Clearview AI Faces Lawsuit on Web Photo Scraping Practices
April 15, 2021
We knew that facial-recognition firm Clearview AI, which sells its software to law enforcement agencies throughout the US, scrapes the Web for our photos and any data connected to them. Several civil liberties groups are trying to put a stop to the practice. The Los Angeles Times reports, “Clearview AI Uses Your Online Photos to Instantly ID You. That’s a Problem, Lawsuit Says.” Writer Johana Bhuiyan tells us the firm has collected more than 3 billion photos from Facebook, Twitter, Google, Venmo, and other sites. We learn:
“It also has caught the attention of civil liberties advocates and activists, who allege in a lawsuit filed Tuesday that the company’s automatic scraping of their images and its extraction of their unique biometric information violate privacy and chill protected political speech and activity. The plaintiffs — four individual civil liberties activists and the groups Mijente and NorCal Resist — allege Clearview AI ‘engages in the widespread collection of California residents’ images and biometric information without notice or consent.’ This is especially consequential, the plaintiffs argue, for proponents of immigration or police reform, whose political speech may be critical of law enforcement and who may be members of communities that have been historically over-policed and targeted by surveillance tactics. Clearview AI enhances law enforcement agencies’ efforts to monitor these activists, as well as immigrants, people of color and those perceived as ‘dissidents,’ such as Black Lives Matter activists, and can potentially discourage their engagement in protected political speech as a result, the plaintiffs say.”
The suit, filed in Alameda County Superior Court, seeks an injunction forcing Clearview to not only cease collecting photos and other biometric information in California, but to also delete all biometric data and personal information from their databases. Meanwhile in Illinois, the American Civil Liberties Union is suing the company, charging it has violated that state’s biometric privacy law. Officials in the European Union and Canada have also expressed concerns. We are unsure how much traction these suits and objections will get, however. Clearview insists it is in full compliance with the law, and cites the First Amendment in defending its databases. Besides, as Bhuiyan notes, citizens are getting used to a low expectation of privacy.
Amazon’s policeware efforts have avoided this type of publicity. Why?
Cynthia Murrell, April 15, 2021
Old Book Illustrations: No Photoshop or Illustrator, Thank You
February 1, 2021
Here is a useful resource—Old Book Illustrations. The site began as a way for the creators to share pictures from their own collection of Victorian and French Romantic books and grew as they explored other collections online. All images are in the public domain. The site’s About page elaborates:
“Although it would have been possible to considerably broaden the time-frame of our pursuit, we chose to keep our focus on the original period in which we started for reasons pertaining to taste, consistency, and practicality: due to obvious legal restrictions, we had to stay within the limits of the public domain. This explains why there won’t be on this site illustrations first published prior to the 18th century or later than the first quarter of the 20th century. We are not the only image collection on the web, neither will we ever be the largest one. We hope however to be a destination of choice for visitors more particularly interested in Victorian and French Romantic illustrations—we understand French Romanticism in its broadest sense and draw its final line, at least in the realm of book illustration, at the death of Gustave Doré. We also focused our efforts on offering as many different paths and avenues as possible to help you find your way to an illustration, whether you are looking for something specific or browsing randomly. The many links organizing content by artist, language, publisher, date of birth, and more are designed to make searching easier and indecision rewarding.”
The site is well organized and easy to either search or browse is several ways—by artists, publishers, subjects, art techniques, book titles, and formats (portrait, landscape, tondo, or square). There is even a “navigation how-to” if one wants a little help getting started. The site also posts articles like biographies and descriptions of cultural contexts. We recommend checking it out and perhaps bookmarking it for future use.
Cynthia Murrell, February 1, 2021
Online Immortality: Suddenly Death Makes Digital Headlines
January 26, 2021
I was surprised. Yes, I was. I read three news stories within a few minutes of their appearing in my newsfeed.
The first — “AI Resurrects Legendary Spanish Singer to Hawk Beer” — explains that Lola Flores appeared in a commercial. No big deal except that Lola Flores died a quarter century ago. The article reports:
The company recreated her voice, face, and features using hours of audiovisual material, more than 5,000 photos, and a painstaking composition and post-production process, according to El País.
Some people found the recreation or deep fake quite sporty. Of course, smart software was used, but the implications for those dead are interesting to ponder. Thumb typers, activate your mobiles!
The second was “Microsoft Patent Details Tech That Could Turn Dead People into AI Chatbots.” The write up explains:
The patent, titled “Creating a conversational chatbot of a specific chatbot of a specific person,” details a system that would access images, voice data, social media posts, electronic messages and the like to “create or modify a special index in the theme of the specific person’s personality.” In some cases, images and video could be used to create a 3D model of the person for extra realism.
Use cases range from a smart chatbot which reminds a 20 year old remote worker for a high tech company to pick up his / her clothes to a digital companion to provide support and solace when life delivers a surprise; for example, “You know you should have taken that other job. No what, smarty pants?” If you want to read the system and method behind this innovative idea hinted at by sci-fi writers, the number is US010853717. Is that my mother saying, “Stephen, tidy your desk. You know what they say about loose papers on desk or did you forget? Like you forget the garbage.”
The third write up was “Backed by Vint Cerf, Emortal Wants to Protect Your Digital Legacy from Bit-Rot.” None of that grieving family member learning via email that Facebook will not permit access to the beloved one’s account. The write up explains:
The company will use Google architecture to preserve digital memories — photographs, documents, correspondence, videos, interviews and more – indefinitely into the future. The idea is that this will ensure that as operating systems, devices and tech evolves, your entire digital legacy will remain safe, secure and accessible — to only those you choose.
The possibility are endless; for instance, targeted advertising for digital mementos, eBay listings for vehicles just like the one the loved one used to drive, and facial recognition matches from social media sites so the loved ones can locate a suitable doppelgänger.
Mashing up these services with virtual reality might provide additional opportunities for monetization. Just as one can insert Bernie Sanders into any Google Street View location, these digital constructs can enhance real time constructs. For information about the Bernie app, navigate to Engadget.
The added bonus: Search engine optimization specialists can use their methods to make sure one’s loved one pops up. Hmmm. That’s not a good phrase but it is close enough for a 2021 cornhole game.
Stephen E Arnold, January 26, 2021
More Pix Online: 700K Images from the Rijksmuseum
January 22, 2021
We spotted this news item: “Over 700,000 Pairings from the Rijksmuseum Online Copyright Free.” These, according to the write up, are copyright free. The source of the money for this project was BankGiro Lottery, which is a culture lottery. I love that phrase “culture lottery.” I wonder if Russian individuals of character will implement similar terminology? You can access the service at this link.
The value of any image collection is one’s ability to locate a picture by artist, date, subject, and hopefully the name of the individual who made the painting possible for the museum to acquire. Art, like yachts, often has a fascinating back-story.
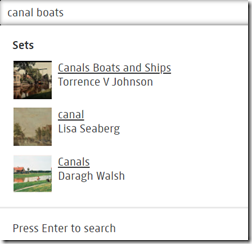
I ran this query: Canal boats.
The system displayed:
I clicked on Canals Boats and Ships. Notice that my “canal” was expanded to include “canals.” The term “boats” was matched exactly.
That’s a step forward considering the issues I have encountered with Internet Archive, Google Life collection, Library of Congress, and other image services.
My family was forced out of Amsterdam in 1605. Perhaps by getting image search to mostly work, the citizens are extending an olive branch to the remaining Arnolds.
Stephen E Arnold, January 22, 2021
Quibi and Its Open Letter: An Idea Probably Not Considered
October 22, 2020
I spotted Quibi’s “An Open Letter…”. The write up states: “…we are winding down the business and looking to sell its content and technology assets.”
I circled this passage: “… we’ve considered and exhausted every option available to us.”
Every option. That’s a categorical affirmative. No black swans, please.
Think of this brilliant observation: “The price of inaction is far greater than the cost of a mistake.” Who said that? Maybe Meg Whitman?
How will those who bet about $1.75 billion on quality content delivered to a mobile device react to my idea which I don’t think the dynamic team of Katzenberg and Whitman thought about?
But here’s the “script” of the overlooked idea. It is very Hollywood-Silicon Valley with graphics, audio, and jazzy Hollywood techniques.
KATZENBERG: We need to do a follow up to my 1992 smash cartoon Aladdin.
WHITMAN: What’s the title?
KATZENBERG: Aladdin 2: Magic Just Happens.
WHITMAN: Dear Jeffrey, what’s the title?
KATZENBERG: Picture this:
1. A poor but motivated duo (that’s us, the dynamic management and creative duo of Katzenberg and Whitman) lose a brief red ink battle with the sinister Dr. Tik Tok.
2. At a yard sale, we (that’s us, the dynamic duo of Katzenberg and Whitman) are looking for quality knick knacks. Whitman spots a copper lamp.
3. A coffee shop in Westwood, perspicacious Meg stroke the lamp.
4. Flash of light. A magic genie appears and orders a cappuccino
5, The dynamic duo gets one wish: To undo the Titanic failure of Quibi.
6. Poof. The genie makes Michael Lynch, founder of Autonomy plc, the cause of Quibi’s failure.
7. A court room: A “Law and Order trial” and — Mr. Lynch guilty.
8. Cut to.. A charity event to fight global warming at the Top of the Mark. The dynamic duo pays investors back.
WHITMAN: Winner!
Yes, an idea possibly not considered. But it may be too late for a quick bite. Lights out.
Stephen E Arnold, October 22, 2020
Matroid: Not Just Math, a Reminder That Google Is Not Search
October 15, 2020
For many people Google is search. Need a pizza? Google it. But for rick media in contexts like streaming video, Google has pizza cheese on its chin.
A venture funding information service called Finsmes published “Matroid Raises $20 Million in Series B Funding.” Add to the firm’s earlier funding, the company has tallied about $33 million to fuel its innovation engine.
Founded in 2016, the company works at the intersection of machine learning (smart software) and image analysis (more smart software). The Finsmes article states:
The company plans to use the new funding to accelerate product development and go-to-market expansion in manufacturing, industrial IOT (IIOT), and video security markets. Led by Reza Zadeh, CEO and Founder, Matroid Matroid is a studio for creating and deploying detectors (computer vision models) to search visual media for people, behavior, objects, and events — no programming required. Once a detector is developed, Matroid can search any live stream or recorded video, providing real time notifications when the object of interest has been detected. Customers use it in construction, manufacturing, security, media, retail and other industries.
Real time analysis of streaming video is a very important search problem. Despite the perception that “Google is search,” the market for a solution is hefty.
Observations:
- The name of the company is borrowed from math wonks
- Law enforcement and intelligence agencies need a solution that works to deal with the video data available to investigators
- Google’s YouTube search illustrates that ad-supported, good enough methods which rely on a creator to index products or tag videos are examples of old-school thinking, maybe Internet dinosaur thinking.
The company will require additional funding. Nailing real time streaming video knowledge generation requires a large hammer.
Stephen E Arnold, October 15, 2020
GSA Government Okays These Drones
October 12, 2020
The General Services Administration has given five manufacturers its blessing to sell their small unmanned aircraft systems (sUAS) to government agencies. GCN examines the development in, “US-Made Small Drones Added to GSA Schedule.” The Defense Innovation Unit (DIU) and the Army’s Short Range Reconnaissance program (SRR) have been working toward this approval for 18 months. That joint effort has developed drones equipped with situational awareness tools that can be deployed quickly. A related DIU project, Blue sUAS, focused on non-DOD applications of drones, like safety inspections, rescue missions, and fighting forest fires. Writer Stephanie Kanowitz informs us:
“The five companies whose products will be available are Altavian, Parrot, Skydio, Teal and Vantage Robotics. … Recognizing a need for drones that government agencies, including the military, could use, Vantage applied to be part of Blue sUAS and tweaked its Vesper unmanned aerial vehicle for federal agency use. Vesper, developed for DIU, differs from Vantage’s first-generation drone, Snap, in that it is ‘substantially more advanced in just about every way,’ including sensors, flight capabilities, security and materials, said Vantage CEO Tobin Fisher. ‘To be specific, on the sensor side, we developed a camera that can see in the dark in 4K and integrated a thermal sensor as well as 18x zoom,’ Fisher said. Additionally, Vesper can fly for 50 minutes and features an extended radio range with an AES 256-encrypted 5-mile link. Vesper is made with components from trusted sources, which Fisher said includes Qualcomm for the onboard processor, Microhard for the radio and SigmaTron International for assembly.”
Impressive. It was crucial that any component that touched data in any way be from a non-Chinese source. For security reasons, the 2020 National Defense Authorization Act prohibits government agencies from purchasing or using drones made in China. The effort goes beyond government agencies, though. Those eye-popping capabilities will soon grace commercial drones, as well. The article quotes the DIU’s Chris Bonzagni:
“These companies have been able to leverage the roughly $18 million in DOD investments to develop spinoff enterprise solutions to offer secure, domestically produced options to enterprise customers worldwide, ultimately adding a much-needed boost to the U.S. sUAS industrial base.”
Ready or not, drones are here to stay and only getting more capable and numerous. Chinese drones are interesting too, but some may phone home.
Cynthia Murrell, October 12, 2020
A New Role for Facial Recognition
October 6, 2020
The travel industry is finding its way around COVID-provoked limitations. Where once travelers were promised a “seamless” experience, they are now promised a “touchless” one, we learn from PhocusWire’s piece, “Touchless Tech: The Simple—and Advanced—Ways Ground Transport Providers Are Encouraging Travel.” Some measures are low-tech, like pledges to clean thoroughly, glove and mask use, and single-passenger rides instead of traditional shuttles. However, others are more technically advanced. The role of facial recognition in “touchless tickets” caught our eye. Writer Jill Menze reports:
“On the rail front, Eurostar has tapped facial-verification technology provider iProov to enable contactless travel from United Kingdom to France. With the solution, passengers can be identified without a ticket or passport when boarding the train, as well as complete border exit processes, at St. Pancras International station without encountering people or hardware. ‘What we’re trying to facilitate for the first time ever is a seamless process of going through ticket and border exit checks contactlessly and more fluidly than it’s ever been possible before using face verification,’ iProov founder and CEO Andrew Bud says. ‘That means, instead of checking people’s ID when they arrive, you check their ID long before. The idea is that you move the process of checking IDs away from the boarding point to the booking point.’ During booking, Eurostar will offer travelers an accelerated pre-boarding option, which allows passengers to scan their identity documentation using Eurostar’s app before using iProov’s facial biometric check, which uses patented controlled illumination to authenticate the user’s identity against the ID document. After that, travelers would not have to show a ticket or passport until they reach their destination.”
Eurostar plans to enact the technology next March, and Bud says other railway entities have expressed enthusiasm. This is an interesting use of facial recognition tech. It seems getting back to business is powerful motivation to innovate.
Cynthia Murrell, October 6, 2020
Quibbling over Quibi
October 1, 2020
Yep, quick bite. Just what investors needed. An money sucking mosquito draining financial blood from clueless investors.
“Why Quibi Failed” is one of those Silicon Valley management analyses I enjoy. The write up received wider distribution by its inclusion in the MSN news channel. Yep, a Microsoft real news operation, not to be confused with Bing news, the messages displayed in Windows 10, or the razzle dazzle about Surface Duo. Hey, I know. Combine the Duo with the quick bite thing. That’s an idea: A $1400 gizmo that plays Quibi content. Winner!
The “Why Quibi Failed” explains that has failed. The write up paints a dire picture:
Since its US debut in April, Quibi seemed destined for such an ending. It badly missed subscriber and viewership targets and in June was on pace to sign up only 2 million paying subscribers by the end of the year (its goal was over 7 million). It was forced to manage reports of mass layoffs and rumors that its founder, Jeffrey Katzenberg, and its CEO, Meg Whitman, were not seeing eye to eye. And now it’s fighting a lawsuit filed by a video company alleging Quibi infringed on its patented technology (Quibi denies this).
In point of fact, the outfit is chugging along and might pull off a sale to another company looking for magic; that is, content. Sounds like Quibi needs to upgrade its public relations unit.
Why has Quibi been bitten where the sun does not shine? The write up turns to one of the wizards leading the charge to the future of entertainment, Jeffrey Katzenberg:
Katzenberg blamed everything on the coronavirus.
The article explains:
Quibi could have invested more in content from celebrities its younger audience might actually appreciate, like YouTube, Instagram, or TikTok stars. Instead, it threw lots of money at the kind of names that older executives might imagine young people enjoy—Jennifer Lopez, Idris Elba, Tyra Banks, Usher, and every teenager’s favorite actor, 53-year-old Kiefer Sutherland.
The idea is that old school Hollywood thinking is not hip to the charms of Bad Bunny or the ever delightful video style of Gamers Nexus.
Other reasons for the alleged failure of Quibi include:
- Content (wait, not a strength)
- Lack of “shareability”
- The format of quick bites; that is, 10 minute chunks of juicy digital goodness.
But wait. There’s no fix, no options, no recommendations.
That’s a bit of a problem with Silicon Valley business thinking. Imagine. Figuring out next steps.
Several observations:
- A closer look at the management track record of the Quibi leadership would be helpful. Hints about “tension” are okay, but let’s dig into the facts like disastrous deals and massive flops suggest that headwinds have been blowing for years
- Quibi’s “chunk at a time” is out of step with the type of real-time, constant-click data available to an outfit like TikTok, Amazon Twitch, and (gasp!) Facebook Instagram Reels. Mismatch? For sure.
- Some information about the production deals for the magical content. With it content is often produced, edited, and distributed from a laptop in an RV camp or from an organic vegan coffee shop; for example, the antics of Kara and Nate and their interesting videos. Quibi did it the Hollywood 1980s way. That’s a money saving idea.
- A bit of digging into the “management style” of Mr. Katzenberg and Ms. Whitman could be complemented with actual interviews of people who knew how these two brilliant leaders interacted with one another.
There is a book waiting to be written about Quibi. If there were functional universities teaching business the old fashioned way, there is at least one case study. The legal antics of Quibi investors might enliven a law review if these print centric publications are still funded.
In short, the analysis like Quibi seems oddly appropriate even with Rona ready to accept the blame. Quick bite? Nope, big chomp in tender places. One may want to consider that Quibi is “actually quite good.” But for whom?
Stephen E Arnold, October 1, 2020
Fujitsu Simplifies, Reduces Costs of Preventing Facial Authentication Fraud
September 25, 2020
Fujitsu says it has developed a cost-effective way to thwart attempts to fool facial recognition systems, we learn from IT-Online’s write-up, “Fujitsu Overcomes Facial Authentication Fraud.” The same factor that makes facial authentication systems more convenient than other verification methods, like images of fingerprints or palm veins, also makes them more vulnerable to fraud—photos of faces are easy to capture and reproduce. We’re told:
“Fujitsu Laboratories has developed a facial recognition technology that uses conventional cameras to successfully identify efforts to spoof authentication systems. This includes impersonation attempts in which a person presents a printed photograph or an image from the internet to a camera. Conventional technologies rely on expensive, dedicated devices like near-infrared cameras to identify telltale signs of forgery, or the user is required to move their face from side to side, which remains difficult to duplicate with a forgery. This leads to increased costs, however, and the need for additional user interaction slows the authentication process. To tackle these challenges, Fujitsu has developed a forgery feature extraction technology that detects the subtle differences between an authentic image and a forgery, as well as a forgery judgment technology that accounts for variations in appearance due to the capture environment. … Fujitsu believes that, by using these technologies, it becomes possible to identify counterfeits using only the information of face images taken by a general-purpose camera and to realize relatively convenient and inexpensive spoofing detection.”
We’re told the company tested the system in a real-world office/ telecommuting setting and confirmed it works as desired. Fujitsu hopes the technology will prove popular as remote work continues and, possibly, grows. The venerable global information and communication tech firm serves many prominent companies in several industries. Based in Tokyo, Fujitsu has been operating since 1935.
Cynthia Murrell, September 25, 2020