Techno-Psych: Perception, Remembering a First Date, and Money
September 9, 2021
Navigate to “Investor Memory of Past Performance Is Positively Biased and Predicts Overconfidence.” Download the PDF of the complete technical paper at this link. What will you find? Scientific verification of a truism; specifically, people remember good times and embellish those memory with sprinkles.
The write up explains:
First, we find that investors’ memories for past performance are positively biased. They tend to recall returns as better than achieved and are more likely to recall winners than losers. No published paper has shown these effects with investors. Second, we find that these positive memory biases are associated with overconfidence and trading frequency. Third, we validated a new methodology for reducing overconfidence and trading frequency by exposing investors to their past returns.
The issue at hand is investors who know they are financial poobahs. Mix this distortion of reality with technology and what does one get? My answer to this question is, “NFTs for burned Banksy art.”
The best line in the academic study, in my view, is:
Overconfidence is hazardous to your wealth.
Who knew? My answer is the 2004 paper called “Overconfidence and the Big Five.” I also think my 89-year-old great grandmother who told me when I was 13, “Don’t be over confident.”
I wonder if the Facebook artificial intelligence wizards were a bit too overconfident in the company’s smart software. There was, if I recall, a question about metatagging a human as a gorilla.
Stephen E Arnold, September 9, 2021
Change Is Coming But What about Un-Change?
September 8, 2021
My research team is working on a short DarkCyber video about automating work processes related to smart software. The idea is that one smart software system can generate an output to update another smart output system. The trend was evident more than a decade ago in the work of Dr. Zbigniew Michalewicz, his son, and collaborators. He is the author of How to Solve It: Modern Heuristics. There were predecessors and today many others following smart approaches to operations for artificial intelligence or what is called by thumbtypers AIOps. The DarkCyber video will become available on October 5, 2021. We’ll try to keep the video peppy because smart software methods are definitely exciting and mostly invisible. And like other embedded components, some of these “modules” will become components, commoditized, and just used “as is.” That’s important because who worries about a component in a larger system? Do you wonder if the microwave is operating at peak efficiency with every component chugging along up to spec? Nope and nope.
I read a wonderful example of Silicon Valley MBA thinking called “It’s Time to Say “Ok, Boomer!” to Old School Change Management.” At first glance, the ideas about efficiency and keeping pace with technical updates make sense. The write up states:
There are a variety of dated methods when it comes to change management. Tl;dr it’s lots of paper and lots of meetings. These practices are widely regarded as effective across the industry, but research shows this is a common delusion and change management itself needs to change.
Hasta la vista Messrs. Drucker and the McKinsey framework.
The write up points out that a solution is at hand:
DevOps teams push lots of changes and this is creating a bottleneck as manual change management processes struggle to keep up. But, the great thing about DevOps is that it solves the problem it creates. One of the key aspects where DevOps can be of great help in change management is in the implementation of compliance. If the old school ways of managing change are too slow why not automate them like everything else? We already do this for building, testing and qualifying, so why not change? We can use the same automation to record change events in real time and implement release controls in the pipelines instead of gluing them on at the end.
Does this seem like circular reasoning?
I want to point out that if one of the automation components operates using probability and the thresholds are incorrect, the data poisoned (corrupted by intent or chance) or the “averaging” which is a feature of some systems triggers a butterfly effect, excitement may ensue. The idea is that a small change may have a large impact downstream; for example, a wing flap in Biloxi could create a flood in the 28th Street Flatiron stop.
Several observations:
- AIOps are already in operation at outfits like the Google and will be componentized in an AWS-style package
- Embedded stuff, like popular libraries, are just used and not thought about. The practice brings joy to bad actors who corrupt some library offerings
- Once a component is up and running and assumed to be okay, those modules themselves resist change. When 20 somethings encounter mainframe code, their surprise is consistent. Are we gonna change this puppy or slap on a wrapper? What’s your answer, gentle reader?
Net net: AIOps sets the stage for more Timnit Gebru shoot outs about bias and discrimination as well as the type of cautions produced by Cathy O’Neil in Weapons of Math Destruction: How Big Data Increases Inequality and Threatens Democracy.
Okay, thumbtyper.
Stephen E Arnold, September 8, 2021
Algolia: Now the Need for Sustainable, Robust Revenue Comes
August 27, 2021
We long ago decided Algolia was an outfit worth keeping an eye on. We were right. Now Pulse 2.0 reports, “Algolia: $150 Million Funding and $2.25 Billion Valuation.” The company closed recently on the Series D funding, bringing its total funding to $315 million. Putting that sum to shame is the hefty valuation touted in the headline. Can the firm live up to expectations? Reporter Annie Baker writes:
“This latest funding round reflects Algolia’s hyper growth fueled by demand for ‘building block’ API software that increases developer productivity, the growth in e-commerce, and digital transformation. And this additional investment enables Algolia to scale and serve the increased demand for the company’s Search and Recommendations products as well as fuel the company’s continued product expansion into adjacent markets and use-cases. … This new funding round caps a landmark year that saw significant growth and product innovation. And Algolia launched with the goal of creating fast, instant, and relevant search and discovery experiences that surfaced the desired information quickly. Earlier this year, the company had announced its new vision for dynamic experiences, advancing beyond search to empower businesses to quickly predict a visitor’s intent on their digital property in real time, in the session, and in the moment. And the business, armed with this visitor intent, can surface dynamic content in the form of search results, recommendations, offers, in-app notifications, and more — all while respecting privacy laws and regulations.”
Baker notes Algolia’s approach is a departure from opaque SaaS solutions and monolithic platforms. Instead, the company works with developers to build dynamic, personalized applications using its API platform. Over the last year and a half, Algolia also added seven new executives to its roster. Headquartered in San Francisco, the company was founded in 2012.
Cynthia Murrell, August 27, 2021
Silicon Valley Neologisms: The Palantir Edition
August 19, 2021
Do you remember the Zuckerland metaverse? (Yes, I know he borrowed the word, but when you are president of a digital country, does anyone dare challenge Zuck the First, Le Roi Numérique?)
Palantir Technologies (the Seeing Stone outfit with the warm up jacket fashion bug) introduced a tasty bit of jargon-market speak in its Q2 2021 earnings call:
Palantir’s meta-constellation software harnesses the power of growing satellite constellations, deploying AI into space to provide insights to decision-makers here on Earth. Our meta-constellation integrates with existing satellites, optimizing hundreds of orbital sensors and AI models and allowing users to ask time-sensitive questions across the entire planet. Important questions like, where are the indicators of wildfires or how are climate changes affecting crop productivity? And when and where are naval fleets conducting operations? Meta-constellation pushes Palantir’s Edge AI technology to a new frontier.
I think meta-constellation is a positive contribution to the American Silicon Valley-Denver lingo.
One of the interesting factoids in the write up is that the average customer “invests” lots of money in the firm’s software and services. The average customer yields $7.9 million. Let’s assume there was a touch of spreadsheet fever whipping the accountants. Chop that down to a couple of million, and the cowboy outfit is doing okay. Now the job is to corral those customers so there is sustainable, recurring revenue and generous profits going forward like little doggies heading to the meat processing facility.
Also, deploying the Palantirians’ system is as easy as cooking some of Cowboy Ken’s beans in an iron pot over a wood fire. The transcript faithfully reports:
In just two days, we were able to deploy an entire solution for this customer, leveraging our out-of-the-box functionality built in foundry, a time line previously unthinkable in the eyes of the customer. And frankly, it would have been unthinkable to us even three years ago, where an equivalent project might have taken three months. This is only possible because of our product. Innovations from software-defined data integration are driving the marginal cost of data integration to 0, archetypes and our no-code technologies that are driving the marginal cost of application development to zero.
Those data cowboys are moving faster than a branded calf on a crisp April morning.
The most interesting factoid is contained in this statement:
Given our strong cash flow position, we repaid our outstanding $200 million term loan facility and are currently debt-free. After paying off the debt, we ended the quarter with $2.3 billion in cash and cash equivalents.
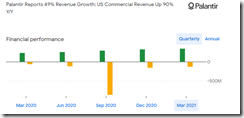
I don’t want to raise a touchy subject, but this chart caught my attention:
That yellow line means that the company is losing money if I am interpreting the Google Finance graph correctly.
It may be helpful to consider that Palantir has never turned a profit. Let’s hope those Colorado transplants can covert expensive cows into hard cash after more than a decade grazing on the range. No digital cows, please. Leave those for the Facebook metaverse which is less than a meta-constellation in JRR Tolkien fantasy space.
Stephen E Arnold, August 19, 2021
Autonomy: An Interesting Legal Document
August 4, 2021
Years ago I did some work for Autonomy. I have followed the dispute between Hewlett Packard and Autonomy. Enterprise search has long been an interest of mine, and Autonomy had emerged as one of the most visible and widely known vendors of search and retrieval systems.
Today (August 3, 2021) I read “Hard Drives at Autonomy Offices Were Destroyed the Same Month CEO Lynch Quit, Extradition Trial Was Told.” The write up contains information with which I was not familiar.
In the write up is a link to “In the City of Westminster Magistrates’ Court The Government of the United States of America V Michael Richard Lynch Findings of Fact and Reasons.” That 62 page document contains a useful summary of the HP – Autonomy deal.
Several observations:
- Generating sustainable revenue for an enterprise search system and ancillary technology is difficult. This is an important fact for anyone engaged in search and retrieval.
- The actions summarized in the document provide a road map of what Autonomy did to maintain its story of success in what has been for decades a quite treacherous market niche. Search is particularly difficult, and vendors have found marketing a heck of a lot easier than delivering a system that meets users’ expectations.
- The information in the document suggests that the American judicial system may find this case a “bridge” between how corporate entities respond to the Wall Street demands for revenue and growth.
Like Fast Search & Transfer, executives found themselves making decisions which make search and retrieval a swamp. Flash forward to the present: Google search is shot through with adaptations to online advertising.
Perhaps the problem is that people expect software to deliver immediate, relevant results. Well, it is clear that most of the search and retrieval systems seeking sustainable revenues have learned that search can deliver good enough results. Good enough is not good enough, however.
Stephen E Arnold, August 4, 2021
YouTube: Serving Consumers or Bullying?
July 26, 2021
Ycombinator included a comment from someone. That comment was flagged. However, the information in the original comment and the observations offered by Ycombinator users are interesting. The information reveals what I characterize as an escalating battle between those who view YouTube videos and YouTube itself. (I am not going to discuss the escalating tension between “creators,” YouTube, and the service Odysee.com.)
First, the Ycombinator item contains this statement:
YouTube is still not happy. Today when I opened the app on my phone, it still showed me an add. It is infuriating at least. This won’t probably make it, but I needed to share. https://imgur.com/a/BM7XoTe
So what? The flagged poster subscribed to YouTube and YouTube still displays advertisements.
Second, the comments include the tools which one can use to block YouTube’s charming and highly relevant, on point, information packed advertisements; for example:
Adguard
Arachnoid
Cercube
Invidious
SmartTube
Sponsorblock
uBlock Origin
Vanced
Third, the fact that YouTube is becoming a cable-tv like operation is interesting as well.
Net net: Do you hear that tick tock? Maybe it is spelled TikTok?
Stephen E Arnold, July 26, 2021
Facebook and Milestones for the Zuck
July 2, 2021
I read “Facebook Reaches $1 Trillion Valuation Faster Than Any Other Company.” The write up reports that the highly esteemed Facebook (WhatsApp and Instagram) have out performed Apple, the Google, the spaceship outfits, and Microsoft. The article reports:
No stranger to breaking records, Facebook has just achieved another: the social media giant’s market cap has exceeded $1 trillion for the first time, reaching the milestone faster than any other company in history.
What has caused this surge in “valuation”? The answer is revealed in “Judge Dismisses Gov’t Antitrust Lawsuits against Facebook.” This separate write up in a news service oh, so close to Microsoft’s headquarters, states:
A federal judge on Monday dismissed antitrust lawsuits brought against Facebook by the Federal Trade Commission and a coalition of state attorneys general, dealing a significant blow to attempts by regulators to rein in tech giants. U.S. District Judge James Boasberg ruled Monday that the lawsuits were “legally insufficient” and didn’t provide enough evidence to prove that Facebook was a monopoly.
Concentration is good, it seems. For social media start ups, have you thought about issuing T shirts with the Zuck’s smiling face printed on them? You can update your Facebook page and do some Instagram posts. Don’t overlook WhatsApp as a way to spread the good news. About the T shirts I mean.
Stephen E Arnold, July 2, 2021
Sci-Hub: Is It Evil Personified in Alexandra Elbakyan, a modern Abaddon?
July 1, 2021
If you are not familiar with professional publishing, you may find “Is the Pirate Queen Scientific Publishing in Real Trouble This Time?” particularly fascinating. Founded by Alexandra Elbakyan in 2011, Sci-Hub has become the go to source of academic or professional publishing materials. One key point: Unlike commercial services, Sci-Hub is a freebie. In the world of Disney infused copyright ideas, Mickey Mouse and research about children’s heart disease are not available without paying. Parking at DisneyLand is a bargain compared to the fees assessed for a single two-page document. The kid’s life? Not part of the copyright approach to government funded research.
If you have some experience with the business models of the big outfits running peer-reviewed publications, you will get a kick out of passages like this one:
According to the publishers who brought the case in India, quite a bit. Pirate sites like Sci-Hub “threaten the integrity of the scientific record, and the safety of university and personal data,” a joint statement reads. It goes on to say that sites like Sci-Hub “have no incentive to ensure the accuracy of scientific articles, no incentive to ensure published papers meet ethical standards, and no incentive to retract or correct articles if issues arise.”
My hunch is that most people who explain that “I am an online expert” cannot differentiate between a blog post, a paper on ArXiv, an IEEE pdf, and a full text document from Lexis. In my experience, few online wizards can answer these questions:
- Once a research paper is complete, does the author have to pay the publisher of the journal to which the write up is submitted?
- Are the “peer reviewers” paid to do the often very, very difficult work of checking that the information in the document is correct, the statistics accurate as far as the reviewers can determine, and the “value” of the document will result in learning, not in harm?
- Are the companies running professional publishing operations monopolies or oligopolies?
- Are documents in professional publishers’ span of control updated, are errors corrected, are cabals of friendly experts disabused from promoting a graduate student’s, friend’s, or colleague’s write up? Are exchanges of favors among reviewers ignored or denied?
- Are errors in online documents corrected after those original documents are posted online?
- Are online documents known to be fraudulent or containing non reproducible results removed from repositories?
- Are libraries subject to ever increasing fees because those institutions might lose accreditation if research content were not provided to students, researchers, and other staff?
- What is the explicit link between tenure at a university and publishing in journals operated by commercial professional publishing companies? Hint: Sword of Damocles and a horse hair.
Struggling with some of the answers? No surprise. Like the pharmaceutical industry and those engaged in SMS spam services, certain information about business methods are not disclosed. And if revealed, the business processes are denied. If you want example, just watch reruns of the investigations of some of the high profile high technology companies testifying before the US Congress.
This “information wants to be free” baloney is not the way “real” online works. Here’s an example. I was asked to submit a version of my law enforcement centric report about Amazon’s policeware. Some person contacted me via LinkedIn and said a draft was due in December 2019. I said, “My report is not for academics. I don’t care if you publish it, just leave me out of the professional publishing razzle dazzle.” I pointed out that I was not an academic; I was not changing anything in the manuscript; and I was not sure if the information in my report would make any sense whatsoever to the handful of people who might read the collection of essays.
I forget about the write up: I never filled out any online forms; I never sent a bill of $1.00 (because I have a policy of getting paid for some of my research); and I routed email from the person who asked me to submit a chapter and the assorted youthful folks at the European publishing company to the Junk folder on my systems.
And what did I receive a couple of days ago? I got an email addressed to “Dear Professor Arnold.” The email wanted me to promote my chapter and the book. Okay, this blog posts is promoting the chapter. Helpful, right? Some of these outfits cannot differentiate between a PhD program drop out and a real live PhD driving for Uber. Keen powers of discrimination for sure.
Net net: Alexandrea Elbakyan, who is a student in everyone’s favorite country, is the enemy. Courts in several countries have determined that Ms. Elbakyan is a threat to learning, knowledge sharing, and “way” research content is to be made available. Yep, Elsevier is waiting for its $15 million check from Ms. Abaddon. Oh, sorry. I meant Ms. Elbakyan.
Stephen E Arnold, July 1, 2021
Is Google Really, Really Killing the Ad Industry?
June 16, 2021
I read “Google Is Also Killing Ad Industry like Apple.” There’s a caveat after this somewhat bold headline:
[Google] promises to put an end to personalized ads starting with Android 12
The write states:
Close to 80% of its revenue comes from advertising. But with pressure from regulators and consumers, Google had no choice but to follow Apple’s lead to protect users’ privacy and data.
Okay, the Google is reacting to what seems like on going legal hassles. Is Google “like Apple”? Well, Apple has diversified its revenue stream. The hardware, the App Store, the subscription businesses, and the other bits and pieces of the company that turn a buck are more robust than Google’s model.
Yep, that’s 80 percent advertising, and it is smart. Well, sort of smart. Some of the ads we’ve have been monitoring on YouTube and our Google Web search results pages seem a bit off the mark for whoever Google thinks “I” am. We love seeing ads for discounted auto insurance, Grammarly to improve the entity’s writing, and blandishments to consume a vegan health drink. Not exactly a cohesive line up of messages, but Google thinks we watch yacht videos, hacker and stolen software videos, and search for weaponized drone manufacturers. Normal stuff for the smart Google system.
That’s the problem. The 80 percent is based on some pretty crazy real life, rules based, and human tuned systems and methods. By virtue of zero meaningful regulation, the Google has become the embodiment of online advertising. Banners, personalized, scammy, whatever Google is there.
What if users opt out of Google data collection?
What difference will that make? The Floc you crowd believes that privacy is Job 1 at the Google. The cheerleaders for the weird “rumble” or “bumble” bundle think that subscriptions are the way to go. Google believes that its solving death and smart auto technology will become big winners. Then there’s the licensing opportunity for DeepMind’s smart software. Those who aren’t keen on saying, “We’ve got the secret sauce for artificial general intelligence” are gone or heading out the door. The AI ethics negative Nellies are history as well.
The problem is the 80 percent thing.
The write up has an answer:
As predicted, Google gave in to pressure from regulators and its users to implement these changes. However, it will be interesting to see, how Google will sustain these changes let alone other third-party ad providers. But only the future will tell how will these changes affect independent and small business owners as Facebook fears. Google recently introduced FLOC (Federated Learning Of Cohorts) an alternative method to replace the third-party cookies on Chrome which makes it difficult for advertisers to track user’s web activities to serve targeted ads. This FLOC will enable interest-based advertising on the web without letting advertisers know your identity. Probably, Google’s alternate solution to the Android app’s future personalized ads will probably reminiscent of FLOC. Overall, this is a welcome change from Google.
Got it? But 80 percent of $196 billion is a lot of smart auto and smart software licensing deals. Therefore, Steve Ballmer’s one trick pony observation is proving to be accurate or at least more accurate than Mr. Ballmer’s basketball team’s free thrown shooting percentage.
Stephen E Arnold, June 16, 2021
Great Moments in PR: Google and France June 2021
June 14, 2021
I am not sure what percentage of Alphabet Google’s annual revenue $268 million represents. My old handheld calculator balks at lots of numbers. I am more of a 00 or 000 kind of old timer. France believes that this figure is fair and appropriate for alleged missteps by the mom and pop online ad company.
I found the article “Google to Improve Ad Practices after Being Slapped with $268 Million Fine” interesting. In fact, I circled in True Blue this passage:
Following the results of this investigation, Google has decided to reach a settlement with the French antitrust authority. As a part of this settlement, the tech giant will have to improve its ad services to offer better interoperability with other platforms, and will also pay a $268 million fine.
Yep, the do better assurance. What was the alleged saying bandied about when Messrs. Brin and Page were roller blading around the Mountain View offices? I think it was this one:
It’s easier to ask forgiveness than it is to get permission.
A slight edit yields:
It’s easier to pay the find than make specific commitments.
Stephen E Arnold, June 14, 2021