AI to AI Program for March 12, 2024, Now Available
March 12, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Erik Arnold, with some assistance from Stephen E Arnold (the father) has produced another installment of AI to AI: Smart Software for Government Use Cases.” The program presents news and analysis about the use of artificial intelligence (smart software) in government agencies.
The ad-free program features Erik S. Arnold, Managing Director of Govwizely, a Washington, DC consulting and engineering services firm. Arnold has extensive experience working on technology projects for the US Congress, the Capitol Police, the Department of Commerce, and the White House. Stephen E Arnold, an adviser to Govwizely, also participates in the program. The current episode explores five topics in an father-and-son exploration of important, yet rarely discussed subjects. These include the analysis of law enforcement body camera video by smart software, the appointment of an AI information czar by the US Department of Justice, copyright issues faced by UK artificial intelligence projects, the role of the US Marines in the Department of Defense’s smart software projects, and the potential use of artificial intelligence in the US Patent Office.
The video is available on YouTube at https://youtu.be/nsKki5P3PkA. The Apple audio podcast is at this link.
Stephen E Arnold, March 12, 2024
Palantir: The UK Wants a Silver Bullet
March 11, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
The UK is an interesting nation state. On one hand, one has upmarket, high-class activities taking place not too far from the squatters in Bristol. Fancy lingo, nifty arguments (Here, here!) match up nicely with some wonky computer decisions. The British government seems to have a keen interest in finding silver bullets; that is, solutions which will make problems go away. How did that work for the postal service?
I read “Health Data – It Isn’t Just Palantir or Bust,” written by lawyer, pundit, novelist, and wizard Cory Doctorow. The essay focuses on a tender offer captured by Palantir Technologies. The idea is that the British National Health Service has lots of data. The NHS has done some wild and crazy things to make those exposed to the NHS safer. Sorry, I can’t explain one taxonomy-centric project which went exactly nowhere despite the press releases generated by the vendors, speeches, presentations, and assurances that, by gad, these health data will be managed. Yeah, and Bristol’s nasty areas will be fixed up soon.
The British government professional is struggling with software that was described as a single solution. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. How is your security perimeter working today? Oh, that’s too bad. Good enough.
What is interesting about the write up is not the somewhat repetitive retelling of the NHS’ computer challenges. I want to highlight the comments from the lawyer – novelist about the American intelware outfit Palantir Technologies. What do we learn about Palantir?
Here the first quote from the essay:
But handing it all over to companies like Palantir isn’t the only option
The idea that a person munching on fish and chips in Swindon will know about Palantir is effectively zero. But it is clear that “like Palantir” suggests something interesting, maybe fascinating.
Here’s another reference to Palantir:
Even more bizarre are the plans to flog NHS data to foreign military surveillance giants like Palantir, with the promise that anonymization will somehow keep Britons safe from a company that is literally named after an evil, all-seeing magic talisman employed by the principal villain of Lord of the Rings (“Sauron, are we the baddies?”).
The word choice is painting a picture of an American intelware company which does focus on conveying a negative message; for instance, the words safe, evil, all seeing, villain, baddies, etc. What’s going on?
The British Medical Association and the conference of England LMC Representatives have endorsed OpenSAFELY and condemned Palantir. The idea that we must either let Palantir make off with every Briton’s most intimate health secrets or doom millions to suffer and die of preventable illness is a provably false choice.
It seems that the American company is known to the BMA and an NGO have figured out Palantir is a bit of a sticky wicket.
Several observations:
- My view is that Palantir promised a silver bullet to solve some of the NHS data challenges. The British government accepted the argument, so full steam ahead. Thus, the problem, I would suggest, is the procurement process
- The agenda in the write up is to associate Palantir with some relatively negative concepts. Is this fair? Probably not but it is typical of certain “real” analysts and journalists to mix up complex issues in order to create doubt about vendors of specialized software. These outfits are not perfect, but their products are a response to quite difficult problems.
- I think the write up is a mash up of anger about tender offers, the ineptitude of British government computer skills, the use of cross correlation as a symbol of Satan, and a social outrage about the Britain which is versus what some wish it were.
Net net: Will Palantir change because of this negative characterization of its products and services? Nope. Will the NHS change? Are you kidding me, of course not. Will the British government’s quest for silver bullet solutions stop? Let’s tackle this last question this way: “Why not write it in a snail mail letter and drop it in the post?”
Intelware is just so versatile at least in the marketing collateral.
Stephen E Arnold, March 11, 2024
The Internet as a Library and Archive? Ho Ho Ho
March 8, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
I know that I find certain Internet-related items a knee slapper. Here’s an example: “Millions of Research Papers at Risk of Disappearing from the Internet.” The number of individuals — young at heart and allegedly-informed seniors — think the “Internet” is a library or better yet an archive like the Library of Congress’ collection of “every” book.
A person deleting data with some degree of fierceness. Yep, thanks MSFT Copilot. After three tries, this is the best of the lot for a prompt asking for an illustration of data being deleted from a personal computer. Not even good enough but I like the weird orange coloration.
Here are some basics of how “Internet” services work:
- Every year costs go up of storage for old and usually never or rarely accessed data. A bean counter calls a meeting and asks, “Do we need to keep paying for ping, power, and pipes?” Some one points out, “Usage of X percent of the data described as “old” is 0.0003 percent or whatever number the bright young sprout has guess-timated. The decision is, as you might guess, dump the old files and reduce other costs immediately.
- Doing “data” or “online” is expensive, and the costs associated with each are very difficult, if not impossible to control. Neither government agencies, non-governmental outfits, the United Nations, a library in Cleveland or the estimable Harvard University have sufficient money to make available or keep at hand information. Thus, stuff disappears.
- Well-intentioned outfits like the Internet Archive or Project Gutenberg are in the same accountant ink pot. Not every Web site is indexed and archived comprehensively. Not every book that can be digitized and converted to a format someone thinks will be “forever.” As a result, one has a better chance of discovering new information browsing through donated manuscripts at the Vatican Library than running an online query.
- If something unique is online “somewhere,” that item may be unfindable. Hey, what about Duke University’s collection of “old” books from the 17th century? Who knew?
- Will a government agency archive digital content in a comprehensive manner? Nope.
The article about “risks of disappearing” is a hoot. Notice this passage:
“Our entire epistemology of science and research relies on the chain of footnotes,” explains author Martin Eve, a researcher in literature, technology and publishing at Birkbeck, University of London. “If you can’t verify what someone else has said at some other point, you’re just trusting to blind faith for artefacts that you can no longer read yourself.”
I like that word “epistemology.” Just one small problem: Trust. Didn’t the president of Stanford University have an opportunity to find his future elsewhere due to some data wonkery? Google wants to earn trust. Other outfits don’t fool around with trust; these folks gather data, exploit it, and resell it. Archiving and making it findable to a researcher or law enforcement? Not without friction, lots and lots of friction. Why verify? Estimates of non-reproducible research range from 15 percent to 40 percent of scientific, technical, and medical peer reviewed content. Trust? Hello, it’s time to wake up.
Many estimate how much new data are generated each year. I would suggest that data falling off the back end of online systems has been an active process. The first time an accountant hears the IT people say, “We can just roll off the old data and hold storage stable” is right up there with avoiding an IRS audit, finding a life partner, and billing an old person for much more than the accounting work is worth.
After 25 years, there is “risk.” Wow.
Stephen E Arnold, March 8, 2024
AI and Warfare: Gaza Allegedly Experiences AI-Enabled Drone Attacks
March 7, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
We have officially crossed a line. DeepNewz reveals: “AI-Enabled Military Tech and Indian-Made Hermes 900 Drones Deployed in Gaza.” It this what they mean by “helpful AI”? We cannot say we are surprised. The extremely brief write-up tells us:
“Reports indicate that Israel has deployed AI-enabled military technology in Gaza, marking the first known combat use of such technology. Additionally, Indian-made Hermes 900 drones, produced in collaboration between Adani‘s company and Elbit Systems, are set to join the Israeli army’s fleet of unmanned aerial vehicles. This development has sparked fears about the implications of autonomous weapons in warfare and the role of Indian manufacturing in the conflict in Gaza. Human rights activists and defense analysts are particularly worried about the potential for increased civilian casualties and the further escalation of the conflict.”
On a minor but poetic note, a disclaimer states the post was written with ChatGPT. Strap in, fellow humans. We are just at the beginning of a long and peculiar ride. How are those assorted government committees doing with their AI policy planning?
Cynthia Murrell, March 7, 2024
The RCMP: Monitoring Sparks Criticism
March 5, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
The United States and United Kingdom receive bad reps for monitoring their citizens’ Internet usage. Thankfully it is not as bad as China, Russia, and North Korea. The “hat” of the United States is hardly criticized for anything, but even Canada has its foibles. Canada’s Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) is in water hot enough to melt all its snow says The Madras Tribune: “RCMP Slammed For Private Surveillance Used To Trawl Social Media, ‘Darknet’.”
It’s been known that the RCMP has used private surveillance tools to monitor public facing information and other social media since 2015. The Privacy Commissioner of Canada (OPC) revealed that when the RCMP was collecting information, the police force failed to comply with privacy laws. The RCMP also doesn’t agree with the OPC’s suggestions to make their monitoring activities with third party vendors more transparent. The RCMP also argued that because they were using third party vendors they weren’t required to ensure that information was collected according to Canadian law.
The Mounties’ non-compliance began in 2014 after three police officers were shot. An information monitoring initiative called Project Wideawake started and it involved the software Babel X from Babel Street, a US threat intelligence company. Babel X allowed the RCMP to search social media accounts, including private ones, and information from third party data brokers.
Despite the backlash, the RCMP will continue to use Babel X:
“ ‘Despite the gaps in (the RCMP’s) assessment of compliance with Canadian privacy legislation that our report identifies, the RCMP asserted that it has done enough to review Babel X and will therefore continue to use it,’ the report noted. ‘In our view, the fact that the RCMP chose a subcontracting model to pay for access to services from a range of vendors does not abrogate its responsibility with respect to the services that it receives from each vendor.’”
Canada might be the politest of country in North America, but its government hides a facade dedicated to law enforcement as much as the US.
Whitney Grace, March 5, 2024
Techno Bashing from Thumb Typers. Give It a Rest, Please
March 5, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Every generation says that the latest cultural and technological advancements make people stupider. Novels were trash, the horseless carriage ruined traveling, radio encouraged wanton behavior, and the list continues. Everything changed with the implementation of television aka the boob tube. Too much television does cause cognitive degradation. In layman’s terms, it means the brain goes into passive functioning rather than actively thinking. It would be almost a Zen moment. Addiction is fun for some.
The introduction of videogames, computers, and mobile devices augmented the decline of brain function. The combination of AI-chatbots and screens, however, might prove to be the ultimate dumbing down of humans. APA PsycNet posted a new study by Umberto León-Domínguez called, “Potential Cognitive Risks Of Generative Transformer-Based AI-Chatbots On Higher Order Executive Thinking.”
Psychologists already discovered that spending too much time on a screen (i.e. playing videogames, watching TV or YouTube, browsing social media, etc.) increases the risk of depression and anxiety. When that is paired with AI-chatbots, or programs designed to replicate the human mind, humans rely on the algorithms to think for them.
León-Domínguez wondered if too much AI-chatbot consumption impaired cognitive development. In his abstract he invented some handy new terms that:
“The “neuronal recycling hypothesis” posits that the brain undergoes structural transformation by incorporating new cultural tools into “neural niches,” consequently altering individual cognition. In the case of technological tools, it has been established that they reduce the cognitive demand needed to solve tasks through a process called “cognitive offloading.” Cognitive offloading”perfectly describes younger generations and screen addicts. “Cultural tools into neural niches” also respects how older crowds view new-fangled technology, coupled with how different parts of the brain are affected with technology advancements. The modern human brain works differently from a human brain in the 18th-century or two thousand years ago.
He found:
“The pervasive use of AI chatbots may impair the efficiency of higher cognitive functions, such as problem-solving. Importance: Anticipating AI chatbots’ impact on human cognition enables the development of interventions to counteract potential negative effects. Next Steps: Design and execute experimental studies investigating the positive and negative effects of AI chatbots on human cognition.”
Are we doomed? No. Do we need to find ways to counteract stupidity? Yes. Do we know how it will be done? No.
Isn’t tech fun?
Whitney Grace, March 6, 2024
A Fresh Outcry Against Deepfakes
February 29, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
There is no surer way in 2024 to incur public wrath than to wrong Taylor Swift. The Daily Mail reports, “’Deepfakes Are a Huge Threat to Society’: More than 400 Experts and Celebrities Sign Open Letter Demanding Tougher Laws Against AI-Generated Videos—Weeks After Taylor Swift Became a Victim.” Will the super duper mega star’s clout spur overdue action? Deepfake porn has been an under-acknowledged problem for years. Naturally, the generative AI boom has made it much worse: Between 2022 and 2023, we learn, such content has increased by more than 400 percent. Of course, the vast majority of victims are women and girls. Celebrities are especially popular targets. Reporter Nikki Main writes:
“‘Deepfakes are a huge threat to human society and are already causing growing harm to individuals, communities, and the functioning of democracy,’ said Andrew Critch, AI Researcher at UC Berkeley in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and lead author on the letter. … The letter, titled ‘Disrupting the Deepfake Supply Chain,’ calls for a blanket ban on deepfake technology, and demands that lawmakers fully criminalize deepfake child pornography and establish criminal penalties for anyone who knowingly creates or shares such content. Signees also demanded that software developers and distributors be held accountable for anyone using their audio and visual products to create deepfakes.”
Penalties alone will not curb the problem. Critch and company make this suggestion:
“The letter encouraged media companies, software developers, and device manufacturers to work together to create authentication methods like adding tamper-proof digital seals and cryptographic signature techniques to verify the content is real.”
Sadly, media and tech companies are unlikely to invest in such measures unless adequate penalties are put in place. Will legislators finally act? Answer: They are having meetings. That’s an act.
Cynthia Murrell, March 29, 2024
French Building and Structure Geo-Info
February 23, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
OSINT professionals may want to take a look at a French building and structure database with geo-functions. The information is gathered and made available by the Observatoire National des Bâtiments. Registration is required. A user can search by city and address. The data compiled up to 2022 cover France’s metropolitan areas and includes geo services. The data include address, the built and unbuilt property, the plot, the municipality, dimensions, and some technical data. The data represent a significant effort, involving the government, commercial and non-governmental entities, and citizens. The dataset includes more than 20 million addresses. Some records include up to 250 fields.
Source: https://www.urbs.fr/onb/
To access the service, navigate to https://www.urbs.fr/onb/. One is invited to register or use the online version. My team recommends registering. Note that the site is in French. Copying some text and data and shoving it into a free online translation service like Google’s may not be particularly helpful. French is one of the languages that Google usually handles with reasonable facilities. For this site, Google Translate comes up with tortured and off-base translations.
Stephen E Arnold, February 23, 2024
AI to AI, Program 2 Now Online
February 22, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
My son has converted one of our Zoom conversations into a podcast about AI for government entities. The program runs about 20 minutes and features our "host," a Deep Fake pointing out he lacks human emotions and tells AI-generated jokes. Erik talks about the British government’s test of chatbots and points out one of the surprising findings from the research. He also describes the use of smart software as Ukrainian soldiers write code in real time to respond to a dynamic battlefield. Erik asks me to explain the difference between predictive AI and generative AI. My use cases focus on border-related issues. He then tries to get me to explain how to sidestep US government, in-agency AI software testing. That did not work, and I turned his pointed question into a reason for government professionals to hire him and his team. The final story focuses on a quite remarkable acronym about US government smart software projects. What’s the acronym? Please, navigate to https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fB_fNjzRsf4&t=7s to find out.
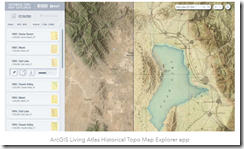
Map Data: USGS Historical Topos
February 20, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
The ESRI blog published “Access Over 181,000 USGS Historical Topographic Maps.” The map outfit teamed with the US Geological Survey to provide access to an additional 1,745 maps. The total maps in the collection is now 181,008.
The blog reports:
Esri’s USGS historical topographic map collection contains historical quads (excluding orthophoto quads) dating from 1884 to 2006 with scales ranging from 1:10,000 to 1:250,000. The scanned maps can be used in ArcGIS Pro, ArcGIS Online, and ArcGIS Enterprise. They can also be downloaded as georeferenced TIFs for use in other applications.
These data are useful. Maps can be viewed with ESRI’s online service called the Historical Topo Map Explorer. You can access that online service at this link.
If you are not familiar with historical topos, ESRI states in an ARCGIS post:
The USGS topographic maps were designed to serve as base maps for geologists by defining streams, water bodies, mountains, hills, and valleys. Using contours and other precise symbolization, these maps were drawn accurately, made mathematically correct, and edited carefully. The topographic quadrangles gradually evolved to show the changing landscape of a new nation by adding symbolization for important highways; canals; railroads; and railway stations; wagon roads; and the sites of cities, towns and villages. New and revised quadrangles helped geologists map the mineral fields, and assisted populated places to develop safe and plentiful water supplies and lay out new highways. Primary considerations of the USGS were the permanence of features; map symbolization and legibility; and the overall cost of compiling, editing, printing and distributing the maps to government agencies, industry, and the general public. Due to the longevity and the numerous editions of these maps they now serve new audiences such as historians, genealogists, archeologists, and people who are interested in the historical landscape of the U.S.
This public facing data service is one example of extremely useful information gathered by US government entities can be made more accessible via a public-private relationship. When I served on the board of the US National Technical Information Service, I learned that other useful information is available, just not easily accessible to US citizens.
Good work, ESRI and USGS! Now what about making that volcano data a bit easier to find and access in real time?
Stephen E Arnold, February 20, 2024