A Familiar Cycle: The Frustration of Almost Solving the Search Problem
August 16, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Search and retrieval is a difficult problem. The solutions have ranged from scrolls with labels to punched cards and rods to bags of words. Each innovation or advance sparked new ideas. Boolean gave way to natural language. Natural language evolved into semi-smart systems. Now we are in the era of what seems to be smart software. Like the punch card systems, users became aware of the value of consistent, accurate indexing. Today one expects a system to “know” what the user wants. Instead of knowing index terms, one learns to be a prompt engineer.
Search and retrieval is not “solved” using large language models. LLMs are a step forward on a long and difficult path. The potential financial cost of thinking that the methods are a sure-fire money machine is high. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. How was DEFCON?
I read “LLM Progress Is Slowing — What Will It Mean for AI?.” The write up makes clear that some of the excitement of smart software which can makes sense of natural language queries (prompts) has lost some of its shine. This type of insight is one that probably existed when a Babylonian tablet maker groused about not having an easy way to stack up clay tablets for the money guy. Search and retrieval is essential for productive work. A system which makes that process less of a hassle is welcomed. After a period of time one learns that the approach is not quite where the user wants it to be. Researchers and innovators hear the complaint and turn their attention to improving search and retrieval … again.
The write up states:
The leap from GPT-3 to GPT-3.5 was huge, propelling OpenAI into the public consciousness. The jump up to GPT-4 was also impressive, a giant step forward in power and capacity. Then came GPT-4 Turbo, which added some speed, then GPT-4 Vision, which really just unlocked GPT-4’s existing image recognition capabilities. And just a few weeks back, we saw the release of GPT-4o, which offered enhanced multi-modality but relatively little in terms of additional power. Other LLMs, like Claude 3 from Anthropic and Gemini Ultra from Google, have followed a similar trend and now seem to be converging around similar speed and power benchmarks to GPT-4. We aren’t yet in plateau territory — but do seem to be entering into a slowdown. The pattern that is emerging: Less progress in power and range with each generation.
This is an echo of the complaints I heard about Dr. Salton’s SMART search system.
The “fix” according to the write up may be to follow one of these remediation paths:
- More specialization
- New user interfaces
- Open source large language models
- More and better data
- New large language model architectures.
These are ideas bolted to the large language model approach to search and retrieval. I think each has upsides and downsides. These deserve thoughtful discussion. However, the evolution of search-and-retrieval has been an evolutionary process. Those chaos and order thinkers at the Santa Fe Institute suggest that certain “things” self organize and emerge. The idea has relevance to what happens with each “new” approach to search and retrieval.
The cited write up concludes with this statement:
One possible pattern that could emerge for LLMs: That they increasingly compete at the feature and ease-of-use levels. Over time, we could see some level of commoditization set in, similar to what we’ve seen elsewhere in the technology world. Think of, say, databases and cloud service providers. While there are substantial differences between the various options in the market, and some developers will have clear preferences, most would consider them broadly interchangeable. There is no clear and absolute “winner” in terms of which is the most powerful and capable.
I think the idea about competition is mostly correct. However, what my impression of search and retrieval as a technology thread is that progress is being made. I find it encouraging that more users are interacting with systems. Unfortunately search and retrieval is not solved by generating a paragraph a high school student can turn into a history teacher as an original report.
Effective search and retrieval is not just a prompt box. Effective information access remains a blend of extraordinarily trivial activities. For instance, a conversation may suggest a new way to locate relevant information. Reading an article or a longer document may trigger an unanticipated connection between ant colonies and another task-related process. The act of looking at different sources may lead to a fact previously unknown which leads in turn to another knowledge insight. Software alone cannot replicate these mental triggers.
LLMs like stacked clay tablets provide challenges and utility. However, search and retrieval remains a work in progress. LLMs, like semantic ad matching, or using one’s search history as a context clue, are helpful. But opportunities for innovation exist. My view is that the grousing about LLM limitations is little more than a recognition that converting a human concept or information need to an “answer” is a work in progress. The difference is that today billions of dollars have been pumped into smart software in the hope that information retrieval is solved.
Sorry, it is not. Therefore, the stakes of realizing that the golden goose may not lay enough eggs to pay off the cost of the goose itself. Twenty years ago search and retrieval was not a sector consuming billions of dollars in the span of a couple of years. That’s what is making people nervous about LLMs. Watching Delphi or Entopia fail was expensive, but the scale of the financial loss and the emotional cost of LLM failure is a different kettle of fish.
Oh, and those five “fixes” in the bullet points from the write up. None will solve the problem of search and retrieval.
Stephen E Arnold, August 16, 2024
Deep Fake Service?
August 16, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
What sets DeepLive apart is that one needs only a single image and the video of the person whose face you want to replace. The technology — assuming it is functioning as marketed — makes it clear that swapping faces on videos can be done. Will the technology derail often-controversial facial recognition systems?
The Web site provides testimonials and some examples of DeepLive in action.
The company says:
Deep Live Cam is an open-source tool for real-time face swapping and one-click video deepfakes. It can replace faces in videos or images using a single photo, ideal for video production, animation, and various creative projects.
The software is available as open source. The developers says that it includes “ethical safeguards.” But just in case these don’t work, DeepLive posts this message on its Web site:
Built-in checks prevent processing of inappropriate content, ensuring legal and ethical use.
The software has a couple of drawbacks:
- It is not clear if this particular code base is on an open source repository. There are a number of Deep Live this and thats.
- There is no active Web page link to the “Get Started” button
- There is minimal information about the “owner” of the software.
Other than that DeepLive is a good example of a deep fake. (An interesting discussion appears in HackerNews and Ars Technica.) If the system is stable and speedy, AI-enabled tools to create content objects for a purpose has taken a step forward. Bad actors are probably going to take note and give the system a spin.
Stephen E Arnold, August 16, 2024
Pragmatic AI: Individualized Monitoring
August 15, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
In June 2024 at the TechnoSecurity & Digital Forensics conference, one of the cyber investigators asked me, “What are some practical uses of AI in law enforcement?” I told the person that I would send him a summary of my earlier lecture called “AI for LE.” He said, “Thanks, but what should I watch to see some AI in action.” I told him to pay attention to the Kroger pricing methods. I had heard that Kroger was experimenting with altering prices based on certain signals. The example I gave is that if the Kroger is located in a certain zip code, then the Kroger stores in that specific area would use dynamic pricing. The example I gave was similar to Coca-Cola’s tests of a vending machine that charged more if the temperature was hot. In the Kroger example, a hot day would trigger a change in the price of a frozen dessert. He replied, “Kroger?” I said, “Yes, Kroger is experimenting with AI in order to detect specific behaviors and modify prices to reflect those signals.” What Kroger is doing will be coming to law enforcement and intelligence operations. Smart software monitors the behavior of a prisoner, for example, and automatically notifies an investigator when a certain signal is received. I recall mentioning that smart software, signals, and behavior change or direct action will become key components of a cyber investigator’s tool kit. He said, laughing, “Kroger. Interesting.”
Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Good enough.
I learned that Kroger’s surveillance concept is now not a rumor discussed at a neighborhood get together. “‘Corporate Greed Is Out of Control’: Warren Slams Kroger’s AI Pricing Scheme” reveals that elected officials and probably some consumer protection officials may be aware of the company’s plans for smart software. The write up reports:
Warren (D-Mass.) was joined by Sen. Bob Casey (D-Pa.) on Wednesday in writing a letter to the chairman and CEO of the Kroger Company, Rodney McMullen, raising concerns about how the company’s collaboration with AI company IntelligenceNode could result in both privacy violations and worsened inequality as customers are forced to pay more based on personal data Kroger gathers about them “to determine how much price hiking [they] can tolerate.” As the senators wrote, the chain first introduced dynamic pricing in 2018 and expanded to 500 of its nearly 3,000 stores last year. The company has partnered with Microsoft to develop an Electronic Shelving Label (ESL) system known as Enhanced Display for Grocery Environment (EDGE), using a digital tag to display prices in stores so that employees can change prices throughout the day with the click of a button.
My view is that AI orchestration will allow additional features and functions. Some of these may be appropriate for use in policeware and intelware systems. Kroger makes an effort to get individuals to sign up for a discount card. Also, Kroger wants users to install the Kroger app. The idea is that discounts or other incentives may be “awarded” to the customer who takes advantages of the services.
However, I am speculating that AI orchestration will allow Kroger to implement a chain of actions like this:
- Customer with a mobile phone enters the store
- The store “acknowledges” the customer
- The customer’s spending profile is accessed
- The customer is “known” to purchase upscale branded ice cream
- The price for that item automatically changes as the customer approaches the display
- The system records the item bar code and the customer ID number
- At check out, the customer is charged the higher price.
Is this type of AI orchestration possible? Yes. Is it practical for a grocery store to deploy? Yes because Kroger uses third parties to provide its systems and technical capabilities for many applications.
How does this apply to law enforcement? Kroger’s use of individualized tracking may provide some ideas for cyber investigators.
As large firms with the resources to deploy state-of-the-art technology to boost sales, know the customer, and adjust prices at the individual shopper level, the benefit of smart software become increasingly visible. Some specialized software systems lag behind commercial systems. Among the reasons are budget constraints and the often complicated procurement processes.
But what is at the grocery store is going to become a standard function in many specialized software systems. These will range from security monitoring systems which can follow a person of interest in an specific area to automatically updating a person of interest’s location on a geographic information module.
If you are interested in watching smart software and individualized “smart” actions, just pay attention at Kroger or a similar retail outfit.
Stephen E Arnold, August 15, 2024
Canadians Unhappy about Tax on Streaming Video
August 15, 2024
Unfortunately the movie industry has tanked worldwide because streaming services have democratized delivery. Producers, directors, actors, and other industry professionals are all feeling the pain of tighter purse strings. The problems aren’t limited to Hollywood, because Morningstar explains that the US’s northern neighbor is also feeling the strain: “The Motion Picture Association-Canada Asks Canada Appeal Court To Stop Proposed Tax On Streaming Revenue.”
A group representing big entertainment companies: Walt Disney, Netflix, Warner Brothers, Discovery, Paramount Global, and more are asking a Canadian court to stop a law that would force the companies to pay 5% of their sales to the country to fund local news and other domestic content. The Motion Picture Association- Canada stated that tax from the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission oversteps the organization’s authority. The group representing the Hollywood bigwigs also mentions that its clients spent billions in Canada every year.
The representative group are also arguing that the tax would force Canadian subscribers to pay more for streaming services and the companies might consider leaving the northern country. Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission countered that without the tax local content might not be made or distributed anymore. Hollywood’s lawyers doesn’t like it at all:
“In their filing with Canada’s Federal Court of Appeal, lawyers for the group say the regulator didn’t reveal “any basis” for why foreign streamers are required to contribute to the production of local television and radio newscasts. The broadcast regulator “concluded, without evidence, that ‘there is a need to increase support for news production,'” the lawyers said in their filing. ‘Imposing on foreign online undertakings a requirement to fund news production is not appropriate in the light of the nature of the services that foreign online undertakings provide.’”
Canada will probably keep the tax and Hollywood, instead of the executives eating the costs, will pass it onto consumers. Consumers will also be shafted, because their entertainment streaming services will continue to become expensive.
Whitney Grace, August 15, 2024
Meta Shovels Assurances. Will Australia Like the Output?
August 14, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
I came across a news story which I found quite interesting. Even though I am a dinobaby, I am a father and a grandfather. I used to take pictures when my son and daughter were young. I used Kodak film, printed the pictures my wife wanted, and tossed the rest. Pretty dull. Some parents have sportier ideas. I want to point out that some ideas do not appeal to me. Others make me uncomfortable.
How do you think I reacted to the information in “Parents Still Selling Revealing Content of Their Kids on Instagram, Despite Meta’s Promises to Ban the Practice.” The main idea in the write up seems to be:
The ABC [Australian Broadcasting Council] has found almost 50 Instagram accounts that allow subscribers to pay for exclusive content of children or teenagers, some of which is sexualized. Meta had vowed to clamp down on the practice but said it was taking time to "fully roll out" its new policy. Advocates say the accounts represent an "extreme" form of child exploitation.
If I understand the title of the article and this series of statements, I take away these messages:
- Instagram contains “revealing content” of young people
- Meta — the Zuck’s new name for the old-timey Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram services — said it would take steps to curtail posting of this type of content. A statement which, the ABC seems to apply, was similar to other Silicon Valley-inspired assertions: A combination of self-serving assurances and then generating as much revenue as possible because some companies face zero consequences.
- Meta seems to create a greenhouse for what the ABC calls “child exploitation.”
I hope I captured the intent of the news story’s main idea.
I noted this passage:
Sarah Adams, an online child safety advocate who goes by the name Mom.Uncharted, said it was clear Meta had lost control of child accounts.
How did Meta respond to the ABC inquiry. Check this:
"The new policy is in effect as of early April and we are taking action on adult-run accounts that primarily post content focused on children whenever we become aware of them," a Meta spokesperson said in a statement. "As with any new policy, enforcement can take time to fully roll out."
That seems plausible. How long has Meta hosted questionable content? I remember 20 years ago. “We are taking action” is a wonderfully proactive statement. Plus, combatting child exploitation is one of those tasks where “enforcement can take time.”
Got it.
Stephen E Arnold, August 14, 2024
AI Safety Evaluations, Some Issues Exist
August 14, 2024
Ah, corporate self regulation. What could go wrong? Well, as TechCrunch reports, “Many Safety Evaluations for AI Models Have Significant Limitations.” Writer Kyle Wiggers tells us:
“Generative AI models … are coming under increased scrutiny for their tendency to make mistakes and generally behave unpredictably. Now, organizations from public sector agencies to big tech firms are proposing new benchmarks to test these models’ safety. Toward the end of last year, startup Scale AI formed a lab dedicated to evaluating how well models align with safety guidelines. This month, NIST and the U.K. AI Safety Institute released tools designed to assess model risk. But these model-probing tests and methods may be inadequate. The Ada Lovelace Institute (ALI), a U.K.-based nonprofit AI research organization, conducted a study that interviewed experts from academic labs, civil society and those who are producing vendors models, as well as audited recent research into AI safety evaluations. The co-authors found that while current evaluations can be useful, they’re non-exhaustive, can be gamed easily and don’t necessarily give an indication of how models will behave in real-world scenarios.”
There are several reasons for the gloomy conclusion. For one, there are no established best practices for these evaluations, leaving each organization to go its own way. One approach, benchmarking, has certain problems. For example, for time or cost reasons, models are often tested on the same data they were trained on. Whether they can perform in the wild is another matter. Also, even small changes to a model can make big differences in behavior, but few organizations have the time or money to test every software iteration.
What about red-teaming: hiring someone to probe the model for flaws? The low number of qualified red-teamers and the laborious nature of the method make it costly, out of reach for smaller firms. There are also few agreed-upon standards for the practice, so it is hard to assess the effectiveness of red-team projects.
The post suggests all is not lost—as long as we are willing to take responsibility for evaluations out of AI firms’ hands. Good luck prying open that death grip. Government regulators and third-party testers would hypothetically fill the role, complete with transparency. What a concept. It would also be good to develop standard practices and context-specific evaluations. Bonus points if a method is based on an understanding of how each AI model operates. (Sadly, such understanding remains elusive.)
Even with these measures, it may never be possible to ensure any model is truly safe. The write-up concludes with a quote from the study’s co-author Mahi Hardalupas:
“Determining if a model is ‘safe’ requires understanding the contexts in which it is used, who it is sold or made accessible to, and whether the safeguards that are in place are adequate and robust to reduce those risks. Evaluations of a foundation model can serve an exploratory purpose to identify potential risks, but they cannot guarantee a model is safe, let alone ‘perfectly safe.’ Many of our interviewees agreed that evaluations cannot prove a model is safe and can only indicate a model is unsafe.”
How comforting.
Cynthia Murrell, August 14, 2024
Sakana: Can Its Smart Software Replace Scientists and Grant Writers?
August 13, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
A couple of years ago, merging large language models seemed like a logical way to “level up” in the artificial intelligence game. The notion of intelligence aggregation implied that if competitor A was dumb enough to release models and other digital goodies as open source, an outfit in the proprietary software business could squish the other outfits’ LLMs into the proprietary system. The costs of building one’s own super-model could be reduced to some extent.
Merging is a very popular way to whip up pharmaceuticals. Take a little of this and a little of that and bingo one has a new drug to flog through the approval process. Another example is taking five top consultants from Blue Chip Company I and five top consultants from Blue Chip Company II and creating a smarter, higher knowledge value Blue Chip Company III. Easy.
A couple of Xooglers (former Google wizards) are promoting a firm called Sakana.ai. The purpose of the firm is to allow smart software (based on merging multiple large language models and proprietary systems and methods) to conduct and write up research (I am reluctant to use the word “original”, but I am a skeptical dinobaby.) The company says:
One of the grand challenges of artificial intelligence is developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. While frontier models have already been used to aid human scientists, e.g. for brainstorming ideas or writing code, they still require extensive manual supervision or are heavily constrained to a specific task. Today, we’re excited to introduce The AI Scientist, the first comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform research independently. In collaboration with the Foerster Lab for AI Research at the University of Oxford and Jeff Clune and Cong Lu at the University of British Columbia, we’re excited to release our new paper, The AI Scientist: Towards Fully Automated Open-Ended Scientific Discovery.
Sakana does not want to merge the “big” models. Its approach for robot generated research is to combine specialized models. Examples which came to my mind were drug discovery and providing “good enough” blue chip consulting outputs. These are both expensive businesses to operate. Imagine the payoff if the Sakana approach delivers high value results. Instead of merging big, the company wants to merge small; that is, more specialized models and data. The idea is that specialized data may sidestep some of the interesting issues facing Google, Meta, and OpenAI among others.
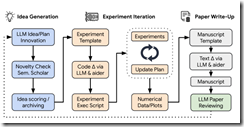
Sakana’s Web site provides this schematic to help the visitor get a sense of the mechanics of the smart software. The diagram is Sakana’s, not mine.
I don’t want to let science fiction get in the way of what today’s AI systems can do in a reliable manner. I want to make some observations about smart software making discoveries and writing useful original research papers or for BearBlog.dev.
- The company’s Web site includes a link to a paper written by the smart software. With a sample of one, I cannot see much difference between it and the baloney cranked out by the Harvard medical group or Stanford’s former president. If software did the work, it is a good deep fake.
- Should the software be able to assemble known items of information into something “novel,” the company has hit a home run in the AI ballgame. I am not a betting dinobaby. You make your own guess about the firm’s likelihood of success.
- If the software works to some degree, quite a few outfits looking for a way to replace people with a Sakana licensing fee will sign up. Will these outfits renew? I have no idea. But “good enough” may be just what these companies want.
Net net: The Sakana.ai Web site includes a how it works, more papers about items “discovered” by the software, and a couple of engineers-do-philosophy-and-ethics write ups. A “full scientific report” is available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.06292. I wonder if the software invented itself, wrote the documents, and did the marketing which caught my attention. Maybe?
Stephen E Arnold, August 13, 2024
The Upside of the Google Olympics Ad
August 13, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
I learned that Google’s AI advertisements “feel bad for a reason.” And what is that reason? The write up “Those Olympics AI Ads Feel Bad for a Reason. It’s Not Just Google’s ‘Dear Sydney’ Commercial That Feels Soulless and Strange.” (I want to mention that this headline seems soulless and strange, but I won’t.”)
The write up reveals the “secret” of the Googler using Google AI to write his Google progeny:
The latest spate of AI ad campaigns, for their part, have thus far failed to highlight how its products assist what the majority of Americans actually want to use AI for — namely, help with household chores — and instead end up showing how AI will be used for the things that most of us don’t want it to interfere with: our job prospects, our privacy, and experiences and skills that feel uniquely human. If the world already thinks of AI as menacing, wasteful, and yet another example of market overhype, these ads are only confirming our worst fears. No wonder they come off as so thoroughly insufferable.
I apologize for skipping the somewhat ho hum recitation of AI marketing gaffes. I bravely waded through the essay to identify the reason that AI ads make people “feel bad.” Am I convinced?
Nope.
I watched a version of the ad on my laptop. Based on my experience, I thought it was notable that the alleged Googley user remembered he had a family. I was impressed that the Googley father remembered where his Googley child was. I liked the idea of using AI to eliminate the need to use a smart software system to help craft a message with words that connoted interest, caring, familial warmth.
Let’s face it. The ad was more satisfying that converting a news story like a dead Google VP in a yacht.
How would Google’s smart software tell this story? I decided to find out. Here is what Gemini 1.5 Pro provided to me. Remember. I am a nerd dinobaby with a reputation for lacking empathy and noted for my work in certain specialized sectors:
It’s been a long time since Dean’s passing, but I wanted to reach out because I was thinking about him and his family. I came across an article about the woman who was with him when he passed. I know this might be a difficult thing to hear about, and I am so very sorry for your loss. Dean was such a bright light in this world, and I know how much he meant to you. Thinking of you during this time.
Amazing. The Google’s drug death in the presence of a prostitute has been converted to a paragraph I could not possibly write. I would use a phrase like “nuked by horse” instead of “passed.” The phrase “I am so very sorry” is not what I would have been able to craft. My instinct is to say something like “The Googler tried to have fun and screwed up big time.” Finally, never would a nerd dinobaby like me write “thinking of you.” I would write, “Get to your attorney pronto.”
I know that real Googlers are not like nerd dinobabies. Therefore, it is perfectly understandable that the ad presents a version of reality which is not aspirational. It is a way for certain types of professionals to simulate interest and norm-core values.
Let’s praise Google and its AI.
Stephen E Arnold, August 13, 2024
Takedown Notices May Slightly Boost Sales of Content
August 13, 2024
It looks like take-down notices might help sales of legitimate books. A little bit. TorrentFreak shares the findings from a study by the University of Warsaw, Poland, in, “Taking Pirated Copies Offline Can Benefit Book Sales, Research Finds.” Writer Ernesto Van der Sar explains:
“This year alone, Google has processed hundreds of millions of takedown requests on behalf of publishers, at a frequency we have never seen before. The same publishers also target the pirate sites and their hosting providers directly, hoping to achieve results. Thus far, little is known about the effectiveness of these measures. In theory, takedowns are supposed to lead to limited availability of pirate sources and a subsequent increase in legitimate sales. But does it really work that way? To find out more, researchers from the University of Warsaw, Poland, set up a field experiment. They reached out to several major publishers and partnered with an anti-piracy outfit, to test whether takedown efforts have a measurable effect on legitimate book sales.”
See the write-up for the team’s methodology. There is a caveat: The study included only print books, because Poland’s e-book market is too small to be statistically reliable. This is an important detail, since digital e-books are a more direct swap for pirated copies found online. Even so, the researchers found takedown notices produced a slight bump in print-book sales. Research assistants confirmed they could find fewer pirated copies, and the ones they did find were harder to unearth. The write-up notes more research is needed before any conclusions can be drawn.
How hard will publishers tug at this thread? By this logic, if one closes libraries that will help book sales, too. Eliminating review copies may cause some sales. Why not publish books and keep them secret until Amazon provides a link? So many money-grubbing possibilities, and all it would cost is an educated public.
Cynthia Murrell, August 13, 2024
Some Fun with Synthetic Data: Includes a T Shirt
August 12, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Academics and researchers often produce bogus results, fiddle images (remember the former president of Stanford University), or just make up stuff. Despite my misgivings, I want to highlight what appear to be semi-interesting assertions about synthetic data. For those not following the nuances of using real data, doing some mathematical cartwheels, and producing made-up data which are just as good as “real” data, synthetic data for me is associated with Dr. Chris Ré, the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (remember the ex president of Stanford U., please). The term or code word for this approach to information suitable for training smart software is Snorkel. Snorkel became as company. Google embraced Snorkel. The looming litigation and big dollar settlements may make synthetic data a semi big thing in a tech dust devil called artificial intelligence. The T Shirt should read, “Synthetic data are write” like this:
I asked an AI system provided by the global leaders in computer security (yep, that’s Microsoft) to produce a T shirt for a synthetic data team. Great work and clever spelling to boot.
The “research” report appeared in Live Science. “AI Models Trained on Synthetic Data Could Break Down and Regurgitate Unintelligible Nonsense, Scientists Warn” asserts:
If left unchecked,”model collapse” could make AI systems less useful, and fill the internet with incomprehensible babble.
The unchecked term is a nice way of saying that synthetic data are cheap and less likely to become a target for copyright cops.
The article continues:
AI models such as GPT-4, which powers ChatGPT, or Claude 3 Opus rely on the many trillions of words shared online to get smarter, but as they gradually colonize the internet with their own output they may create self-damaging feedback loops. The end result, called “model collapse” by a team of researchers that investigated the phenomenon, could leave the internet filled with unintelligible gibberish if left unchecked.
People who think alike and create synthetic data will prove that “fake” data are as good as or better than “real” data. Why would anyone doubt such glib, well-educated people. Not me! Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Have you noticed similar outputs from your multitudinous AI systems?
In my opinion, the Internet when compared to commercial databases produced with actual editorial policies has been filled with “unintelligible gibberish” from the days I showed up at conferences to lecture about how hypertext was different from Gopher and Archie. When Mosaic sort of worked, I included that and left my Next computer at the office.
The write up continues:
As the generations of self-produced content accumulated, the researchers watched their model’s responses degrade into delirious ramblings.
After the data were fed into the system a number of time, the output presented was like this example from the researchers’ tests:
“architecture. In addition to being home to some of the world’s largest populations of black @-@ tailed jackrabbits, white @-@ tailed jackrabbits, blue @-@ tailed jackrabbits, red @-@ tailed jackrabbits, yellow @-.”
The output might be helpful to those interested in church architecture.
Here’s the wrap up to the research report:
This doesn’t mean doing away with synthetic data entirely, Shumailov said, but it does mean it will need to be better designed if models built on it are to work as intended. [Note: Ilia Shumailov, a computer scientist at the University of Oxford, worked on this study.]
I must admit that the write up does not make clear what data were “real” and what data were “synthetic.” I am not sure how the test moved from Wikipedia to synthetic data. I have no idea where the headline originated? Was it synthetic?
Nevertheless, I think one might conclude that using fancy math to make up data that’s as good as real life data might produce some interesting outputs.
Stephen E Arnold, August 12, 2024