Palantir: Fear Is Good. Fear Sells.
June 18, 2024
President Eisenhower may not have foreseen AI when he famously warned of the military-industrial complex, but certain software firms certainly fit the bill. One of the most successful, Palantir, is pursuing Madison Avenue type marketing with a message of alarm. The company’s co-founder, Alex Karp, is quoted in the fear-mongering post at right-wing Blaze Media, “U.S. Prepares for War Amid Growing Tensions that China Could Invade Taiwan.”
After several paragraphs of panic over tensions between China and Taiwan, writer Collin Jones briefly admits “It is uncertain if and when the Chinese president will deploy an attack against the small country.” He quickly pivots to the scary AI arms race, intimating Palantir and company can save us as long as we let (fund) them. The post concludes:
“Palantir’s CEO and co-founder Alex Karp said: ‘The way to prevent a war with China is to ramp up not just Palantir, but defense tech startups that produce software-defining weapons systems that scare the living F out of our adversaries.’ Karp noted that the U.S. must stay ahead of its military opponents in the realm of AI. ‘Our adversaries have a long tradition of being not interested in the rule of law, not interested in fairness, not interested in human rights and on the battlefield. It really is going to be us or them.’ Karp noted that the U.S. must stay ahead of its military opponents in the realm of AI. You do not want a world order where our adversaries try to define new norms. It would be very bad for the world, and it would be especially bad for America,’ Karp concluded.”
Wow. But do such scare tactics work? Of course they do. For instance, we learn from DefenseScoop, “Palantir Lands $480M Army Contract for Maven Artificial Intelligence Tech.” That article reports on not one but two Palantir deals: the titular Maven expansion and, we learn:
“The company was recently awarded another AI-related deal by the Army for the next phase of the service’s Tactical Intelligence Targeting Access Node (TITAN) ground station program, which aims to provide soldiers with next-generation data fusion and deep-sensing capabilities via artificial intelligence and other tools. That other transaction agreement was worth $178 million.”
Those are just two recent examples of Palantir’s lucrative government contracts, ones that have not, as of this writing, been added this running tally. It seems the firm has found its winning strategy. Ramping up tensions between world powers is a small price to pay for significant corporate profits, apparently.
Cynthia Murrell, June 18, 2024
AI May Not Be Magic: The Salesforce Signal
June 10, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
Salesforce has been a steady outfit. However, the company suffered a revenue miss, its first in about a quarter century. The news reports cited broad economic factors like “macro headwinds.” Salesforce, according to the firm’s chief people officer, the company has been experimenting with AI for “over a decade.” But the magic of AI was not able to ameliorate the company’s dip or add some chrome trim to its revenue guidance.
John Milton’s god character from Paradise Lost watches the antics of super-sophisticated artificial intelligence algorithms. This character quickly realizes that zeros and ones crafted by humans and enhanced by smart machines is definitely not omniscient, omnipresent, and omnipotent character who knows everything before it happens no matter what the PR firms or company spokesperson asserts. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Good enough.
Piecing together fragments of information, it appears that AI has added to the company’s administrative friction. In a Fortune interview, recycled for MSN.com, consider these administrative process examples:
- The company has deployed 50 AI tools.
- Salesforce has an AI governance council.
- There is an Office of Ethical and Humane Use, started in 2019.
- Salesforce uses surveys to supplement its “robust listening strategies.”
- There are phone calls and meetings.
Some specific uses of AI appear to address inherent design constraints in Salesforce software; for example, AI has:
saved employees 50,000 hours within one business quarter, and the bot answered nearly 370,000 employee questions, according to the company. Merging into Project Basecamp, the company’s project management platform, has resolved 88,000 worker requests, speeding up issue resolution from an average of 48 hours to just 30 minutes.
What’s the payoff to the bottom line? That information is scant. What we know is that Salesforce may not be benefiting from the additional AI investment or the friction AI’s bureaucratic processes imposes on the company.
What’s this mean for those who predict that AI will change everything? I continue to think about the two ends of the spectrum: Go fast and break things crowd and the stop AI contingent.
First, the type of AI which is the one that does high school essay writing is easy to understand. These systems work as long as the subject matter clumps into piles of factoids which limit the craziness of the algorithms’ outputs. The topic “How to make a taco” is nailed down. The topic “How to decrypt Telegram’s encryption system” is not. Big brains can explain why the taco question is relatively hallucination free but not why the Telegram question generates useless drivel. I have, therefore, concluded, “Limited, narrow domain questions are okay for AI.”
Second, the current systems are presented as super wonderful. An example is the steady flow of PR about Google DeepMind’s contributions to biological science. Yet Google’s search system generates baloney. I think the different is that whacking away at proteins is a repetitive combinatorial problem. Calling the methods AI is similar to describing Daylight Chemical Information Systems a manifestation of the Oracle at Delphi is hogwash. PR erases important differences in critical lines of research. Does Google DeepMind feel shame? Let’s ask IBM Watson. That will be helpful. PR has a role; it is not AI.
Third, the desire for a silver bullet is deep-seated in many Peter Principle managers. These “leaders” of “leadership teams” don’t know what to do. Managing becomes figuring out risks. AI has legs, so let’s give that pony a chance to win the cart race. But pony cart races are trivial. The real races require winning three competitions. Few horses pull of that trick. I watch in wonder the launch, retreat, PR explanation, and next launch of some AI outfits. The focus seems to be on getting $20 per month. Degrading the service. Asking for more money. Then repeat.
The lack of AI innovation is becoming obvious. From the starter’s gun cracking in time with Microsoft’s AI announcement in January 2023 how much progress has been made?
We have the Salesforce financial report. We have the management craziness at OpenAI. We have Microsoft investing in or partnering with a number of technology outfits, including one in Paris. We have Google just doddering and fumbling. We have lawsuits. We have craziness like Adobe’s “owning” any image created with its software. We have start ups which bandy about the term “AI” like a shuttlecock at a high school in India badminton league. We have so many LinkedIn AI experts, I marvel that no one pins these baloney artists to a piece of white bread. We have the Dutch police emphasizing home-grown AI which helped make sense of the ANOM phone stings when the procedures are part of most policeware systems. Statistics, yes. AI, no. Clustering, yes. AI, no. Metadata assignment, yes. AI, no. The ANOM operation took place about 2017 to its shut down four years later. AI? Nope.
What does the lack of financial payoff and revenue generating AI solutions tell me? My answer to this question is:
- The cost of just using and letting prospects use an AI system are high. Due to the lack of a Triple Crown contender, no company has the horse or can afford the costs of getting the nag ready to race and keeping the animal from keeling over dead.
- The tangible results are tough to express. Despite the talk about reducing the costs of customer service, the cost of the AI system and the need to have humans ride herd on what the crazed cattle-like algorithms yield is not evident to me. The Salesforce experience is that AI cannot fix or make the Slack system generate oodles of cost savings or revenues from new, happy customers.
- The AI systems, particularly the services promoted via Product Hunt, are impossible for me to differentiate. Some do images, but the functions are similar. Some AI system do text things. Okay. But what’s new? Money is being spent to produce endless variations and me-too services. Fun for some. But boring and a waste of time to a dinobaby like me.
Net net: With economic problems growing in numerous sectors, those with money or a belief that garlic will kill Count Vampire, Baron of Revenue Loss are in for a surprise. Sorry. No software equivalent to Milton’s eternal, all-knowing, omnipotent God. I won’t tell the PR people. That Salesforce signal is meaningful.
Stephen E Arnold, June 10, 2024
Selling AI with Scare Tactics
June 6, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
Ah, another article with more assertions to make workers feel they must adopt the smart software that threatens their livelihoods. AI automation firm UiPath describes “3 Common Barriers to AI Adoption and How to Overcome Them.” Before marketing director Michael Robinson gets to those barriers, he tries to motivate readers who might be on the fence about AI. He writes:
“There’s a growing consensus about the need for businesses to embrace AI. McKinsey estimated that generative AI could add between $2.6 to $4.4 trillion in value annually, and Deloitte’s ’State of AI in the Enterprise’ report found that 94% of surveyed executives ‘agree that AI will transform their industry over the next five years.’ The technology is here, it’s powerful, and innovators are finding new use cases for it every day. But despite its strategic importance, many companies are struggling to make progress on their AI agendas. Indeed, in that same report, Deloitte estimated that 74% of companies weren’t capturing sufficient value from their AI initiatives. Nevertheless, companies sitting on the sidelines can’t afford to wait any longer. As reported by Bain & Company, a ‘larger wedge’ is being driven ‘between those organizations that have a plan [for AI] and those that don’t—amplifying advantage and placing early adopters into stronger positions.’”
Oh, no! What can the laggards do? Fret not, the article outlines the biggest hurdles: lack of a roadmap, limited in-house expertise, and security or privacy concerns. Curious readers can see the post for details about each. As it happens, software like UiPath’s can help businesses clear every one. What a coincidence.
Cynthia Murrell, June 6, 2024
Publication Founded by a Googler Cheers for Google AI Search
June 5, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
To understand the “rah rah” portion of this article, you need to know the backstory behind Search Engine Land, a news site about search and other technology. It was founded by Danny Sullivan, who pushed the SEO bandwagon. He did this because he was angling for a job at Google, he succeeded, and now he’s the point person for SEO.
Another press release touting the popularity of Google search dropped: “Google SEO Says AI Overviews Are Increasing Search Usage.” The author Danny Goodwin remains skeptical about Google’s spiked popularity due to AI and despite the bias of Search Engine Land’s founder.
During the QI 2024 Alphabet earnings call, Google/Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai said that the search engine’s generative AI has been used for billions of queries and there are plans to develop the feature further. Pichai said positive things about AI, including that it increased user engagement, could answer more complex questions, and how there will be opportunities for monetization.
Goodwin wrote:
“All signs continue to indicate that Google is continuing its slow evolution toward a Search Generative Experience. I’m skeptical about user satisfaction increasing, considering what an unimpressive product AI overviews and SGE continues to be. But I’m not the average Google user – and this was an earnings call, where Pichai has mastered the art of using a lot of words to say a whole lot of nothing.”
AI is the next evolution of search and Google is heading the parade, but the technology still has tons of bugs. Who founded the publication? A Googler. Of course there is no interaction between the online ad outfit and an SEO mouthpiece. Un-uh. No way.
Whitney Grace, June 5, 2024
So AI Is — Maybe, Just Maybe — Not the Economic Big Kahuna?
June 3, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
I find it amusing how AI has become the go-to marketing word. I suppose if I were desperate, lacking an income, unsure about what will sell, and a follow-the-hyperbole-type person I would shout, “AI.” Instead I vocalize, “Ai-Yai-Ai” emulating the tones of a Central American death whistle. Yep, “Ai-Yai-AI.”
Thanks, MSFT Copilot. A harbinger? Good enough.
I read “MIT Professor Hoses Down Predictions AI Will Put a Rocket under the Economy.” I won’t comment upon the fog of distrust which I discern around Big Name Universities, nor will I focus my adjustable Walgreen’s spectacles on MIT’s fancy dancing with the quite interesting and decidedly non-academic Jeffrey Epstein. Nope. Forget those two factoids.
The write up reports:
…Daron Acemoglu, professor of economics at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, argues that predictions AI will improve productivity and boost wages in a “blue-collar bonanza” are overly optimistic.
The good professor is rowing against the marketing current. According to the article, the good professor identifies some wild and crazy forecasts. One of these is from an investment bank whose clients are unlikely to be what some one percenters perceive as non-masters of the universe.
That’s interesting. But it pales in comparison to the information in “Few People Are Using ChatGPT and Other AI Tools Regularly, Study Suggests.” (I love suggestive studies!) That write up reports about a study involving Thomson Reuters, the “trust” outfit:
Carried out by the Reuters Institute and Oxford University and involving 6,000 respondents from the U.S., U.K., France, Denmark, Japan, and Argentina, the researchers found that OpenAI’s ChatGPT is by far the most widely used generative-AI tool and is two or three times more widespread than the next most widely used products — Google Gemini and Microsoft Copilot. But despite all the hype surrounding generative AI over the last 18 months, only 1% of those surveyed are using ChatGPT on a daily basis in Japan, 2% in France and the UK, and 7% in the U.S. The study also found that between 19% and 30% of the respondents haven’t even heard of any of the most popular generative AI tools, and while many of those surveyed have tried using at least one generative-AI product, only a very small minority are, at the current time, regular users deploying them for a variety of tasks.
My hunch is that these contrarians want clicks. Well, the tactic worked for me. However, how many of those in AI-Land will take note? My thought is that these anti-AI findings are likely to be ignored until some of the Big Money folks lose their cash. Then the voices of negativity will be heard.
Several observations:
- The economics of AI seem similar to some early online ventures like Pets.com, not “all” mind you, just some
- Expertise in AI may not guarantee a job at a high-flying techno-feudalist outfit
- The difficulties Google appears to be having suggest that the road to AI-Land on the information superhighway may have some potholes. (If Google cannot pull AI off, how can Bob’s Trucking Company armed with Microsoft Word with Copilot?)
Net net: It will be interesting to monitor the frequency of “AI balloon deflating” analyses.
Stephen E Arnold, June 3, 2024
x
NSO Group: Making Headlines Again and Again and Again
May 31, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
NSO Group continues to generate news. One example is the company’s flagship sponsorship of an interesting conference going on in Prague from June 4th to the 6th. What’s interesting mean? I think those who attend the conference are engaged in information-related activities connected in some way to law enforcement and intelligence. How do I know NSO Group ponied up big bucks to be the “lead sponsor”? Easy. I saw this advertisement on the conference organizer’s Web site. I know you want me to reveal the url, but I will treat the organizer in a professional manner. Just use those Google Dorks, and you will locate the event. The ad:
What’s the ad from the “lead sponsor” say? Here are a few snippets from the marketing arm of NSO Group:
NSO Group develops and provides state-of-the-art solutions, designed to assist in preventing terrorism and crime. Our solutions address diverse strategical, tactical and operational needs and scenarios to serve authorized government agencies including intelligence, military and law enforcement. Developed by the top technology and data science experts, the NSO portfolio includes cyber intelligence, network and homeland security solutions. NSO Group is proud to help to protect lives, security and personal safety of citizens around the world.
Innocent stuff with a flavor jargon-loving Madison Avenue types prefer.
Citizen’s Lab is a bit like mules in an old-fashioned grist mill. The researchers do not change what they think about. Source: Royal Mint Museum in the UK.
Just for some fun, let’s look at the NSO Group through a different lens. The UK newspaper The Guardian, which counts how many stories I look at a year, published “Critics of Putin and His Allies Targeted with Spyware Inside the EU.” Here’s a sample of the story’s view of NSO Group:
At least seven journalists and activists who have been vocal critics of the Kremlin and its allies have been targeted inside the EU by a state using Pegasus, the hacking spyware made by Israel’s NSO Group, according to a new report by security researchers. The targets of the hacking attempts – who were first alerted to the attempted cyber-intrusions after receiving threat notifications from Apple on their iPhones – include Russian, Belarusian, Latvian and Israeli journalists and activists inside the EU.
And who wrote the report?
Access Now, the Citizen Lab at the Munk School of Global Affairs & Public Policy at the University of Toronto (“the Citizen Lab”), and independent digital security expert Nikolai Kvantiliani
The Citizen Lab has been paying attention to NSO Group for years. The people surveilled or spied upon via the NSO Group’s Pegasus technology are anti-Russia; that is, none of the entities will be invited to a picnic at Mr. Putin’s estate near Sochi.
Obviously some outfit has access to the Pegasus software and its command-and-control system. It is unlikely that NSO Group provided the software free of charge. Therefore, one can conclude that NSO Group could reveal what country was using its software for purposes one might consider outside the bounds of the write up’s words cited above.
NSO Group remains one of the — if not the main — poster children for specialized software. The company continues to make headlines. Its technology remains one of the leaders in the type of software which can be used to obtain information for a mobile device. There are some alternatives, but NSO Group remains the Big Dog.
One wonders why Israel, presumably with the Pegasus tool, could not have obtained information relevant to the attack in October 2023. My personal view is that having Fancy Dan ways to get data from a mobile phone, human analysts have to figure out what’s important and what to identify as significant.
My point is that the hoo-hah about NSO Group and Pegasus may not be warranted. Information without the trained analysts and downstream software may have difficulty getting the information required to take a specific action. Israel’s lack of intelligence means that software alone can’t do the job. No matter what the marketing material says or how slick the slide deck used to brief those with a “need to know” appears — software is not intelligence.
Will NSO Group continue to make headlines? Probably. Those with access to Pegasus will make errors and disclose their ineptness. Citizen’s Lab will be at the ready. New reports will be forthcoming.
Net net: Is anyone surprised Mr. Putin is trying to monitor anti-Russia voices? Is Pegasus the only software pressed into service? My answer to this question is: “Mr. Putin will use whatever tool he can to achieve his objectives.” Perhaps Citizen’s Lab should look for other specialized software and expand its opportunities to write reports? When will Apple address the vulnerability which NSO Group continues to exploit?
Stephen E Arnold, May 31, 2024
Apple Fan Misses the Obvious: MSFT Marketing Is Tasty
May 28, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
I love anecdotes seasoned investigators offer at law enforcement and intelligence conferences. Statements like “I did nothing wrong” are accompanied by a weapon in a waistband. Or, “You can take my drugs.” Yep, those are not informed remarks in some situations. But what happens when poohbahs and would-be experts explain in 2,600 words how addled Microsoft’s announcements were at its Build conference. “Microsoft’s Copilot PC and the M3 Mac Killer Myth” is an interesting argumentative essay making absolutely clear as fresh, just pressed apple cider in New Hampshire. (Have you ever seen the stuff?)
The Apple Cider judge does not look happy. Has the innovation factory failed with filtration? Thanks, MSFT Copilot. How is that security initiative today?
The write up provides a version of “tortured poet” writing infused with techno-talk. The object of the write up is to make as clear as the aforementioned apple cider several points to which people are not directing attention; to wit:
- Microsoft has many failures; for example, the Windows Phone, Web search, and, of course, crappy Windows in many versions
- Microsoft follows what Apple does; for example, smart software like facial recognition on a user’s device
- Microsoft fouled up with its Slate PC and assorted Windows on Arm efforts.
So there.
Now Microsoft is, according to the write up:
Today, Microsoft is doing the exact same lazy thing to again try to garner some excitement about legacy Windows PCs, this time by tacking an AI chat bot. And specifically, the Bing Chat bot nobody cared about before Microsoft rebranded it as Copilot. Counting the Surface tablet and Windows RT, and the time Microsoft pretended to "design" its own advanced SoC just like Apple by putting RAM on a Snapdragon, this must be Microsoft’s third major attempt to ditch Intel and deliver something that could compete with Apple’s iPad, or M-powered Macs, or even both.
The article provides a quick review of the technical innovations in Apple’s proprietary silicon. The purpose of the technology information is to make as clear as that New Hampshire, just-pressed juice that Microsoft will continue its track record of fouling up. The essay concludes with this “core” statement flavored with the pungency of hard cider:
Things incrementally change rapidly in the tech industry, except for Microsoft and its photocopy culture.
Interesting. However, I want to point out that Microsoft created a bit of a problem for Google in January 2023. Microsoft’s president announced its push into AI. Google, an ageing beastie, was caught with its claws retracted. The online advertising giant’s response was the Sundar & Prabhakar Comedy Show. It featured smart software which made factual errors, launched the Code Red or whatever odd ball name Googlers assigned to the problem Microsoft created.
Remember. The problem was not AI. Google “invented” some of the intestines of OpenAI’s and Microsoft’s services. The kick in the stomach was marketing. Microsoft’s announcement captured attention and made — much to the chagrin of the online advertising service — look old and slow, not smooth and fast like those mythical US Navy Seals of technology. Google dropped the inflatable raft and appears to be struggling against a rather weak rip tide.
What Microsoft did at Build with its semi-wonky and largely unsupported AI PC announcement was marketing. The Apple essay ignores the interest in a new type of PC form factor that includes the allegedly magical smart software. Mastery of smart software means work, better grades, efficiency, and a Cybertruck filled with buckets of hog wash.
But that may not matter.
Apple, like Google, finds itself struggling to get its cider press hooked up and producing product. One can criticize the Softies for technology. But I have to admit that Microsoft is reasonably adept at marketing its AI efforts. The angst in the cited article is misdirected. Apple insiders should focus on the Microsoft marketing approach. With its AI messaging, Microsoft has avoided the craziness of the iPad’s squashing creativity.
Will the AI PC work? Probably in an okay way. Has Microsoft’s AI marketing worked? It sure looks like it.
Stephen E Arnold, May 28, 2024
Googzilla Versus OpenAI: Moving Up to Pillow Fighting
May 17, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
Mike Tyson is dressed in a Godzilla outfit. He looks like a short but quite capable Googzilla. He is wearing a Google hat. (I have one, but it is soiled. Bummer.) Googzilla is giving the stink eye to Sam AI-Man, who has followed health routines recommended by Huberman Lab and Anatoly, the fellow who hawks supplements after shaming gym brutes dressed as a norm core hero.
Sam AI-Man asks an important question. Googzilla seems to be baffled. But the cane underscores that he is getting old for a thunder lizard selling online advertising. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. How are the security initiatives coming along? Oh, too bad.
Now we have the first exhibition: Googzilla is taking on Sam AI-Man.
I read an analysis of this high-stakes battle in “ChatGPT 4o vs Gemini 1.5 Pro: It’s Not Even Close.” The article appeared in the delightfully named online publication “Beebom.” I am writing in Beyond Search, which is — quite frankly — a really boring name. But I am a dinobaby, and I am going to assume that Beebom has a much more tuned in owner operator.
The article illustrates a best practice in database comparison, just tweaked to provide some insights into how alike or different the Googzilla is from the AI-Man. There’s a math test. There is a follow the instructions query. There is an image test. A programming challenge. You get the idea. The article includes what a reader will need to run similar brain teasers to Googzilla and Sam AI-Man.
Who cares? Let’s get to the results.
The write up says:
It’s evidently clear that Gemini 1.5 Pro is far behind ChatGPT 4o. Even after improving the 1.5 Pro model for months while in preview, it can’t compete with the latest GPT-4o model by OpenAI. From commonsense reasoning to multimodal and coding tests, ChatGPT 4o performs intelligently and follows instructions attentively. Not to miss, OpenAI has made ChatGPT 4o free for everyone.
Welp. This statement is not going to make Googzilla happy. Anyone who plays Foosball with the beastie today will want to be alert that re-Fooses are not allowed. You lose when you what the ball out of the game.
But the sun has not set over the Googzilla computer lab. The write up opines:
The only thing going for Gemini 1.5 Pro is the massive context window with support for up to 1 million tokens. In addition, you can upload videos too which is an advantage. However, since the model is not very smart, I am not sure many would like to use it just for the larger context window.
I chuckled at the last line of the write up:
If Google has to compete with OpenAI, a substantial leap is required.
Several observations:
- Who knows the names of the “new” products Google rolled out?
- With numerous “new” products, has Google a grand vision or is it one of those high school stunts in which passengers in a luxury car jump out and run around the car shouting. Then the car drives off?
- Will Google’s management align its AI with its staff management methods in the context of the regulatory scrutiny?
- Where’s DeepMind in this somewhat confusing flood of “new” smart products?
Net net: Google is definitely showing the results of having its wizards work under Code Red’s flashing lights. More pillow fights ahead. (Can you list the “new” products announced at Google I/O? Don’t worry. Neither can I.)
Stephen E Arnold, May 17, 2024
Apple and a Recycled Carnival Act: Woo Woo New New!
May 13, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
A long time ago, for a project related to a new product which was cratering, one person on my team suggested I read a book by James B. Twitchell. Carnival Culture: The Trashing of Taste in America provided a broad context, but the information in the analysis of taste was not going to save the enterprise software I was supposed to analyze. In general, I suggest that investment outfits with an interest in online information give me a call before writing checks to the tale-spinning entrepreneurs.
A small creative spark getting smashed in an industrial press. I like the eyes. The future of humans in Apple’s understanding of the American datasphere. Wow, look at those eyes. I can hear the squeals of pain, can’t you?
Dr. Twitchell did a good job, in my opinion, of making clear that some cultural actions are larger than a single promotion. Popular movies and people like P.T. Barnum (the circus guy) explain facets of America. These two examples are not just entertaining; they are making clear what revs the engines of the US of A.
I read “Hating Apple Goes Mainstream” and realized that Apple is doing the marketing for which it is famous. The roll out of the iPad had a high resolution, big money advertisement. If you are around young children, squishy plastic toys are often in small fingers. Squeeze the toy and the eyes bulge. In the image above, a child’s toy is smashed in what seems to me be the business end of a industrial press manufactured by MSE Technology Ltd in Turkey.
Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Glad you had time to do this art. I know you are busy on security or is it AI or is AI security or security AI? I get so confused.
The Apple iPad has been a bit of an odd duck. It is a good substitute for crappy Kindle-type readers. We have a couple, but they don’t get much use. Everything is a pain for me because the super duper Apple technology does not detect my fingers. I bought the gizmos so people could review the PowerPoint slides for one of my lectures at a conference. I also experimented with the iPad as a teleprompter. After a couple of tests, getting content on the device, controlling it, and fiddling so the darned thing knew I was poking the screen to cause an action — I put the devices on the shelf.
Forget the specific product, let’s look at the cited write ups comments about the Apple “carnival culture” advertisement. The write up states:
Apple has lost its presumption of good faith over the last five years with an ever-larger group of people, and now we’ve reached a tipping point. A year ago, I’m sure this awful ad would have gotten push back, but I’m also sure we’d heard more “it’s not that big of a deal” and “what Apple really meant to say was…” from the stalwart Apple apologists the company has been able to count on for decades. But it’s awfully quiet on the fan-boy front.
I think this means the attempt to sell sent weird messages about a company people once loved. What’s going on, in my opinion, is that Apple is explaining what technology is going to do to people who once used software to create words, images, and data exhaust will be secondary to cosmetics of technology.
In short, people and their tools will be replaced by a gizmo or gizmos that are similar to bright lights and circus posters. What do these artifacts tell us. My take on the Apple iPad M4 super duper creative juicer is, at this time:
- So what? I have an M2 Air, and it does what I hoped the two touch insensitive iPads would do.
- Why create a form factor that is likely to get crushed when I toss my laptop bad on a security screening belt? Apple’s products are, in my view, designed to be landfill residents.
- Apple knows in its subconscious corporate culture heat sink that smart software, smart services, and dumb users are the future. The wonky expensive high-resolution shouts, “We know you are going to be out of job. You will be like the yellow squishy toy.”
The message Apple is sending is that innovation has moved from utility to entertainment to the carnival sideshow. Put on your clown noses, people. Buy Apple.
Stephen E Arnold, May 13, 2024
Google Stomps into the Threat Intelligence Sector: AI and More
May 7, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
This essay is the work of a dinobaby. Unlike some folks, no smart software improved my native ineptness.
Before commenting on Google’s threat services news. I want to remind you of the link to the list of Google initiatives which did not survive. You can find the list at Killed by Google. I want to mention this resource because Google’s product innovation and management methods are interesting to say the least. Operating in Code Red or Yellow Alert or whatever the Google crisis buzzword is, generating sustainable revenue beyond online advertising has proven to be a bit of a challenge. Google is more comfortable using such methods as [a] buying and trying to scale it, [b] imitating another firm’s innovation, and [c] dumping big money into secret projects in the hopes that what comes out will not result in the firm’s getting its “glass” kicked to the curb.
Google makes a big entrance at the RSA Conference. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Have you considerate purchasing Google’s threat intelligence service?
With that as background, Google has introduced an “unmatched” cyber security service. The information was described at the RSA security conference and in a quite Googley blog post “Introducing Google Threat Intelligence: Actionable threat intelligence at Google Scale.” Please, note the operative word “scale.” If the service does not make money, Google will “not put wood behind” the effort. People won’t work on the project, and it will be left to dangle in the wind or just shot like Cricket, a now famous example of animal husbandry. (Google’s Cricket was the Google Appliance. Remember that? Take over the enterprise search market. Nope. Bang, hasta la vista.)
Google’s new service aims squarely at the comparatively well-established and now maturing cyber security market. I have to check to see who owns what. Venture firms and others with money have been buying promising cyber security firms. Google owned a piece of Recorded Future. Now Recorded Future is owned by a third party outfit called Insight. Darktrace has been or will be purchased by Thoma Bravo. Consolidation is underway. Thus, it makes sense to Google to enter the threat intelligence market, using its Mandiant unit as a springboard, one of those home diving boards, not the cliff in Acapulco diving platform.
The write up says:
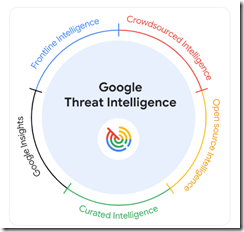
we are announcing Google Threat Intelligence, a new offering that combines the unmatched depth of our Mandiant frontline expertise, the global reach of the VirusTotal community, and the breadth of visibility only Google can deliver, based on billions of signals across devices and emails. Google Threat Intelligence includes Gemini in Threat Intelligence, our AI-powered agent that provides conversational search across our vast repository of threat intelligence, enabling customers to gain insights and protect themselves from threats faster than ever before.
Google to its credit did not trot out the “quantum supremacy” lingo, but the marketers did assert that the service offers “unmatched visibility in threats.” I like the “unmatched.” Not supreme, just unmatched. The graphic below illustrates the elements of the unmatchedness:
Credit to the Google 2024
But where is artificial intelligence in the diagram? Don’t worry. The blog explains that Gemini (Google’s AI “system”) delivers
AI-driven operationalization
But the foundation of the new service is Gemini, which does not appear in the diagram. That does not matter, the Code Red crowd explains:
Gemini 1.5 Pro offers the world’s longest context window, with support for up to 1 million tokens. It can dramatically simplify the technical and labor-intensive process of reverse engineering malware — one of the most advanced malware-analysis techniques available to cybersecurity professionals. In fact, it was able to process the entire decompiled code of the malware file for WannaCry in a single pass, taking 34 seconds to deliver its analysis and identify the kill switch. We also offer a Gemini-driven entity extraction tool to automate data fusion and enrichment. It can automatically crawl the web for relevant open source intelligence (OSINT), and classify online industry threat reporting. It then converts this information to knowledge collections, with corresponding hunting and response packs pulled from motivations, targets, tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), actors, toolkits, and Indicators of Compromise (IoCs). Google Threat Intelligence can distill more than a decade of threat reports to produce comprehensive, custom summaries in seconds.
I like the “indicators of compromise.”
Several observations:
- Will this service be another Google Appliance-type play for the enterprise market? It is too soon to tell, but with the pressure mounting from regulators, staff management issues, competitors, and savvy marketers in Redmond “indicators” of success will be known in the next six to 12 months
- Is this a business or just another item on a punch list? The answer to the question may be provided by what the established players in the threat intelligence market do and what actions Amazon and Microsoft take. Is a new round of big money acquisitions going to begin?
- Will enterprise customers “just buy Google”? Chief security officers have demonstrated that buying multiple security systems is a “safe” approach to a job which is difficult: Protecting their employers from deeply flawed software and years of ignoring online security.
Net net: In a maturing market, three factors may signal how the big, new Google service will develop. These are [a] price, [b] perceived efficacy, and [c] avoidance of a major issue like the SolarWinds’ matter. I am rooting for Googzilla, but I still wonder why Google shifted from Recorded Future to acquisitions and me-too methods. Oh, well. I am a dinobaby and cannot be expected to understand.
Stephen E Arnold, May 7, 2024