Google: Making a Buck Is the Name of the Game
December 30, 2024
 This blog post was crafted by a still-living dinobaby.
This blog post was crafted by a still-living dinobaby.
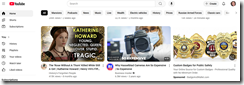
This is a screenshot of YouTube with an interesting advertisement. Take a look:
Here’s a larger version of the ad:
Now here’s the landing page for the teaser which looks like a link to a video:
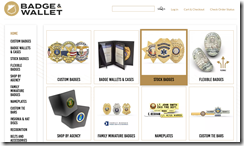
The site advertising on YouTube.com is Badgeandwallet.com. The company offers a number of law enforcement related products. Here’s a sample of the badges available to a person exploring the site:
How many law enforcement officers are purchasing badges from an ad on YouTube? At some US government facilities, shops will provide hats and jackets with agency identification on them. However, to make a purchase, a visitor to the store must present current credentials.
YouTube.com and its parent are under scrutiny for a number of the firm’s business tactics. I reacted negatively to the inclusion of this advertisement in search results related to real estate in Beverly Hills, California.
Is Google the brilliant smart software company it says it is, or is the company just looking to make a buck with ads likely to be viewed by individuals who have little or nothing to do with law enforcement or government agencies?
I hope that 2025 will allow Google to demonstrate that it wants to be viewed as a company operating with a functioning moral compass. My hunch is that I will be disappointed as I have been with quantum supremacy and Googley AI.
Stephen E Arnold, December 30, 2025
Meta, Politics, and Money
October 24, 2024
Meta and its flagship product, Facebook, makes money from advertising. Targeted advertising using Meta’s personalization algorithm is profitable and political views seem to turn the money spigot. Remember the January 6 Riots or how Russia allegedly influenced the 2016 presidential election? Some of the reasons those happened was due to targeted advertising through social media like Facebook.
Gizmodo reviews how much Meta generates from political advertising in: “How Meta Brings In Millions Off Political Violence.” The Markup and CalMatters tracked how much money Meta made from Trump’s July assassination attempt via merchandise advertising. The total runs between $593,000 -$813,000. The number may understate the actual money:
“If you count all of the political ads mentioning Israel since the attack through the last week of September, organizations and individuals paid Meta between $14.8 and $22.1 million dollars for ads seen between 1.5 billion and 1.7 billion times on Meta’s platforms. Meta made much less for ads mentioning Israel during the same period the year before: between $2.4 and $4 million dollars for ads that were seen between 373 million and 445 million times. At the high end of Meta’s estimates, this was a 450 percent increase in Israel-related ad dollars for the company. (In our analysis, we converted foreign currency purchases to current U.S. dollars.)”
The organizations that funded those ads were supporters of Palestine or Israel. Meta doesn’t care who pays for ads. Tracy Clayton is a Meta spokesperson and she said that ads go through a review process to determine if they adhere to community standards. She also that advertisers don’t run their ads during times of strife, because they don’t want their goods and services associates with violence.
That’s not what the evidence shows. The Markup and CalMatters researched the ads’ subject matter after the July assassination attempt. While they didn’t violate Meta’s guidelines, they did relate to the event. There were ads for gun holsters and merchandise about the shooting. It was a business opportunity and people ran with it with Meta holding the finish line ribbon.
Meta really has an interesting ethical framework.
Whitney Grace, October 24, 2024
What Can Cyber Criminals Learn from Automated Ad Systems?
October 10, 2024
 The only smart software involved in producing this short FOGINT post was Microsoft Copilot’s estimable art generation tool. Why? It is offered at no cost.
The only smart software involved in producing this short FOGINT post was Microsoft Copilot’s estimable art generation tool. Why? It is offered at no cost.
My personal opinion is that most online advertising is darned close to suspicious or outright legal behavior. “New,” “improved,” “Revolutionary” — Sure, I believe every online advertisement. But consider this: For hundreds of years those in the advertising business urged a bit of elasticity with reality. Sure, Duz does it. As a dinobaby, I assert that most people in advertising and marketing assume that reality and a product occupy different parts of a data space. Consequently most people — not just marketers, advertising executives, copywriters, and prompt engineers. I mean everyone.
An ad sales professional explains the benefits of Facebook, Google, and TikTok-type of sales. Instead of razor blades just sell ransomware as stolen credit cards. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. How are those security remediation projects with anti-malware vendors coming? Oh, sorry to hear that.
With a common mindset, I think it is helpful to consider the main points of “TikTok Joins the AI-Driven Advertising Pack to Compete with Meta for Ad Dollars.” The article makes clear that Google and Meta have automated the world of Madison Avenue. Not only is work mechanical, that work is informed by smart software. The implications for those who work the old fashioned way over long lunches and golf outings are that work methods themselves are changing.
The estimable TikTok is beavering away to replicate the smart ad systems of companies like the even more estimable Facebook and Google type companies. If TikTok is lucky as only an outfit linked with a powerful nation state can be, a bit of competition may find its way into the hardened black boxes of the digital replacement for Madison Avenue.
The write up says:
The pitch is all about simplicity and speed — no more weeks of guesswork and endless A/B testing, according to Adolfo Fernandez, TikTok’s director, global head of product strategy and operations, commerce. With TikTok’s AI already trained on what drives successful ad campaigns on the platform, advertisers can expect quick wins with less hassle, he added. The same goes for creative; Smart+ is linked to TikTok’s other AI tool, Symphony, designed to help marketers generate and refine ad concepts.
Okay, knowledge about who clicks what plus automation means less revenue for the existing automated ad system purveyors. The ideas are information about users, smart software, and automation to deliver “simplicity and speed.” Go fast, break things; namely, revenue streams flowing to Facebook and Google.
Why? Here’s a statement from the article answering the question:
TikTok’s worldwide ad revenue is expected to reach $22.32 billion by the end of the year, and increase 27.3% to $28.42 billion by the end of 2025, according to eMarketer’s March 2024 forecast. By comparison, Meta’s worldwide ad revenue is expected to total $154.16 billion by the end of this year, increasing 23.2% to $173.92 billion by the end of 2025, per eMarketer. “Automation is a key step for us as we enable advertisers to further invest in TikTok and achieve even greater return on investment,” David Kaufman, TikTok’s global head of monetization product and solutions, said during the TikTok.
I understand. Now let’s shift gears and ask, “What can bad actors learn from this seemingly routine report about jockeying among social media giants?”
Here are the lessons I think a person inclined to ignore laws and what’s left of the quaint notion of ethical behavior:
- These “smart” systems can be used to advertise bogus or non existent products to deliver ransomware, stealers, or other questionable software
- The mechanisms for automating phishing are simple enough for an art history or poli-sci major to use; therefore, a reasonably clever bad actor can whip up an automated phishing system without too much trouble. For those who need help, there are outfits like Telegram with its BotFather or helpful people advertising specialized skills on assorted Web forums and social media
- The reason to automate are simple: Better, faster, cheaper. Plus, with some useful data about a “market segment”, the malware can be tailored to hot buttons that are hard wired to a sucker’s nervous system.
- Users do click even when informed that some clicks mean a lost bank account or a stolen identity.
Is there a fix for articles which inform both those desperate to find a way to tell people in Toledo, Ohio, that you own a business selling aftermarket 22 inch wheels and alert bad actors to the wonders of automation and smart software? Nope. Isn’t online marketing a big win for everyone? And what if TikTok delivers a very subtle type of malware? Simple and efficient.
Stephen E Arnold, October 10, 2024
A Moment to Remember: Google Explains Its Competitive Posture
September 16, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
What happens when those with insight into the Google talk in a bar to friends? Answer: Complete indifference. Question: What happens when a former Google employee’s comments are captured in a form which can be discovered by the prosecution in a trial? Answer: A peak inside Googzilla’s kimono.
An observer is horrified by the site revealed when an ex-Google professional talks about what’s inside the Googzilla kimono. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Good enough.
“Ex-Google Exec Said Goal Was to Crush Competition, Trial Evidence Shows” reports that Google wanted to “crush” the competition. Google wanted a “monopoly.” Here’s what the Reuters’ article reports via its “trust” filter:
“We’ll be able to crush the other networks and that’s our goal,” David Rosenblatt, Google’s former president of display advertising, said of the company’s strategy in late 2008 or early 2009, according to notes shown in court…. “We’re both Goldman and NYSE,” he said, he said, according to the notes, referring to one of the world’s biggest stock exchanges at the time and one of its biggest market makers. “Google has created what’s comparable to the NYSE or London Stock Exchange; in other words, we’ll do to display what Google did to search,” Rosenblatt said.
On the surface, Mr. Rosenblatt is articulating what some folks have been asserting for years. Several observations:
- Google has been running free for a long time. Why?
- If true, the statement makes the outcome of EU litigation almost certain. Google will have to pay and change in ways which may be resisted by the nation-state of Google
- The comment reflects the machismo of the high tech US company and its hubris. Pride and vanity are believed by some to be a fundamental sin.
So what?
- Deconstructing what Google has built over the years may be quite difficult, maybe impossible. Well, that ends one line of retribution.
- If one breaks up Google and severs advertising, who can afford to buy it. Maybe the US should punt and nationalize the outfit. Why not let GSA run it? That would be exciting in my opinion.
- Google apologizes and keeps on doing what it has been doing for the last 25 years by filing appeals, lobbying, and waiting out government lawyers who often come and go as Google says, “I was neither / Living nor dead, and I knew nothing.”
Net net: The Google is gonna Google no matter what.
Stephen E Arnold, September 18, 2024
Meta Leadership: Thank you for That Question
August 26, 2024
Who needs the Dark Web when one has Facebook? We learn from The Hill, “Lawmakers Press Meta Over Illicit Drug Advertising Concerns.” Writer Sarah Fortinsky pulls highlights from the open letter a group of House representatives sent directly to Mark Zuckerberg. The rebuke follows a March report from The Wall Street Journal that Meta was under investigation for “facilitating the sale of illicit drugs.” Since that report, the lawmakers lament, Meta has continued to run such ads. We learn:
The Tech Transparency Project recently reported that it found more than 450 advertisements on those platforms that sell pharmaceuticals and other drugs in the last several months. ‘Meta appears to have continued to shirk its social responsibility and defy its own community guidelines. Protecting users online, especially children and teenagers, is one of our top priorities,’ the lawmakers wrote in their letter, which was signed by 19 lawmakers. ‘We are continuously concerned that Meta is not up to the task and this dereliction of duty needs to be addressed,’ they continued. Meta uses artificial intelligence to moderate content, but the Journal reported the company’s tools have not managed to detect the drug advertisements that bypass the system.”
The bipartisan representatives did not shy from accusing Meta of dragging its heels because it profits off these illicit ad campaigns:
“The lawmakers said it was ‘particularly egregious’ that the advertisements were ‘approved and monetized by Meta.’ … The lawmakers noted Meta repeatedly pushes back against their efforts to establish greater data privacy protections for users and makes the argument ‘that we would drastically disrupt this personalization you are providing,’ the lawmakers wrote. ‘If this personalization you are providing is pushing advertisements of illicit drugs to vulnerable Americans, then it is difficult for us to believe that you are not complicit in the trafficking of illicit drugs,’ they added.”
The letter includes a list of questions for Meta. There is a request for data on how many of these ads the company has discovered itself and how many it missed that were discovered by third parties. It also asks about the ad review process, how much money Meta has made off these ads, what measures are in place to guard against them, and how minors have interacted with them. The legislators also ask how Meta uses personal data to target these ads, a secret the company will surely resist disclosing. The letter gives Zuckerberg until September 6 to respond.
Cynthia Murrell, August 26, 2024
Good News: Meta To Unleash Automated AI Ads
August 19, 2024
Facebook generated its first revenue streams from advertising. Meta, Facebook’s parent company, continues to make huge profits from ads. Its products use cookies for targeted ads, collect user information to sell, and more. It’s not surprising that AI will soon be entering the picture says Computer Weekly: “Meta’s Zuckerberg Looks Ahead To AI-Generated Adverts.”
Meta increased its second-quarter revenues 22% from its first quarter. The company also reported that the cost of revenue increased by 23% due to higher infrastructure costs and Reality Labs needing a lot of cash. Zuckerberg explained that advertisers used to reach out to his company about the target audiences they wanted to reach. Meta eventually became so advanced that its ad systems predicted target audiences better than the advertisers. Zuckerberg plans for Meta to do the majority of work for advertising agencies. All they will need to provide Meta will be a budget and business objective.
Meta is investing and developing technology to make more money via AI. Meta is playing the long game:
“When asked about the payback time for investments in AI, Meta’s chief financial officer, Susan Li, said: ‘On our core AI work, we continue to take a very return on investment-based approach. We’re still seeing strong returns as improvements to both engagement and ad performance have translated into revenue gains, and it makes sense for us to continue investing here.’
Looking at generative AI (GenAI), she added: “We don’t expect our GenAI products to be a meaningful driver of revenue in 2024, but we do expect that they’re going to open up new revenue opportunities over time that will enable us to generate a solid return off of our investment…’”
Meta might see a slight dip in profit margins because it is investing in better technology, but AI generated ads will pay for themselves, literally.
Whitney Grace, August 19, 2024
The Upside of the Google Olympics Ad
August 13, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
I learned that Google’s AI advertisements “feel bad for a reason.” And what is that reason? The write up “Those Olympics AI Ads Feel Bad for a Reason. It’s Not Just Google’s ‘Dear Sydney’ Commercial That Feels Soulless and Strange.” (I want to mention that this headline seems soulless and strange, but I won’t.”)
The write up reveals the “secret” of the Googler using Google AI to write his Google progeny:
The latest spate of AI ad campaigns, for their part, have thus far failed to highlight how its products assist what the majority of Americans actually want to use AI for — namely, help with household chores — and instead end up showing how AI will be used for the things that most of us don’t want it to interfere with: our job prospects, our privacy, and experiences and skills that feel uniquely human. If the world already thinks of AI as menacing, wasteful, and yet another example of market overhype, these ads are only confirming our worst fears. No wonder they come off as so thoroughly insufferable.
I apologize for skipping the somewhat ho hum recitation of AI marketing gaffes. I bravely waded through the essay to identify the reason that AI ads make people “feel bad.” Am I convinced?
Nope.
I watched a version of the ad on my laptop. Based on my experience, I thought it was notable that the alleged Googley user remembered he had a family. I was impressed that the Googley father remembered where his Googley child was. I liked the idea of using AI to eliminate the need to use a smart software system to help craft a message with words that connoted interest, caring, familial warmth.
Let’s face it. The ad was more satisfying that converting a news story like a dead Google VP in a yacht.
How would Google’s smart software tell this story? I decided to find out. Here is what Gemini 1.5 Pro provided to me. Remember. I am a nerd dinobaby with a reputation for lacking empathy and noted for my work in certain specialized sectors:
It’s been a long time since Dean’s passing, but I wanted to reach out because I was thinking about him and his family. I came across an article about the woman who was with him when he passed. I know this might be a difficult thing to hear about, and I am so very sorry for your loss. Dean was such a bright light in this world, and I know how much he meant to you. Thinking of you during this time.
Amazing. The Google’s drug death in the presence of a prostitute has been converted to a paragraph I could not possibly write. I would use a phrase like “nuked by horse” instead of “passed.” The phrase “I am so very sorry” is not what I would have been able to craft. My instinct is to say something like “The Googler tried to have fun and screwed up big time.” Finally, never would a nerd dinobaby like me write “thinking of you.” I would write, “Get to your attorney pronto.”
I know that real Googlers are not like nerd dinobabies. Therefore, it is perfectly understandable that the ad presents a version of reality which is not aspirational. It is a way for certain types of professionals to simulate interest and norm-core values.
Let’s praise Google and its AI.
Stephen E Arnold, August 13, 2024
Curating Content: Not Really and Maybe Not at All
August 5, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
Most people assume that if software is downloaded from an official “store” or from a “trusted” online Web search system, the user assumes that malware is not part of the deal. Vendors bandy about the word “trust” at the same time wizards in the back office are filtering, selecting, and setting up mechanisms to sell advertising to anyone who has money.
Advertising sales professionals are the epitome of professionalism. Google the word “trust”. You will find many references to these skilled individuals. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Good enough.
Are these statements accurate? Because I love the high-tech outfits, my personal view is that online users today have these characteristics:
- Deep knowledge about nefarious methods
- The time to verify each content object is not malware
- A keen interest in sustaining the perception that the Internet is a clean, well-lit place. (Sorry, Mr. Hemingway, “lighted” will get you a points deduction in some grammarians’ fantasy world.)
I read “Google Ads Spread Mac Malware Disguised As Popular Browser.” My world is shattered. Is an alleged monopoly fostering malware? Is the dominant force in online advertising unable to verify that its advertisers are dealing from the top of the digital card deck? Is Google incapable of behaving in a responsible manner? I have to sit down. What a shock to my dinobaby system.
The write up alleges:
Google Ads are mostly harmless, but if you see one promoting a particular web browser, avoid clicking. Security researchers have discovered new malware for Mac devices that steals passwords, cryptocurrency wallets and other sensitive data. It masquerades as Arc, a new browser that recently gained popularity due to its unconventional user experience.
My assumption is that Google’s AI and human monitors would be paying close attention to a browser that seeks to challenge Google’s Chrome browser. Could I be incorrect? Obviously if the write up is accurate I am. Be still my heart.
The write up continues:
The Mac malware posing as a Google ad is called Poseidon, according to researchers at Malwarebytes. When clicking the “more information” option next to the ad, it shows it was purchased by an entity called Coles & Co, an advertiser identity Google claims to have verified. Google verifies every entity that wants to advertise on its platform. In Google’s own words, this process aims “to provide a safe and trustworthy ad ecosystem for users and to comply with emerging regulations.” However, there seems to be some lapse in the verification process if advertisers can openly distribute malware to users. Though it is Google’s job to do everything it can to block bad ads, sometimes bad actors can temporarily evade their detection.
But the malware apparently exists and the ads are the vector. What’s the fix? Google is already doing its typical A Number One Quantumly Supreme Job. Well, the fix is you, the user.
You are sufficiently skilled to detect, understand, and avoid such online trickery, right?
Stephen E Arnold, August 5, 2024
Judgment Before? No. Backing Off After? Yes.
August 5, 2024
I wanted to capture two moves from two technology giants. The first item is the report that Google pulled the oh-so-Googley ad about a father using Gemini to write personal note to his daughter. If you are not familiar with the burst of creative marketing, you can glean a few details from “Google Pulls Gemini AI Ad from Olympics after Backlash.” The second item is the report that according to Bloomberg, “Apple Pulls Commercial After Thai Backlash, Calls for Boycott.”
I reacted to these two separate announcements by thinking about what these do it-reverse it decisions suggest about the management controls at two technology giants.
Some management processes operated to think up the ad ideas. Then the project had to be given the green light from “leadership” at the two outfits. Next third party providers had to be enlisted to do some of the “knowledge work”. Finally, I assume there were meetings to review the “creative.” Finally, one ad from several candidates was selected by each firm. The money paid. And then the ads appeared. That’s a lot of steps and probably more than two or three people working in a cube next to a Foosball tables.
Plus, the about faces by the two companies did not take much time. Google caved after a few days. Apple also hopped on its havester and chopped the India advertisement quickly as well. Decisiveness. Actually decisiveness after the fact.
Why not less obvious processes like using better judgment before releasing the advertisements? Why not focus on working with people who are more in tune with audience reactions than being clever, smooth talking, and desperate-eager for big company money?
Several observations:
- Might I hypothesize that both companies lack a fabric of common sense?
- If online ads “work,” why use what I would call old-school advertising methods? Perhaps the online angle is not correct for such important messaging from two companies that seem to do whatever they want most of the time?
- The consequences of these do-then-undo actions are likely to be close to zero. Is that what operating in a no-consequences environment fosters?
I wonder if the back away mentality is now standard operating procedure. We have Intel and nVidia with some back-away actions. We have a nation state agreeing to a plea bargain and the un-agreeing the next day. We have a net neutraility rule, then don’t, then we do, and now we don’t. Now that I think about it, perhaps because there are no significant consequences, decision quality has taken a nose dive?
Some believe that great complexity sets the stage for bad decisions which regress to worse decisions.
Stephen E Arnold, August 5, 2024
Google and Its Smart Software: The Emotion Directed Use Case
July 31, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
How different are the Googlers from those smack in the middle of a normal curve? Some evidence is provided to answer this question in the Ars Technica article “Outsourcing Emotion: The Horror of Google’s “Dear Sydney” AI Ad.” I did not see the advertisement. The volume of messages flooding through my channels each days has allowed me to develop what I call “ad blindness.” I don’t notice them; I don’t watch them; and I don’t care about the crazy content presentation which I struggle to understand.
A young person has to write a sympathy card. The smart software is encouraging to use the word “feel.” This is a word foreign to the individual who wants to work for big tech someday. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Do you have your hands full with security issues today?
Ars Technica watches TV and the Olympics. The write up reports:
In it, a proud father seeks help writing a letter on behalf of his daughter, who is an aspiring runner and superfan of world-record-holding hurdler Sydney McLaughlin-Levrone. “I’m pretty good with words, but this has to be just right,” the father intones before asking Gemini to “Help my daughter write a letter telling Sydney how inspiring she is…” Gemini dutifully responds with a draft letter in which the LLM tells the runner, on behalf of the daughter, that she wants to be “just like you.”
What’s going on? The father wants to write something personal to his progeny. A Hallmark card may never be delivered from the US to France. The solution is an emessage. That makes sense. Essential services like delivering snail mail are like most major systems not working particularly well.
Ars Technica points out:
But I think the most offensive thing about the ad is what it implies about the kinds of human tasks Google sees AI replacing. Rather than using LLMs to automate tedious busywork or difficult research questions, “Dear Sydney” presents a world where Gemini can help us offload a heartwarming shared moment of connection with our children.
I find the article’s negative reaction to a Mad Ave-type of message play somewhat insensitive. Let’s look at this use of smart software from the point of view of a person who is at the right hand tail end of the normal distribution. The factors in this curve are compensation, cleverness as measured in a Google interview, and intelligence as determined by either what school a person attended, achievements when a person was in his or her teens, or solving one of the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences brain teasers. (These are shared at cocktail parties or over coffee. If you can’t answer, you pay the bill and never get invited back.)
Let’s run down the use of AI from this hypothetical right of loser viewpoint:
- What’s with this assumption that a Google-type person has experience with human interaction. Why not send a text even though your co-worker is at the next desk? Why waste time and brain cycles trying to emulate a Hallmark greeting card contractor’s phraseology. The use of AI is simply logical.
- Why criticize an alleged Googler or Googler-by-the-gig for using the company’s outstanding, quantumly supreme AI system? This outfit spends millions on running AI tests which allow the firm’s smart software to perform in an optimal manner in the messaging department. This is “eating the dog food one has prepared.” Think of it as quality testing.
- The AI system, running in the Google Cloud on Google technology is faster than even a quantumly supreme Googler when it comes to generating feel-good platitudes. The technology works well. Evaluate this message in terms of the effectiveness of the messaging generated by Google leadership with regard to the Dr. Timnit Gebru matter. Upper quartile of performance which is far beyond the dead center of the bell curve humanoids.
My view is that there is one positive from this use of smart software to message a partially-developed and not completely educated younger person. The Sundar & Prabhakar Comedy Act has been recycling jokes and bits for months. Some find them repetitive. I do not. I am fascinated by the recycling. The S&P Show has its fans just as Jack Benny does decades after his demise. But others want new material.
By golly, I think the Google ad showing Google’s smart software generating a parental note is a hoot and a great demo. Plus look at the PR the spot has generated.
What’s not to like? Not much if you are Googley. If you are not Googley, sorry. There’s not much that can be done except shove ads at you whenever you encounter a Google product or service. The ad illustrates the mental orientation of Google. Learn to love it. Nothing is going to alter the trajectory of the Google for the foreseeable future. Why not use Google’s smart software to write a sympathy note to a friend when his or her parent dies? Why not use Google to write a note to the dean of a college arguing that your child should be admitted? Why not let Google think for you? At least that decision would be intentional.
Stephen E Arnold, July 31, 2024
How
How
How
How
How