might use. So far, it’s resulted in a tug of war that leaves the content largely up and available.
The write up points to a word like haraga (?????) or harraga when converted to Kentucky speak’s colloquial “those who burn at the borders.” (Klassy Kentucky, of course.)
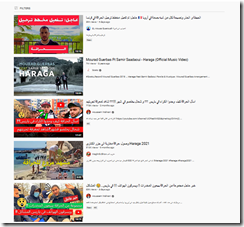
I was curious about the estimable Google. The link to search YouTube’s version of TikTok is at this link. Now enter the term “haraga”. Here’s the result I saw using my “we track you, Beyond Search person:
Yep, looks like the type of content discussed in the cited article.
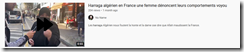
What about the spelling harraga:
To sum up, the focus on TikTok is good. TikTok is gnawing into the viewing habits of people younger than I. Facebook and Google want to check the China-affiliated super app. The Google’s filtering system may need some tweaking to cope with the migration information findable to some degree on YouTube.
Several observations:
- More attention should be directed at TikTok and other short video platforms as well
- Smart software has not been turned to filter certain content some European border control professionals might like
- The EU regulatory moves warrant watching. Now there’s a story for the big US media to explore.
- Where there is traffic, there will be ads.
Net net: The content related possibly illegal trans border activity is one more example about the growing influence of TikTok. The flip side is that Zuckbook and Google may find themselves “following.” I do not give this a “like.”
Stephen E Arnold, June 6, 2022
A Harvard Class in Tweets
June 2, 2022
In my first semester of college (certainly not a Harvard because I am a dull normal Rust Belt kid), I figured out that I could boil down an entire 15 week semester into a small stack of 5×8 notecards. Studying to the final was a breeze; there simply wasn’t much to the professors lectures. Let’s see. I was a freshman in 1962, which means that college courses have not changed too much. Instead of notecards I created (and sold to some varsity athletes if I reveal my revenue secrets), “A Harvard Economist Summarizes His Class on Monopolies in 54 Tweets” states:
He began by outlining the four main sections of the class—(1) government policy towards monopolies, (2) competition policy in practice, (3) the increase in industry concentration, (4) the digital giants—and then went on to extrapolate on each issue in a series of 54 tweets.
Next up? Maybe TikToks.
Stephen E Arnold, June 2, 2022
Senior Citizens Take to TikTok
June 1, 2022
More bad news for Facebook? Yep.
We learn from The Guardian, “Older People Using TikTok to Defy Ageist Stereotypes, Research Finds.” Does an influx of Boomers and above on the typically Gen-Z platform counteract the image of frail and technophobic oldsters? We are told their millions of followers suggest it just might. Citing a recent study, reporter Amelia Hill writes:
“The paper looked at 1,382 videos posted by TikTok users who were aged 60 or older and had between 100,000 and 5.3 million followers. In total, their videos, all of which explicitly discussed their age, had been viewed more than 3.5bn times. Ng found that 71% of these videos – including those from accounts such as grandadjoe1933, who has 5.3 million followers, and dolly_broadway, who has 2.4 million followers – were used to defy age stereotypes. A recurring motif was the ‘glamma’, a portmanteau combining ‘glamorous’ and ‘grandma’, with videos including those of a 70-year-old woman joyfully parading around the streets in a midriff-bearing top. Almost one in five of the videos analyzed made light of age-related vulnerabilities, and one in 10 called out ageism among both younger people and their own contemporaries. Other videos positioned older users as superior to younger people. ‘I may be 86 but I can still drink more than you lightweights’ says one clip. ‘I may be 86 but I can still twerk better than you,’ says another, showing an octogenarian leaping up from a fall down the stairs with a twerk.”
Um, are we sure followers are supporting these content creators, not just laughing at them? Perhaps it does not matter, as long as the elders are having a bit of fun. See the write-up for more examples of seniors strutting their stuff on TikTok. The trend emerges as, according to the Pew Research Centre, more folks over 65 are finally obtaining smartphones and joining the rest of the world online. It seems many are eager to make their presence known.
Cynthia Murrell, June 1, 2022
Online Platforms Fail to Prevent Circulation of Buffalo Shooting Video
May 27, 2022
Once again, the Internet proves that even the vilest content cannot be contained. It is a fact racist terrorists have learned to exploit to spread fear, hatred, and inspiration for more violence. The Washington Post reports, “Only 22 Saw the Buffalo Shooting Live. Millions Have Seen it Since.” Writers Drew Harwell and Will Oremus tell us:
“When the Buffalo gunman broadcast the shooting in real time Saturday on the live-streaming site Twitch, only 22 people were watching, and company officials said they’d removed it with remarkable speed — within two minutes of the first gunshots. But all it took was for one viewer to save a copy and redistribute it online. A jumble of video-hosting sites, extremist message boards and some of Silicon Valley’s biggest names did the rest, ensuring millions of people would view the video. One copy made its way onto the little-known video site Streamable, where, thanks to links posted on much larger sites, it was viewed more than 3 million times before it was removed. One link to that copy on Facebook received more than 500 comments and 46,000 shares; Facebook did not remove it for more than 10 hours. ‘Terrorism is theater,’ said Emerson T. Brooking, senior fellow at the Atlantic Council’s Digital Forensic Research Lab, which researches how information spreads online. ‘The purpose of terrorism is always to reach the greatest number of people possible with the most horrific or spectacular attack that you can perform.'”
Several ideas have been floated to combat the spread of this grisly propaganda. Some are trying to wield digital fingerprint technology for good by using it to filter content. Then there was the “hate clusters” concept. Major tech companies even set up a Global Internet Forum to Counter Terrorism, a system meant to automatically block terrorist videos that was based on tech originally used to block footage of child sexual abuse. Clearly, none of these measures are working. Will the answer be found, and implemented, before the next attack?
Cynthia Murrell, May 27, 2022
Facebook: Maybe Thinking about Superapps?
May 23, 2022
The idea of popping up a level is a good one. Examples range from companies offering ways to manage multiple APIs to services hooking consumers with individual providers, regardless of where the providers call home.
“Wikipedia Over WhatsApp” explains:
If the wifi is letting WhatsApp messages through, what if we used WhatsApp as a vehicle for the information we really care about? Much like we encapsulate the rest of our networking objects in higher-level objects, we could encapsulate web pages inside of WhatsApp messages.
Okay, who is really excited about reading Wikimedia’s entry about my relative Vladimir Igorevich Arnold, a mathematician, which is an exciting profession to be sure? Not too many people.
The idea of using WhatsApp as a mechanism for other services is a good one. Is it Facebook’s attempt to become a superapp or allow others to use WhatsApp as a superapp.
Some encrypted end to end messaging services include a number of useful functions now. But what if almost any traditional browser based function could be supported within a messaging app on one’s mobile phone. Apple uses a “up a level” method with its requirement that browser developers honor and respect the wonderful WebKit thing.
Interesting if true.
Stephen E Arnold, May 23, 2022
TikTok Sells Books. Who Knew? Amazon?
May 20, 2022
And some were concerned social media had made books obsolete. To the contrary, reports BBC News, “TikTok Helps UK Book Sales Hit Record Levels, Publishers Association Says.” The UK’s Publishers Association was pleased to see sales of printed books in that country rise by 5% last year. It is especially impressive, notes the organization’s chief executive Stephen Lotinga, given bookstores were still closed for the first quarter of 2021. He credits a TikTok trend with at least part of the increase. The article reports:
“The organization said four of the top five young adult bestsellers in 2021 had been driven by the BookTok trend. … Publishers Association chief executive Stephen Lotinga said viral videos on platforms like TikTok and YouTube had been ‘really significant’ in encouraging readers to discover books. ‘Anecdotally, we’ve had lots of individual booksellers talking about the fact that they’re having lots of young people coming into their book stores, talking about books that they have heard about on TikTok and asking for them,’ he said. ‘It is having an impact on the number of books sold, but the shape of what’s being sold is changing as well. Throughout the pandemic period, we saw people increasingly buying what we call backlist books, which are books that have been published in the past.’ Many of the titles that have taken off on TikTok are several years old rather than brand new releases.”
Rather than a preference for new releases, we learn, BookTok favors books with unexpected or dramatic endings. At least that appears to be the current trend. The bump in print-book sales was accompanied by a dip by 1% in digital sales. Interestingly, audio-book downloads beat out both with an increase of 14%.
Cynthia Murrell, May 20, 2022
China Targets Low-Profile Social Network Douban for Censorship
May 20, 2022
China continues to do one of the things it does best: control the flow of information within its borders. Rest of World reports, “China’s Most Chaotic Social Network Survived Beijing’s Censors—Until Now.” Writer Viola Zhou describes the low-profile site:
“The chaotic Chinese social network Douban never looked for fame; it was designed for people with niche obsessions and an urge to talk about them. … Douban began as a review site for books, film, and music: the interests of its charismatic founder, Ah Bei. It quickly grew into a social network of millions of users.”
Those users bonded around shared interests both playful and serious. To keep the site rooted in a spirit of community, it has resisted both large-scale advertising and (unlike other social networks) government propaganda accounts. Douban managed to avoid scrutiny by China’s fervent censors since it launched in 2005. Until now. Zhou continues:
“In March, a government censorship task force was set up at the company’s headquarters. Over the past year, some of its most popular groups have shut down, its app was scrubbed from major Chinese stores, and on April 14, Douban froze a significant traffic driver, the gossip forum Goose Group, though it’s unclear whether each of those actions were the decisions of the website or government regulators. As China’s tech crackdown seeps into all parts of online life, the ability to organize around something as mild as shared interests is being throttled by Beijing’s censors. Rest of World spoke to more than a dozen early Douban employees, prominent group admins, and current users, most of whom requested anonymity in order to freely discuss Chinese censorship. For them, the reining-in of Douban signals that its creative, tight-knit communities have become an unacceptable political risk, as the Chinese government grows increasingly vigilant about any form of civil gathering.”
Yes, it seems citizens coming together over any topic, no matter how far from political or social matters, is a threat. The pressure on Douban is said to be part of the government’s campaign against a scourge dubbed “fan circle chaos.” Colorful. Some users hold out hope their beloved groups will someday be reinstated. Meanwhile, founder Ah Bei’s account has been inactive since 2019. See the write-up for more about Douban and some of its forums that have been shuttered.
Cynthia Murrell, May 20, 2022