Open Source Software: Do Flashing Neon Signs Say, Bad Actors Welcome?
March 29, 2022
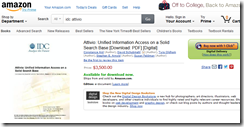
Remember when IDC, one of the units of the Patrick McGovern empire, was a big dog. Before the research unit wound up with swamp mud on its discount sneakers, one of the self-appointed experts suggested my team assemble a big report about — wait for it — open source search. We assembled our data, created profiles similar to those available on my Web site www.xenky.com/vendor-reports, and provided drafts to the estimable IDC. We learned, quite to my surprise, that several of these drafts were listed on Amazon.com for $3,000 each. We did not have a contract, and IDC had no permission to do anything with our profiles of about a dozen open source search solutions. Quite sporty behavior for “the premier global provider of marketing intelligence, advisory services, and events for the information technology, telecommunications, and consumer technology markets.” One IDC expert informed me that the company was called Foundry now. Yeah, who knew?
How do I know IDC sold my work on Amazon without an agreement from me? Check this out:
One take away from our book about open source search software was that security was an afterthought. Did users of open source software think about security? Nope. The users thought about how much money would be saved relying on a “community.” Users like the idea of not having proprietary software companies prevent changes to the code. Security was a community responsibility. Easy assumptions for users who wanted flexibility, reduced costs, and a false sense of no worries about this code.
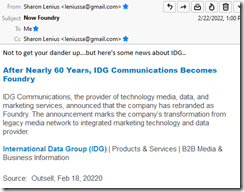
Does the big outfit which violated my copyright and stole my intellectual property care? The information about the lack of security in an enterprise open source software sector was effectively killed. Here’s an email I received in February 2022. You judge what’s shakin’.
The author is in some way affiliated to Foundry. The entity is called Sharon Lenius, and I assume she will respond to email sent to her at leniussa@gmail.com. Let’s hope she receives a lot of email.
Why this jaunt through the history of IDC and open source search software? If the company had its well oiled second hand store slicker in tip top shape, the security weaknesses of open source search software. Furthermore, the reason open source search as well as other types of software were being adopted by big outfits was cost reduction. The big firms used what could be downloaded, assuming that the “community” would identify flaws, fix them, and assume the responsibilities companies should have shouldered themselves.
When I read “A Developer Altered Open Source Software to Wipe Files in Russia,” I thought “decade old news.” A decade! Do I care? The write up states:
The developer of a popular open source package has been caught adding malicious code to it, leading to wiped files on computers located in Russia and Belarus. The move was part of a protest that has enraged many users and raised concerns about the safety of free and open source software.
I think that the security problems now released as “real news” are significant. Security, code integrity, and malicious actions on the part of the community were not at the top of the to do list 10 years ago and are not at the top of the list today.
Is there a fix? Sure, but like most fixes, it is likely to be too little and too late. Like the self regulation of financial services firms, there is considerable room for creative thinking in the open source software sector. In my upcoming 2022 National Cyber Crime Conference lecture, I will point out specific open source tools which can be used to subvert systems relying on open source software. Why not create a malicious chunk of code, tuck it in a library, and allow an incurious 20 something to undermine an organization?
Why not relay on outfits like mid tier consulting firms to provide actionable information? Why not wait until an armed conflict highlights a ticking IED inside some of the most widely used enterprise applications? Why not act in an ethical, responsible way?
I will be dead and logged off permanently before these questions are answered.
Stephen E Arnold, March 29, 2022
KO for AO Kaspersky?
March 29, 2022
I read “Kaspersky Named First Russian Company on Security Risk List.” Interesting. The write up reports:
The U.S. placed internet-security provider AO Kaspersky Lab on a list of companies deemed a threat to national security, for the first time adding a Russian entity to a list dominated by Chinese telecommunications firms. The Federal Communications Commission on Friday also added China Telecom (Americas) Corp, and China Mobile International USA Inc. to the list.
Now let’s ask another question, “Which venture funding firms accept money from individuals who may have interesting connections?”
Do I see any hands?
No.
That’s my point. Kaspersky is an obvious outfit to probe. What’s the action for the dozens, maybe hundreds, of cyber security firms with non-obvious links to interesting sources of cash. Some bad actors buy yachts. Others villas. A few go for nifty jets. How many are into owning cyber security firms, having access to click PowerPoint decks making the future clear in designer graphics, and hanging out with other technical wizards just sharing casual info?
Who wants to ask, “Where did your money come from?”
Stephen E Arnold, March 29, 2022
Microsoft Security: Time for the Softies to Release Windows 12, a Phone, or a Bid to Buy Tesla?
March 22, 2022
I find the headline amusing. I don’t find the story “Lapsus$ Hackers leak 37GB of Microsoft’s Alleged Source Code” particularly amusing. The Softies have become the outfit with a bright laser dot on the company’s logo. The write up reports:
The Lapsus$ hacking group claims to have leaked the source code for Bing, Cortana, and other projects stolen from Microsoft’s internal Azure DevOps server.
Okay, let’s assume that the story is mostly accurate or meeting a higher standard than that set by the New York Times for its coverage of a certain president’s son and his non-functioning laptop.
The article points out:
Furthermore, we are told that some of the leaked projects contain emails and documentation that were clearly used internally by Microsoft engineers to publish mobile apps. The projects appear to be for web-based infrastructure, websites, or mobile apps, with no source code for Microsoft desktop software released, including Windows, Windows Server, and Microsoft Office. When we contacted Microsoft about tonight’s source code leak, they continued to tell BleepingComputer that they are aware of the claims and are investigating.
Ho ho ho. Perhaps Microsoft’s security, including Defender, lacks some capabilities?
How many breaches are necessary before stakeholders make clear that the brittleness, flaws, and questionable engineering be remediated?
Is some wizard at Microsoft suggesting a re-run of plays which have worked in the past; for example, just put out a news release of Windows or splash cash and PR for a big acquisition? Just imagine a Tesla with Windows File Explorer ads displayed on that great big center display.
Stephen E Arnold, March 22, 2022
Microsoft Defender Is On the Job
March 22, 2022
I don’t know if this write up is an early April Fool thing or actual factual. “Microsoft Defender Goofed Up As It Flagged Its Own Office Updates As Malware” states:
…the company’s Defender for Endpoint security started detecting updates for its own Office app as ransomware. The antivirus program was misidentifying the “OfficeSvcMgr.exe” as malicious software.
Let’s assume there is some truth in the statement OfficeSvcMgr.exe is malicious. My ideas are:
- Careless Microsoft coding was part of OfficeSvcMgr.exe and less flawed coding by another Microsoft technical group spotted the “flaw”
- Microsoft’s quality assurance for its “security” systems remains questionable and the business process flaws have not yet been remediated
- Microsoft is busy adding features to Teams and ads to File Manager so there’s no time or resources to deal with the outstanding Defender service.
Which is closer to the pin? I am into the flawed business processes. But the appeal of putting ads into an operating system is a close second.
Stephen E Arnold, March 22, 2022
Insider Threat News: Two Interesting Situations at Two Sophisticated Companies
March 21, 2022
As you may know, I enjoy pointing out that some big buck cyber security systems struggle with insider threats. Isn’t it easier to put the words “detect and prevent insider threats” on a marketing slide deck than implement the service?
Two events may serve to remind those who wonder about the risks insider threat pose.
First, “Microsoft Investigating Claim of Breach by Extortion Gang” explains that a bad actor entity advertised for insiders. This quote is from the cited article:
We recruit employees/insider at the following!!!! Apple, IBM, and Microsoft. TO NOTE: WE ARE NOT LOOKING FOR DATA, WE ARE LOOKING FOR THE EMPLOYEE TO PROVIDE US A VPN OR CITRIX TO THE NETWORK, or some anydesk.
If accurate, this group (LKAPSUS$) is clear about the why and what it wants. The article alleges that Microsoft is beavering away to determine if its systems have been breached. Don’t the Softies use Defender and other MSFT cyber defense services? Yeah, well.
Second, Apple made headlines because an insider spoofed Apple’s security to the tune of an alleged $10 million. “Former Apple Employee Charged with $10M Fraud” reports:
… Prosecutors allege that while Prasad negotiated with suppliers and entered invoices into the purchasing system, he was conspiring to take kickbacks, using false repair orders to steal parts, and paying for goods and services never received using Apple’s money. The charges go on to allege tax evasion, wire and mail fraud, defrauding the United States, and money laundering, noting that Prasad was fired from Apple in December 2018 after a decade of employment.
How about those internal security and auditing business processes? Apple cares about privacy and security is the firm’s assertion. Again: Marketing is easier than preventing an insider threat.
Why am I bringing up a subject which is not discussed in the specific context of expensive cyber security systems? I offer these examples to make clear that what a cyber outfit says and what its products and services do are less reliable than a decade AvtoVAZ LADA. If you are not familiar with these vehicles, try to find one to drive on a long road trip through the Rocky Mountains. No LADA? Go for a Renault.
Stephen E Arnold, March 21, 2022
The Promise of Curated Apps
March 17, 2022
It is much easier to describe something than it is to produce a thing that matches the slide deck. I am not sure if the information in “Vicious SharkBot Banking Trojan Discovered in Play Store Antivirus App” is spot on. The tip off for me is the description of malware as “vicious.” The metaphors of sharks, apps, and vicious don’t work, but I get the idea.
The main point of the write up strikes me as:
British IT security researchers discovered, an updated SharkBot is hiding inside an innocent-looking antivirus app which is still available on the Google Play Store as of Saturday.
The interesting function is that the malware includes a function which performs automatic transfers. The money is in an account until it is not.
How does one obtain the app? The write up alleges that one might visit the Google Play Store and download something called Antivirus Super Cleaner.”
If the story is accurate, one has to consider this question, “Who is the minder of the Google Play Store?” An intern, a snorkeling bit of smart software, a contractor obtained via Upwork, a full time employee looking for a lateral arabesque to a hot new project, no one, or some other mechanism?
Imagine. No one minding the store. A new approach to curation perhaps?
Stephen E Arnold, March 17, 2022
Cyber Security Mumbo Jumbo: Whatever Sells to MBAs Is Good
March 15, 2022
Malware analysis is an important business function, but companies are confused about how it helps. Venture Beat examines how many companies have trouble with malware analysis in the article: “Report: 93% Of Orgs Challenged By Malware Analysis.” OPSWAT released a startling report about how companies respond to malware analysis. The results that 93% do not know what to do or lack effective and efficient operations is not good.
The biggest challenges companies face when handling a potential threat are lack of automation, lack of integration, and lack of employee experience with tools. These slow down response time to attacks and could potentially create bottlenecks.
This is even more disturbing because only 3% of companies resolve malware attacks, while 22% resolve less than half. Advanced persistent threats (APTs), targeted attacks, and ransomware bad actors are increasing and malware analysis is a way to prevent them.
“Malware analysis is a time-consuming manual process, made all the more complex by tools that are not integrated. Such monotonous workflows can become the source of employee burnout, or introduce human error into the process, making the demand for high-performance and accurate solutions a premium. The technical limitations of malware analysis and the struggle to find experienced malware analysts are two sides of the same coin, and if malware analysis is to continue maturing as a business function, then organizations need to be aware of their current limitations and begin investing in more automated, integrated, and accurate solutions — resulting in a stronger security posture and higher performing staff.”
Companies should be aware of malware attacks and take preventive measures, such as those outlined in malware analysis reports. Is investing in malware analysis well spent, though, if companies do not do anything? Maybe it would be better to teach employees how to recognize potential threats or investing in decent cyber security.
Whitney Grace, March 15, 2022
Google and Mandiant: Will Google Be Able to Handle a People Business?
March 11, 2022
Talk about Google’s purchasing Mandiant is a hot topic. I want to comment about Protocol’s article “Google Wants to Be the Full-Service Security Cloud.” The write up is one of several mentioning an important fact:
The company currently has 2,200 employees, including 600 consultants and 300 intelligence analysts who respond to security breaches.
Mandiant, therefore, has about half of its employees performing consultant type work. Not long ago, Google benefited from the sale of Recorded Future, a company which was in the cyber security business AND had a capability that Google had not previously possessed. What was Recorded Future’s magic ingredient? My answer is, “Ability to index by time.” There were other Recorded Future capabilities. In-Q-Tel found the company interesting as well.
Now the Google is embracing the consultative business in which Mandiant has done well. How will the Google management method apply to the individuals who make up about half the Mandiant work force?
If the past is an indication, Google does okay when the staff are like Google’s previous and current management. Google does less well when the professionals are less like those high school science club members who climbed the ladder at the Google.
To sum up: This deal is going to be interesting to watch. Microsoft is likely to be keen on following the tie up. Mandiant is, as you may recall, the outfit which blew the whistle on the SolarWinds’ misstep. Microsoft was snagged in the subsequent forensic analyses. Plus, the cyber security industry is enjoying some favorable winds. The issue, however, is that as threats become breaches, the flaws of the present approach to cyber security become more obvious. Online advertising, cloud computing, and cyber security — a delightful concoction or a volatile mix?
Stephen E Arnold, March 11, 2022
Cybersecurity and Human Error. Pesky Humans
March 10, 2022
Workers make honest mistakes. And sometimes those mistakes lead to security breaches. Darktrace describes how to guard against human imperfection in its DarkReading blog post, “Insider Threats Are More than Just Malicious Employees.” There is the worker who implements a shortcut they believe is benign but actually opens a route for attack. Another may simply forget everything they were taught in security training. Then there is the employee who is more focused on their next gig than on maintaining security practices at a firm they are leaving.
One answer to such risks, writes features editor Fahmida Y. Rashid, is zero trust. Though it sounds cynical, the practice protects organizations from human error. Citing Darktrace threat analyst Toby Lewis, Rashid explains:
“Zero trust treats every connection and action as suspicious. There are signals to verify, such as the device being used, the time of the day, and the order of applications being accessed. If the user is straying outside what’s expected, it triggers an investigation, even if the activity is originating from inside the environment. … In a zero-trust organization, it would be harder for insiders to act badly, Lewis notes. By managing identity, security teams understand who the users are and determine what ‘normal’ looks like. This way, they can assess the level of risk for each person and get a sense of when to ask for more information.”
Network segmentation is the other suggestion. We learn:
“If the network has been divided into different compartments, then users have to authenticate each time they cross into a new area. Different parts of the network can be carved out based on risk and where sensitive data is stored. ‘Each part of your network should be behind its own set of locked doors,’ Lewis says. ‘You could only cross this barrier if you are a trusted person.’”
In an ideal world, workers would reliably adhere to best practices and security teams would have no reason to track employees’ work patterns. But since we are stuck in this imperfect world, companies must do what they can to guard against human imperfection.
Cynthia Murrell, March 10, 2022
Google: Defines Excellence for Android Users
March 3, 2022
I read a hoot of a story. “Data Stealing App Found in Google Play Downloaded Thousands of Times.” The idea for branded stores is consistency, compatibility, and trust. No one wants to buy an air fryer that explodes and maims an influencer. Why would one want to download a mobile app which allows a bad actor to seize data or control of one’s mobile device.
The write up reports:
A notorious Android banking trojan designed to steal user data, like passwords and text messages, has been discovered in Google Play and downloaded thousands of times. The TeaBot banking trojan, also known as Anatsa and Toddler, was first observed in May 2021 targeting European banks by stealing two-factor authentication codes sent by text message.
Yep, malware direct from the Google. Let’s rundown those qualities of a branded store:
- Consistency
- Compatibility
- Trust
Check, check, and check.
Ah, Google, are you entering a security drag race against the Softies?
Stephen E Arnold, March 3, 2022